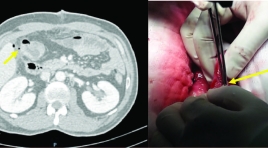
Đặc điểm hình ảnh X quang cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán bục xì miệng nối ống tiêu hóa
04/12/2019 12:11:04 | 0 binh luận
Describsing the features of computed tomography in diagnosting of anastomotic leak SUMMARY Purpose: Describe the features of anastomotic leak on computed tomography (CT). Materials and Methods: Retrospective studies described case series of patients who were diagnosed anastomotic leak at University Medical Center at HCMC and Cho Ray hospital from December 2014 to June 2018, and had CT scan before surgery. The CT features of anastomotic leak were collected. Results: There were 31 patients. Mean age 58, ratio male/female 1,8. Peri-anastomotic gas-fluid collection 58,1 %; density of peri-anastomotic fluid collection varies from 5 HU to 30 HU (mean # 20,3 HU); extraluminal gas in contact with the anastomosis 71,0 %. Only 1 case that has mural discontinuity sign (3,2 %). Intraluminal bowel contrast CT scan was used in 2 cases and both had extravasation (100 %). Conclusion: CT scan is valuable in helping to diagnose anatomotic leak. Two most common and signficant signs in the diagnosis are perianastomotic gas-fluid collection and extra-luminal gas in contact with the anastomosis. Key words: Anastomotic leak, computed tomography findings.
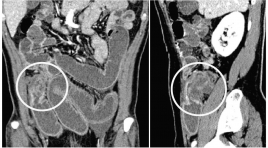
Giá trị cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán phân biệt các u nguyên phát thường gặp ở ruột non
04/12/2019 20:32:12 | 1 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives: The purpose of the this study was to analyze imaging roles to assessthe diagnostic capacity for differentiating the common primary small bowel tumors. Methods: We performed a retrospective study from the medical database from January 2015 to May 2018 at University medical center and Cho Ray hospital. The inclusion criteria were as follows: pathologically proven primary small bowel neoplasms andpatients were performed MDCT with intravenous contrast media. Radiologist were blinded to the pathological information, reviewed the image findings according to the data collection paper. Radiologist collects the characteristics of neoplasm such as anatomical distribution, growth, enhancement, wall thickening patterns, size, hyperplasia vascular on tumor surfaces and lymph node characteristics. Then, comparing each findings to pathology report to access specificity, sensitivity and positive predictive value (PPV) of them. Results : A total of 98 patients met the criteria for analysis in thepresent retrospective study, 31 adenocarcinomas, 22 lymphomas, 30 GISTs anf 15 others. The extramural growth pattern isreliable prediction of GIST, with PPV of 82.3%. All of GISTs show moderate to avid enhancement. Tumor density of greater than or equal to 110 HU is likely to be GIST, with PPV of84.9%. Proliferation of blood vessels on tumor surfaces can help discriminate GIST from the others, with PPV of92%. Bowel wall thickening is the common patternof adenocarcinoma and lymphoma. Apple-core-like, shoulder defect and focal involvement are probably findings of adenocarcinoma, with PPV of 81.8%, 71.4% and 76.9%, respectively. Aneurysmal dilatation of the lumen and marked thickening wall bowel equal or greater than 25mm can strongly suggest lymphoma, with PPV of 87.5% and 72.7%, respectively. Enlarged lymph node with shorter axis greater than 20mmor multiple lymph nodes fused together forming a bulky massare likely to be lymphoma, with specificity of 100%. Conclusion : MDCT findings could potentially be useful to differentiate the common primary small bowel neoplasms based on analyzing specific imaging characteristics of each tumor after classifying by growth pattern lesion. Keywords : Small bowel neoplasm, differentiate
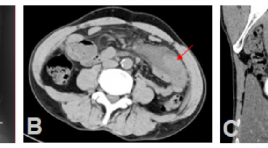
Tụy lạc chỗ tại ruột non với biến chứng viêm hoại tử ruột: Báo cáo một trường hợp hiếm và tổng kết trên y văn
15/04/2020 20:42:50 | 0 binh luận
Ectopic pancreas in the wall of intestine complicated with necrotic and inflamed intestine: A case report and review literature SUMMARY Background: Ectopic pancreas is a rare congenital condition characterized by pancreatic tissues located outside normal of confines of pancreas and lacking any anatomic or vascular connection with main pancreas. It can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract but rarely are found in small intestine. Its preoperative diagnosis is difficult because the clinical symptoms are often nonspecific. We introduce a case of ectopic pancreas in the intestinal wall complicated with necrotic and inflamed intestine, which received a treatment by resection. Case presentation : A 44 years old man attended to Bach Mai hospital due to acute abdominal pain in epigastrium as result of gastrointestinal perforation. Contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) of abdomen showed a mesenteric mass surrounded by inflamed fat in the left lower quadrant abdomen. In addition, CT images also suggested necrosis of the bowel wall next to the mass caused by twisting the mesentery and mesenteric vessels (whirlpool sign). The patient underwent local surgical resection and following histology revealed ectopic pancreatic tissues in the wall of intestine and necrosis of intestine. Conclusion : Although ectopic pancreas is rare, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a mesenteric or intestinal mass surrounded by necrotic and inflamed intestine. Keyword: Ectopic pancreas, mesenteric mass, intestinal mass, whirlpool sign.

Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và đánh giá tính chất xâm lấn, di căn của ung thư dạ dày trên cắt lớp vi tính đa dãy
01/04/2020 16:03:31 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics and the invasion, abdominal metastases of gastric cancer with MDCT SUMMARY Purposes: Describe imaging characteristics and assess value of MDCT in evaluating the invasion, abdominal metastase of gastric adenocarcinoma based on the 7 th AJCC guidelines. Materials and methods: From 4/2014 to 3/2015, there are 32 consecutive patients with gastric adenocarcinoma were undergone 64-slide-CT. All of them were undergone operation with pathology after surgery. Results: The average age is 63 years old, and male/ female=2/1. In 37.2% of cases gastric carcinoma is located on antrum. About macroscopic type, the forth type (linitis plastica) rates are highest 68.8%. The thickness of gastric cancer is pricipal 15-19 mm, all of cases heterogeneous enhancement. There are 17 cases invasion adjacent organs, in which tranverse colon is 8 cases and pancreas is 7 cases. Evaluating the value of diagnosis peritoneal metastase between MDCT and surgical resection is appropriated with medial level Kappa = 0.53, the sensitivity is 75%, the specificity is 89.3%. The overall accuracy of T staging is 62.5% (T1 66.7%, T2-T3 69.2%, T4a 44.4%, and T4b 71.4%). Diagnosis lymph nodes metastasis based on the diameter has got the low valuation with p>0.05, based on the short axis diameter is < 8mm and ≥8mm has got p <0.05. About the shape of lymph nodes, based on irregular shape, peripheral enhancement and round shape to evaluate metastasis with p <0.05. Conclusion: MDCT with multi-planar reformatted images has increased the accuracy of T and N staging, evaluated the invasion, abdominal metastase of gastric cancer on MDCT.
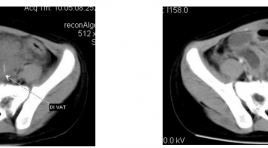
Áp xe cạnh đại tràng xich ma do dị vật phát hiện trên CLVT
01/04/2020 09:14:07 | 0 binh luận
A case report of parasigmoidabcess due to foreign body SUMMARY We present the case of parasigmoidabscess due to foreign body that was diagnosed and treated in NHP, Hanoi. The childaged 4 years old, hospitalized with abdominal paint, fever and diarrhea. The child was examined by Abdominal Ultrasound, CT scanner. Operation revealed the diagnosis of parasigmoidabscess due to foreign body.
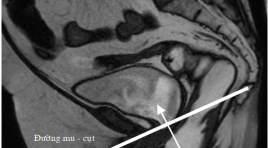
Đánh giá đặc điểm sa trực tràng kiểu túi ở bệnh nhân rối loạn chức năng sàn chậu bằng cộng hưởng từ động
31/03/2020 19:09:28 | 0 binh luận
Evaluation of rectocele in patients with pelvic floor dysfunction by dynamic magnetic resonance imaging SUMMARY Objectives : Rectocele is a bulge or a prolapse of the anterior rectal wall into the posterior vaginal wall. It is relatively common with diversified and nonspecific symptoms. Clinical examination is easily confused and/or sometimes omitted the prolapse of other pelvic organs. Imaging to assess the pelvic floor dysfunction is an important and useful diagnostic test, especially dynamic MR. Methods : Our study was cross-sectional descriptive. Patients with pelvic floor dysfunction were undergone clinical examinations and then were indicated to have dynamic MR scanning at Ho Chi Minh City Medical University by anorectic doctor, urologist and gynecologist. Results: 1.863 patients were evaluated from January 2008 to June 2012. Most of them are women, middle-aged and used to give birth. The rate of rectocele with its depth from 2 to 4 cm was 77.9%, mainly with the shape of “finger”. The depth of more than 2 cm with the shape of “bag” has the high risk of stagnancy. The factor of age and being used to give birth have a significant relation with rectocele (p<0.001). The rate of rectocele in the group of anismus was 64.2%. The combination of the prolapse of more than one pelvic chamber accounted for 77.4% (p<0.001). Conclusions : Dynamic MR of the pelvic floor helps to diagnose in details the characteristics of the rectocele and other pelvic organ prolapse, helping clinicians to choose the appropriate treatments.
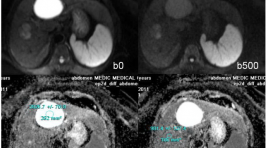
Vai trò của ADC trong chẩn đoán phân biệt giữa tổn thương lành tính và ác tính ở gan
31/03/2020 15:26:23 | 0 binh luận
summary Purpose : Assessing the role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) measurement in differentiation of benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions. Methods and Materials: Retrospectively evaluated the 248 patients cases, executed hepatic MRI at Medic Medical center, from on February 2011 to on February 2013, age range 41 - 78years, with 142 benign hepatocellular lesions (30 FNHs, 9 HCAs, 63 hemangiomas and 40 cysts) and 104 malignant lesions (76 HCC and 28 metastasis) diagnosed, 50 patients had normal liver. All the patients executed Diffusion weighted imaging - MRI with three b values (0, 500, 800 sec/mm2) on the Siemens Avanto 1,5T MRI. Results : We found difference between ADC of benign lesions compared with malignant lesions (mean ± standard deviation): ADC of normal liver (1.242 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.33), FNH-HCA (1.742 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.40), Hemangiomas (2.084 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.46), Cyst (2.861 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.34), HCC (1.093× 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.37), Metastasis (1.126 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.48). ADC of benign lesions: (2.327 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.41), compared with malignant lesions: (1.113 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.39). Conclusion: Mean value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) contribute to differential diagnosis between benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions.
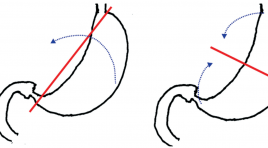
Xoắn dạ dày ở trẻ em đặc điểm lâm sàng và siêu âm
03/04/2020 12:32:30 | 0 binh luận
Gastric volvulus in children: clinical and sonographic findings summa ry Objectives : The purpose of this study is to present the clinical and sonographic findings of gastric volvulus in children. Materials and methods: We reviewed all cases of gastric volvulus operated in our hospital and having preoperative ultrasound from 2008 to 2010. Results : From 2008 to 2010, there were 13 cases of gastric volvulus, of these, 11 acute and 2 chronic cases. Age ranged from 2 months to 12 years. Male: female was 4:9. Illness duration were 1-10 days for acute volvulus and 6 months to 2 years for chronic cases. Vomiting, abdominal pain and epigastric distension were 100%, 84.6% and 69.2% respectively. Associated anomalies such as wandering spleen, asplenism and diaphragmatic anomaly were 46%, 15.4% and 15.4% respectively. In acute gastric volvulus, ultrasound revealed dilated and fluid-filled stomach in 100%, fluid-fluid level in 90.9% and longitudinal septal sign in 81.8%; Plain radiograph showed single large gas bubble in 91%, one case had bubble in the left hemithorax. In acute cases, ultrasound diagnosed correctly in 84.6%. Two chronic cases that ultrasound and plain radiograph did not detect were diagnosed with UGI study. Conclusion s: Acute gastric volvulus can be diagnosed with specific sonographic findings. Chronic cases can be detected with upper gastrointestinal series. Keywords: gastric volvulus, children, ultrasound.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












