ĐẶC ĐIỂM XÉT NGHIỆM VÀ HÌNH ẢNH CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ TUYẾN YÊN TRÊN BỆNH NHÂN MẮC HỘI CHỨNG CUSHING PHỤ THUỘC ACTH
23/01/2024 11:48:10 | 0 binh luận
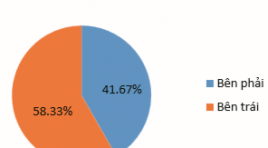
TÓM TẮT Mục tiêu : Khảo sát hình ảnh tuyến yên trên cộng hưởng từ ở những bệnh nhân mắc hội chứng Cushing phụ thuộc ACTH. Đối tượng và phương pháp nghiên cứu: Nghiên cứu mô tả cắt ngang 15 bệnh nhân (12 nữ, 3 nam) được chẩn đoán mắc hội chứng Cushing phụ thuộc ACTH và được chụp cộng hưởng từ tuyến yên từ tháng 10/2022 đến tháng 10/2023. Kết quả nghiên cứu: Tỷ lệ nam/nữ = 1/4. Tuổi trung bình 38,47 ± 10,78 (27-62). Tất cả bệnh nhân đều có nồng độ ACTH huyết tương >10pg/ml, phù hợp với chẩn đoán lâm sàng hội chứng Cushing phụ thuộc ACTH. Bệnh nhân quan sát thấy u tuyến yên trên cộng hưởng từ chiếm 80%. Kích thước u trung bình là 4,59 ± 1,77mm, 100% u là microadenoma, phân loại độ I, giai đoạn 0 theo phân loại của Hardy-Wilson. Nhóm u đồng tín hiệu trên các chuỗi xung T1W và T2W chiếm tỷ lệ cao nhất, lần lượt là 83,4% và 58,3%. Trên chuỗi xung tiêm thuốc động học, tất cả u biểu hiện là nốt ngấm thuốc kém. Kết luận: Hình ảnh u tuyến yên trên cộng hưởng từ rất đa dạng, đặc biệt là đặc điểm tín hiệu của u. Việc đánh giá kết hợp trên chuỗi xung động học sau tiêm thuốc đối quang từ là cần thiết để chẩn đoán đối với những trường hợp u kích thước nhỏ và đồng tín hiệu trên các chuỗi xung thường quy. Từ khóa: cộng hưởng từ, u tuyến yên, hội chứng Cushing phụ thuộc ACTH, microadenoma, phân loại Hardy-Wilson
NGHIÊN CỨU BƯỚC ĐẦU KẾT QUẢ CHỤP VÀ NÚT MẠCH TRONG ĐIỀU TRỊ CHẢY MÁU TIÊU HÓA DƯỚI
17/10/2023 17:15:40 | 0 binh luận
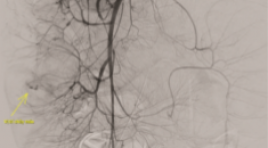
SUMMARY Background: Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (ALGB) is an urgent, potentially life-threatening emergency, especially in case endoscopy is not identifiable or uncontrollable in management bleeding. Following the development of technology and applying minimal invasive modalities, endovascular treatment is more and more to be applied. Primary endpoint: Figure out the rate of technical success, the clinical success and the complication relating to bowel ischemia of embolization in ALGB. Secondary endpoint: Figure out the rate of negative bleeding finding angiograms in diagnosis of ALGB Method: Retrospective cohort study Results: From 01/2019 to 01/2022, 23 embolisms were performed in total 35 procedures of 24 patients. There were 12 angiographies with negative bleeding finding result (34.3%). In embolization procedure, first embolisms were 21/23 and two procedures were re-embolism. The rate of technical success after first embolisms was 95.2% and clinical success reaches 76.2%. There was no major complication relating to bowel ischemia. Conclusion: Transcatheter angiographic embolization is a safe and effective management for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding with minimal invasive. Keywords : acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding, embolization, endovascular
GIÁ TRỊ CỦA CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ DỊ VẬT ỐNG TIÊU HÓA SẮC NHỌN
13/10/2023 17:05:44 | 0 binh luận
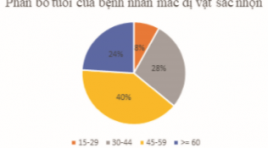
SUMMARY Ingested foreign bodies are one of the reasons why patients need to be hospitalized in the emergency room. Although most gastrointestinal foreign bodies can be eliminated from the body on their own, there are still some cases that cause complications, even death. In terms of foreign body morphology, there are 3 main groups, sharp-pointed foreign bodies, round foreign bodies and long foreign bodies, of which sharp-pointed foreign bodies are the group that often causes complications, especially perforation complications. There are many methods to diagnose this condition such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT) and endoscopy. In recent years, the popularity of CT has made this method widely used in the assessment of sharp-pointed gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Objective: In order to evaluate the effectiveness of CT in diagnosing sharp foreign bodies, we would like to conduct the study "Value of computed tomography in evaluation of sharp-pointed ingested foreign bodies". Subjects and research methods: A descriptive study of 25 patients with sharp-pointed foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract who underwent CT scan at the Radiology Department of Hanoi Medical University Hospital for 2 years, and underwent endoscopic and surgical or percutaneous intervention to remove of foreign bodies. Results: The most common site for foreign bodies was the jejunum, followed by the stomach, colon, and esophagus. Transmural foreign body accounted for the highest rate (14/25 cases). The most common complication of sharp-pointed foreign body on CT is perforation with 16/25 cases, followed by abscess with 04/25 cases. CT scan has high sensitivity and specificity in evaluating complications of sharp-pointed foreign bodies. Conclusion: CT has an important role in detecting and diagnosing sharp-pointed gastrointestinal foreign bodies as well as evaluating associated complications. Key word: Ingested foreign bodies, foreign bodies, complications of foreign bodies, sharp-pointed foreign bodies, sharp-pointed
NHẬN XÉT SỰ AN TOÀN CỦA DẪN LƯU BỂ THẬN QUA DA DƯỚI HƯỚNG DẪN CỦA SIÊU ÂM VÀ DSA Ở BỆNH NHÂN TẮC NGHẼN ĐƯỜNG BÀI XUẤT CAO
13/10/2023 16:35:42 | 0 binh luận
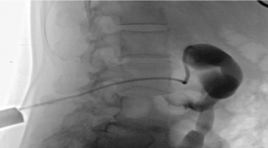
SUMMAR Aim : to access the safety and complications of Percutaneous Nesphrostomy in obstructed urinary upper tract. Patients and methods : a cross-sectional descriptive study was performed on 45 patients who were diagnosed with pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis due to obstructed urinary upper tract at the Radiology Department, Ha Noi Medical Hospital from 6/2021 to 8/2022. Results: 100% of patients who have hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis taken broad-spectrum antibiotics before performing percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN). Position to drain into renal pelvis: 93.3% from the inferior pole, 6.7% from the middle pole. 91.1% of patients were performed successfully Percutaneous Nephrostomy the first time and 8.9% of patients needed in the second time. The successful rate of Percutaneous Nephrostomy was 100%. Time to complete procedure on average 19.5±4.5 minutes. Bleeding complications accounted for 2.2% (n=1), Sepsis complications accounted 6.7% (n=3). Catheter obstruction was 18% (n=8). The size of the sonde drainage 8F was used for patients with Hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis in grades I and II. The size of the sonde drainage 10-12F was used for patients with Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis in grades III and IV. Conclusion: Percutaneous nephrostomy is a minimal, safe, effective treatment procedure. Keywords : Renal Nephrosis, Pyelonephritis, Percutaneous Nephrostomy

Hướng dẫn phòng, chẩn đoán và xử trí phản vệ Thông tư 51/2017/TT-BYT và một số lưu ý
25/08/2021 14:43:19 | 0 binh luận

Vai trò của KTV trong việc chuẩn bị bệnh nhân chụp CT có têm cản quang và cách xử lý các phản ứng sau têm
25/08/2021 14:49:25 | 1 binh luận
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












