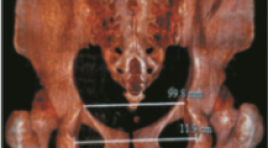
KHẢO SÁT KÍCH THƯỚC KHUNG CHẬU Ở PHỤ NỮ VIỆT NAM TRƯỞNG THÀNH BẰNG CHỤP CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH
22/01/2024 16:36:43 | 0 binh luận
Mở đầu: Xác định các thông số khung chậu nữ bình thường hỗ trợ chẩn đoán bất xứng đầu chậu chính xác hơn, giảm tỷ lệ mổ lấy thai không cần thiết. Chụp cắt lớp vi tính (CLVT) có thể đo kích thước khung chậu. Mục tiêu : Xác định kích thước, các yếu tố ảnh hưởng ở người phụ nữ Việt Nam trưởng thành. Đối tượng và phương pháp nghiên cứu : Thực hiện cắt ngang mô tả trên 257 phụ nữ trưởng thành được chụp CLVT bụng - chậu; đo các kích thước và so sánh theo nhóm tuổi, tiền sử số lần sinh, chiều cao. Kết quả : Các kích thước trung bình của khung chậu: đường kính liên hợp sản khoa và ngang giữa là 11,8 ± 0,9 cm, 12,2 ± 0,9 cm; đường kính trước sau eo giữa và lưỡng gai là 11,2 ± 0,8 cm, 10,6 ± 0,8 cm. Các đường kính ở nhóm ≥ 40 tuổi nhỏ hơn khi so sánh với nhóm 30 – 39 tuổi và nhóm 18 -29 tuổi, p ≤ 0,05. Các đường kính eo giữa và đường kính trước sau eo dưới ở nhóm chưa sinh nhỏ hơn nhóm đã sinh, p ≤ 0,05. Các đường kính ở nhóm ≤ 145 cm nhỏ hơn nhóm > 145cm, p ≤ 0,05. Kết luận: Nghiên cứu đưa ra giá trị tham khảo cho các đường kính khung chậu phụ nữ Việt Nam trưởng thành, có thể hỗ trợ chẩn đoán bất xứng đầu chậu chính xác hơn. Từ khóa : Đường kính khung chậu nữ, CLVT

Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ 1.5 tesla trong chấn thương dây chằng, sụn chêm khớp gối
06/05/2021 17:39:25 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: Image Characteristic of ligament and meniscus injuries of the kneee on 1.5Tesla magnetic resonance imaging at Duc Giang hospital. Methods: The cross-sectional retrospective study of 98 patients with diagnosed of knee injuries by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at Duc Giang Hospital from January 2018 to January 2020, aimed to comments on MRI appearance features in knee injury. The cross sectional study on the statistical basis of data to make comments on the MRI features in the diagnosis of knee injury, using Siemen Essenza 1.5 Tesla MRI with knee joint coil. Result: The most common age is from 20 to 40 years old. Male prominent. MRI can detect osseous edema with 35.7% in tibia and Femur is 23,5%, 94.9% anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and 5.1% posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury. On the other hand, there were 45,9% medial meniscal and 25,5% lateral meniscal injury. We saw 2% tibial collateral ligament and 1% fibular collateral ligament. Conclusion: MRI imaging features play an important role in diagnosing and accessing the severity of knee injury. Keywords: ligament, meniscus, knee injury, MRI, ACL, PCL
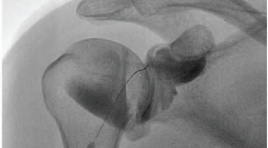
Nghiên cứu hiệu quả điều trị bệnh đông cứng khớp vai bằng phương pháp tiêm nong khớp vai dưới hướng dẫn của DSA
06/05/2021 15:00:46 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective : The objective was to explore the efectiveness of fluoroscopic-guided hydrodilatation of glenohumeral joint for the treatment of frozen shoulder Materials and Methods: The prospective study 38 shoulders with primary adhesive capsulitis were treated with hydrodilatation between August 2017 and July 2020 in Radiology Centre- Bach Mai Hospital. The patient were hydrodilatation with corticosteroid injection performed via an anterior approach under fluoroscopy. Patients were followed up at baseline and at 2 and 4 weeks postintervention with Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) scores, VAS scores, and ROM in abduction, forward flexion, external rotation. Results: A total of 38 consecutive patients with frozen shoulder underwent a distension arthrogram. There were 20 females and 18 males with a mean age of 59,6 (range : 43-91). The mean visual analogue pain score pre-distension was 6,1, two weeks and four weeks post-distension the mean score had significantly improved to 4,1 and 2,9. Mean baseline SPADI score for the patients pre-distension was 65, two weeks and four weeks post-distension the mean score had significantly improved to 45 and 32. Flexion improved from a mean of 76 degrees pre-distension with 106 degrees at 2 weeks and with 131 degrees at 4 weeks. Abduction improved from a mean of 75 degrees pre-distension with 107 degrees at 2 weeks and with 133 degrees at 4 weeks. External rotation improved from 20 degrees pre-distension with 36 degrees at 2 weeks and 53 degrees at 4 weeks. The patients receiving hydrodilatation demonstrated significant improvement in VAS scores and ROM in flexion, abduction, and external rotation at 8 weeks. No patient suffered any significant complication from hydrodilatation and, in particular, there were no intra-articular infections. Conclusion: Review of the literature and the results presented here indicate that arthrographic capsular distension progressing using fluid containing cortisone is a fairly effective treatment for adhesive capsulitis. Distension arthrography seems to he a promising treatment for adhesive capsulitis. Arthrographic shoulder capsule distension was performed through an anterior-lateral approach under fluoroscopic guidance is accurate, reliable and minimally invasive. Keyword: Hydrodilatation, adhesive capsulitis
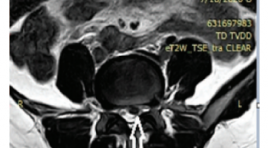
Tương quan của hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ với triệu chứng lâm sàng của bệnh thoát vị đĩa đệm cột sống thắt lưng
06/05/2021 17:26:04 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Abtracts: Retrospective study of patients diagnosed with clinical disc herniation and magnetic resonance and had surgery at the Orthopedic and Spinal Trauma Department, Bach Mai Hospital. Results: 29.5% of patients in this study involved L5 - S1 disc herniation and 45.5% of patients with L4 - L5 disc herniation. Spinal Syndrome, Nerve Root Syndrome and Sensory Disorders are the most common symptoms. Nutritional disorders and sphincter disorders are found in posterior disc herniations and in the graft holes, in the L4-L5 and L5-S1 layers. Magnetic resonance is of high value in the diagnosis of lumbar spinal disc hernias and hernias, in diagnosing hernias, sensitivity from 97.9 %% - 100%, specificity from 98.1% - 100% accuracy from 98.2% - 100%; In the diagnosis of a specific herniation layer, the sensitivity ranges from 95.5% - 100%, the specificity is 90% - 100%, the accuracy is 94.2% - 100%. Conclusion: In our study, correlation in shown between clinical findings and MRI results. The most common clinical symptoms are spinal syndrome and nerve root syndrome. Disc herniation often protrusions, herniated backwards and in the L4-L5 layer. Magnetic resonance is of high value in diagnosing types and layer lumbar spinal disc hernias with accuracy from 94.2%-100%. Key words: Disc degeneration, Disc herniation, Magnetic resonance imaging
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"














