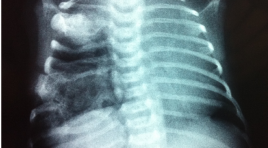
Nhân một trường hợp u mô thừa trung mô thành ngực hiếm gặp ở trẻ em
31/03/2020 19:58:11 | 0 binh luận
Mesenchymal hamartoma of the chest wall in infancy - Case report SUMMARY We present the case of the chest wall tumor in children that was diagnosed and treated in NHP, Hanoi. The child aged 6 month old which was attended to hospital with an asymptomatic chest-wall mass. The child was examined by chest X ray, thoracic CT scanner and MRI. Biopsy of the tumor revealed the diagnosis of mesenchymal hamartoma of the chest wall.

Nhân một trường hợp ung thư tế bào vảy phổi di căn xương sọ
31/03/2020 19:41:09 | 0 binh luận
Skull metastasis arising from pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma: A case report SUMMARY Introduction: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung represents 30% of all non-small cell lung carcinomas. It arises from dysplasia of squamous epithelium of the bronchi and is strongly associated with cigarette smoking. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung is known to produce metastases in the brain parenchyma. Case presentation : We present the case of a 77-year-old woman with an unusual presentation of metastatic carcinoma of the lung. The case demonstrated a squamous cell carcinoma of the lung with an intracranial metastatic lesion destroying the parietal bone and extending into the extra cranial soft tissue. A visible deformity as a result of the metastasis was evident on physical examination, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography demonstrated extensive bone destruction. Conclusion : Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung with an intracranial metastatic lesion is rare in the world literature. The case report demonstrates an unusual disease presentation with an intra-cranial metastasis invading through the skull. Keywords : Destruction of bone; Metastasis; Squamous cell carcinoma.
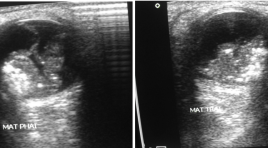
Chẩn đoán hình ảnh tồn tại và quá thể kính nguyên thủy ( TTTKNT)
31/03/2020 16:06:09 | 0 binh luận
Persistence and hyperplasia of primitive vitreous humor (PHPV) SUMMARY Objective: To present three rare cases of PHPV in baby which were diagnosed with USG and CT scanner at 2 different syndromes. The authors want to find out the diagnostic imaging capability of this affection on each syndrome. Material and methode: Cross-section description study of 3 cases with USG and CT scanner. Result: The patient parent discover when the baby always rubs the eyes because they can’t see anything. Other clinical examination, the diagnosis is set with UGS as a solid mass in the vitreous corpus, no adherence in the macula, no hypervascularization on color Doppler image some small calcified nodes at all 2 eyes leading to total blindness. One of two patient has associated anomalies of the brain: turricephaly, corpus callosum atrophy, lissenpachygyria calling Aicardi syndrome. CT scanner is indicated only to set the differential diagnosis of retinoblastoma with calcification and possible extension in the retrobulbar space and optic nerv. Conclusion: PHPV is a rare anomaly, difficult to prenatale diagnose but easy post delivery by USG, needing probe over 10 MHz and color doppler; transcranial sonogaphy gives avaluable image. CT is indicated only to detecte calcification for rule out retinoblastoma. IRM is not necessary except intend to investigate brain malformation. Key word: vitreous humor.
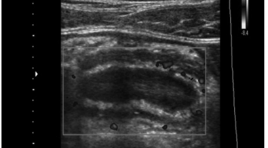
Lồng ruột thừa
31/03/2020 13:45:57 | 0 binh luận
Case Report summa ry Appendiceal intussusception is not a common disease and is rarely diagnosed preoperatively. In our case, a 25-year-old male patient living in Ho Chi Minh City came to Medic Medical Center complaining about his epigastric abdominal pain, which lasting for 3 days. His body temperature was not high and he did not have any other symptoms. He recalled similar pain which had gone away without any treatment three months ago. Abdominal ultrasound showed abnormalities in appendix and cecum. During performing colonoscopy, we suspected appendiceal intussusception, and following computed tomography showed the images of enlarged appendix with fluid-filled lumen and signs of intussusception at the appendix base. The patient underwent an operation to remove the appendix and appendiceal intussusception was confirmed. Microscopic result was consistent with chronic appendicitis.
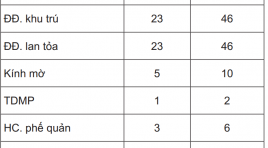
Khảo sát hình ảnh viêm phổi trên chụp cắt lớp điện toán ở bệnh nhi nhiễm HIV
31/03/2020 12:52:30 | 0 binh luận
Evaluating the images of pneumonia on CT Scan in HIV- infected children summa ry Objective: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the pulmonary lesions on CT of pneumonia in HIV infected children and causing agents. Material and methods : Fifty HIV infected children with pneumonia was selected over a 10-month period at the Chilren Hospital N1. All patients were indicated the chest radiogram, the CT with constrate media and the nasotreacheal aspiration to exame microbiology included bacteria, BK, fungus and Pneumocystis jiroveci. Results : Of 50 patients, 62% is baterial pneumonia, PCP 29% and tuberculosis 18%. Lesions on CT included alveolar condensation account for 88%, ground glass 30%, bronchial syndrome 20% and lymphadenopathy 20%. The ground glass lesion present in all PCP, 100%. Eighty percent of tuberculosis children have lymphadenopathy with central necrosis and peripheral enhancement. These two kinds of lesions present a little in bacterial pneumonia group. Conclusion: Ground glass images on chest CTscans may allow confident diagnosis for PCP in HIV infected children. To diagnose thoracic tuberculosis, CT scans are useful to detect the typic tuberculous lymphadenopathies. Keywords: HIV, pneumonia, children, PCP.
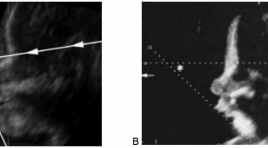
Hội chứng Pierre Robin nhân một trường hợp
03/04/2020 10:33:27 | 0 binh luận
Pierre Robin syndrome. Study case SUMMARY Pierre Robin (PRS) is considered as rare frequency among fetal malformations. It presents with a classic triad of micrognathia, glossoptosis and cleft palate which is presenting the maxillo-facial CT fi nding. This typical PRS case is describing together with a short literature review about all CT anormaly images for diagnosis and express its performance. Keywords : Cleft palate, feeding plate, micrognathia, palatal feeding obturator, Pierre Robin sequence.
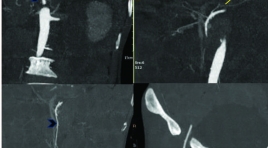
Báo cáo lâm sàng: can thiệp nội mạch cấp cứu điều trị võ giả phình động mạch lách có tình trạng sốc mất máu - một biến chứng ở bệnh nhân viêm tụy cấp
17/03/2020 11:30:29 | 0 binh luận
Splenic artery pseudoaneurysm rupture with hemorrhagic shockas complication of acute pancreatitis treated with emergency endovascular interventions: A case report SUMMARY Background : Rupture of splenic artery pseudoaneurysm (SAPs)secondary to pancreatitis is a uncommon complication, but one with a high mortality rate. Patient generally presented with gastrointestinal bleeding’s symptoms ranging from mild anemia to hemorrhagic shock.Contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) plays an important role in diagnosis, but digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the gold-standard method to determine the correct diagnosis and make treatment planning. Nowadays, SAPs have been managed with many methods. Endovascular intervention remains the first choice asminimal invasion and a waste of the short time,especially for emergency cases. This article describes a case of SAPs rupture complicated by chronic pancreatitis. Patient admidtted with hypovolemic shock andsuccessfully treated using endovascular coil embolization. Case presentation: A 46 years old man with a past medical histoty of pancreatitisattended to Bach Mai hospital due to hemorrhagic shock as result of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. He was intubated and received platelet infusion in secondary hospital.Upper gastrointestinal endoscopyshowed bleeding from the major duodenal papilla, but the source of bleeding remained obscured. CTrevealedrupture of splenic artery pseudoaneurysm causing haemosuccuspancreaticus and duodenal bleeding. Patient immediately managed with coil embolizationby Sandwich technique.After procedure, anemia was controlled steady, butsigns of peritonitis began to appear. At that time, CT images discovered multiple abcesses in hypogastric region and alsso suspectednecrosis of the colonic wall. The patient underwentcolectomy and colostomy in left lumbar region. On the 20th day, he was discharged from hospital with no symptoms and normal blood test. Conclusion: Treatment of acute gastrointestinal bleeding from a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm rupture need to access rapidly and manage reasonably. Emergency endovascular interventions should be the first selection to prevent continous bleeding. Keyword: splenic artery aneurysm rupture, hemorrhagic shock, pancreatitis, emergency endovascular interventions.
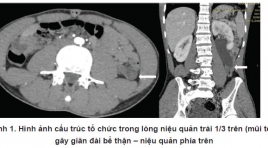
Polyp niệu quản lành tính gây tắc nghẽn đường bài tiết cao: Báo cáo trường hợp case lâm sàng tại bệnh viện Việt Đức
17/03/2020 11:25:13 | 0 binh luận
Benign ureteral polyp causing upper urinary tract obstruction: a case report at Viet Duc hospital SUMMARY Fibroepithelial ureteral polyp is a benign neoplasm,derived from mesodermal tissue and is a cause of upper urinary tract obstruction. The etiology and pathogenic mechanism are unknown. Preoperation diagnosis of ureteral polyps is difficult. However, multidetector CT, especially CT urography in excretory phase gives some suggestive signs of ureteral polyp. We reporta 27- year- old man with left back pain and diagnosed congenital left ureteral stenosis 3 years ago, untreated, and this time presenting with increasing back pain and upper ureteral tract obstruction, admitted Viet Duc University Hospital. On CT imaging, the patient was diagnosed upper ureteral tract obstruction due to ureteral tumor. The patient underwent a laparoscopic surgery and was diagnosed to be fibroepithelial ureteral polypin operation and histologic examination. This case illustrates a rare cause of urinary obstruction that should be considered when the imaging findings and presentation are atypical for more common etiologies of ureteral obstruction. Keywords : fibroepithelial ureteral polyps, ureteral polyps, ureteral obstruction
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












