Bác sĩ siêu âm cần làm gì để hạn chế sự lây lan của COVID-19
18/05/2020 15:53:44 | 1 binh luận
Covid-19 (coronavirus disease 19) đang là một trong những thách thức lớn nhất cho thế giới trong thời điểm hiện tại. Những tác động của coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) không chỉ đơn thuần lên sức khỏe, mà còn ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến kinh tế và cuộc sống của người dân trên toàn cầu. Một vài nước đã thông báo rằng họ đang trải phải qua một trong những tình huống tồi tệ nhất trong hơn 100 năm vừa qua.
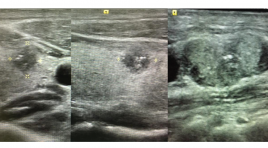
GIÁ TRỊ SIÊU ÂM TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN UNG THƯ TUYẾN GIÁP
15/11/2021 18:00:40 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To determine the value of ultrasound in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Subjects and methods: A cross-sectional descriptive study on 98 patients with thyroid nodules who came for treatment at the Military Institute of Medical Radiology and Oncology, from April 2020 to March 2021. Results: The size of malignant nodules was mainly less than 2cm. Thyroid cancer lesions were mainly characterized by highly hypoechoic on ultrasound (61.19%). Thyroid cancer nodules had taller-than-wide feature (Sensitivity: 76.12%; specificity: 86.96%; positive predictive value: 89.47%; negative predictive value: 71.43%; accuracy: 80.53%.); irregular border feature (sensitivity: 98.51%; specificity: 86.96%; positive predictive value: 91.67%; negative predictive value: 97.56%; accuracy: 93.81%); microcalcification characteristics (sensitivity: 73.13%; specificity: 91.30%; positive predictive value: 92.45%; negative predictive value: 70.00%; accuracy: 80,53%). TIRADS value in thyroid cancer diagnosis with sensitivity: 94.03%; specificity: 86.96%; positive predictive value: 91.30%; negative predictive value: 90.91%; Accuracy: 91.15%. Conclusion: The features of hypoechoic nodules, taller-than-wide shape, irregular border, microcalcification characteristics, and TIRADS 4, TIRADS 5 scores had high prognostic value for thyroid cancer. Keywords: Ultrasound, thyroid cancer.
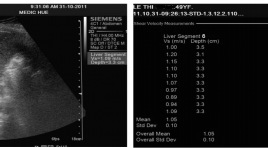
Gía trị vận tốc sóng biến dạng lan truyền trong mô gan người bình thường đo được qua kĩ thuật xung áp lực nén siêu âm
02/04/2020 14:13:54 | 0 binh luận
Value of average velocity of shear wave in hepatic fibrous parenchyma by using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. (ARF I) SUMMARY: Objectives: Evaluation the average velocity of shear wave in hepatic fibrosis(ARFI) according to Metavir classification. Methods: 241 of healthy volunteers with normal liver function test values and 160 patients, diagnosed of chronic liver disease based on serologic test of hepatitis and history of alcoholic abuse, were selected for the study. Among these patients, there are 23 patients having histologic results for grading hepatic fibrosis based on Metavir classification Shear wave velocity measurements, expressed in meters per second, were taken in liver segment 7 or 8 at deepth from 3 to 4 cm below the body surface. Results: Average velocity of shear wave in healthy liver is 1.05 ± 0.092 m/s, of fibrosis is 1.97± 0.59 m/s. A statistically significant difference in shear wave velocity between two groups is noted (P <.001). Conclusions : Velocity of shear wave in hepatic parenchyma measured by using ARFI increase significantly in fibrous parenchyma based on histologic results.

Siêu âm Doppler các bệnh lý thận
20/11/2019 15:15:43 | 0 binh luận
Siêu âm thường được dùng như một trong những biện pháp chẩn đoán hình ảnh ban đầu bệnh lý thận dù độ chuyên biệt không caoSiêu âm màu Doppler và siêu âm màu năng lượng đã làm cho siêu âm trở nên đầy ấn tượng trong chẩn đoán và xử trí nhiều loại bệnh lý thận. Siêu âm B-mode với độ phân giải cao chỉ có thể cung cấp các chi tiết giải phẫu chứ không thể thông tin về chức năng thận. Tuy nhiên, siêu âm màu Doppler và siêu âm màu năng lượng đã làm tăng khả năng chẩn đoán của siêu âm khi đánh giá về thận. Thí dụ siêu âm Doppler ảnh đôi có thể cung cấp thông tin về chức năng khi khảo sát huyết động học của thận vốn bình thường có nhiều mạch máu. Thoạt đầu siêu âm Doppler được dùng để khám tổng lực về các thận ghép, nhưng hiện nay được dùng để khám hầu hết các loại bệnh lý thận.

So sánh tính tương hợp giữa siêu âm đàn hồi S-Shearwave và Fibroscan qua khảo sát 100 bệnh nhân cóbệnh lý gan mạn tính
13/04/2020 10:51:39 | 0 binh luận
Nội dung 1. Đặt vấn đề 2. Tổng quan 3. Đối tượng và phương pháp nghiên cứu 4. Kết quả nghiên cứu 5 Kết luận
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












