
Giá trị của sinh thiết lõi dưới hướng dẫn cắt lớp vi tnh trong chẩn đoán bản chất các khối u vùng bụng
25/08/2021 12:50:50 | 0 binh luận
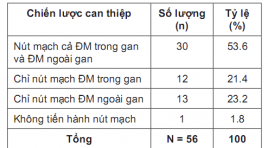
Đánh giá hiệu quả nút mạch ngoài gan của ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan tại Trung tâm ĐIỆN QUANG Bệnh viện BẠCH Mai
06/05/2021 14:27:58 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: Evaluation the effectiveness of the extrahepatic arterial chemoembolization on treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Subjects and methods: There is a non-controlled prospective intervention study in HCC patients with tumors which had blood supply from extrahepatic arteries from July 2019 to August 2020 in Radiology center of Bach Hospital. Results: . Our study was performed on 56 patients including 48 men (85.7%) and 8 women (14.3%) who were diagnosed with HCC. The mean age were 58.29 ± 10,849 years old. The rate of successful approaching to the extrahepatic vessel branches was 83.05%. There were 2 patients (3.58%) had acute complications during and immediately after intervention. Special complications related directly to the extra-hepatic embolization were observed in 14 patients (25%). After an average of 2.25 ± 0.919 months of follow-up, 1 patient (1.8%) re-examined due to rupture of liver tumor, the remaining 55 patients (98.2%) were reexamined by appointment. The results of tumor response according to mRECIST with complete response, partial response, stable disease and progressive disease were 3.6%, 52.7%, 25.5%, and 18.2% respectively. Conclusion : The results of the extrahepatic arterial chemoembolization in our study had high rates of the successful approaching to the extrahepatic vessel branches, the intervention safety and the post-intervention tumor response. Key words: TACE, Extrahepatic artery supply to HCC
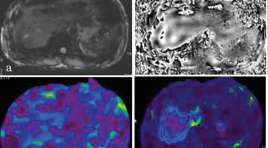
Cộng hưởng từ đàn hồi gan: nguyên lý, kỹ thuật và ứng dụng lâm sàng
05/05/2021 17:35:14 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Magnetic resonance elastography of liver is a technique for evaluation of liver stiffness and is currently considered the most accurate non-invasive imaging technology for evaluation of liver fibrosis. MRE used a phase-contrast sequence which examinate the propagation of mechnical waves in the liver parenchyma to generate to images depicting the stiffness of tissure. Hepatic fibrosis increases the stiffness. MRE can detected early fibrosis and evaluated stage of liver fibrosis through changes of the stiffness of liver parenchyma. MRE is more accurate than US elastography in the evaluation liver fibrosis. MRE has been used commonly in the word. Choray hospital is one of the first hospital to implement MRE in Viet Nam. In this lecture, we will introduce the basic principles, techniques and clinical applications of liver MRE. Keywords: Magnetic resonance elastography, liver, stiffness, fibrosis, cirrosis, principle, technique, applications
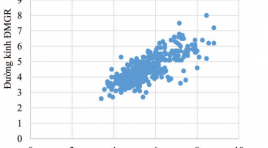
Ứng dụng X quang cắt lớp vi tính trong đánh giá mối tương quan giữa kích thước mạch máu gan với các yếu tố tuổi, giới tính và dạng giải phẫu
05/05/2021 17:13:29 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: The study aimed to determine the correlation between dimensions of hepatic vessels (including hepatic arteries, portal and hepatic veins) and aging, gender and anatomical variants factors, using multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Design: We conducted a retrospective study of 611 adults (344 Male, 277 Female, mean age 55.0 ± 13.1 years), who were clinically examined and underwent abdominal MDCT with iodinated contrast agents for different complaints at the University Medical Center between August 2017 and August 2018. MDCT images were stored on the picture archiving and communication system (PACS) and processed to create multiplanar reformation (MPR), curved planar reformation (CPR), maximum intensity projection (MIP), volume rendering (VR) images which were subsequently used to measure the length and diameter of hepatic arteries, portal, and hepatic veins. Also to determine the correlation between dimensions of hepatic vessels and aging, gender and anatomical variants factors. Results: The average diameter of common hepatic artery in the variant group was smaller than in the normal group. The length of common hepatic artery increased with age (P<0.05). There was a strong correlation (R = 0.77, P <0.05 ) for the diameters between the common hepatic and proper hepatic arteries. The diameters of main portal vein, right portal vein and left portal vein decreased with age (P<0.05). The male group had diameters of hepatic artery and portal vein greater than the female one. There is no correlaton between the dimension of hepatic veins and some factors of anatomy, age and gender. Conclusions: MDCT might be considered a safe and accurate imaging modality with high sensitivity in assessing the correlation between dimensions of hepatic vessels and the factors of age, gender and anatomical variants.
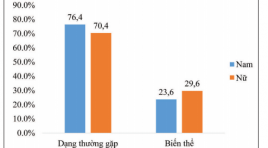
Khảo sát hình thái mạch máu gan và các biến thể giải phẫu bằng hình chụp x quang cắt lớp vi tính
05/05/2021 17:08:09 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Aims: To identify the prevalence of normal anatomy and vascular variants of hepatic vessels by using multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of 611 adults who, for different reasons, came to university medical center Hochiminh city, all underwent abdominal MDCT with contrast material. From the data stored in PACS, using image processing applications (MPR, CPR, MIP, VR) to investigate anatomy of the hepatic artery, the portal vein and the hepatic vein systems. Results: From 08/2017 to 08/2018 at University Medical Center, HCMC, a total of 564 of the 611 patients had the common hepatic artery originated the celiac axis, anatomic variations were seen in 7.7% of patients. 9 of 10 anatomic types (criteria laid by Michels ‘s classification) were identified in our study, type 1 (the typical type) seen in 73.6% cases, we also found 5 other types of the hepatic artery not mentioned in Michels classification (3.1%). Normal anatomy of portal vein was identified in 84.1% of cases. Trifurcation - the most popular type of portal vein variants was seen in 11.3% of patients. The common trunk between the left hepatic vein and the median hepatic vein was seen in 58.6% cases. The accessory right hepatic veins were identified in 45.5% of the patients. There were not correlation between kinds of hepatic vascular variants (p>0.05). Conclusion : Hepatic vascular anatomy plays an important role in hepatectomy, pancreaticoduodenectommy and living liver transplantation. Because of high prevalence of vascular variants, knowledge of these abnormalities and their frequency is of major importance for the surgeon * Bệnh viện ĐHYD TP. HCM. as well as the radiologist.
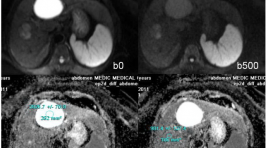
Vai trò của ADC trong chẩn đoán phân biệt giữa tổn thương lành tính và ác tính ở gan
31/03/2020 15:24:03 | 0 binh luận
summary Purpose : Assessing the role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) measurement in differentiation of benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions. Methods and Materials: Retrospectively evaluated the 248 patients cases, executed hepatic MRI at Medic Medical center, from on February 2011 to on February 2013, age range 41 - 78years, with 142 benign hepatocellular lesions (30 FNHs, 9 HCAs, 63 hemangiomas and 40 cysts) and 104 malignant lesions (76 HCC and 28 metastasis) diagnosed, 50 patients had normal liver. All the patients executed Diffusion weighted imaging - MRI with three b values (0, 500, 800 sec/mm2) on the Siemens Avanto 1,5T MRI. Results : We found difference between ADC of benign lesions compared with malignant lesions (mean ± standard deviation): ADC of normal liver (1.242 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.33), FNH-HCA (1.742 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.40), Hemangiomas (2.084 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.46), Cyst (2.861 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.34), HCC (1.093× 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.37), Metastasis (1.126 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.48). ADC of benign lesions: (2.327 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.41), compared with malignant lesions: (1.113 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.39). Conclusion: Mean value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) contribute to differential diagnosis between benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions.
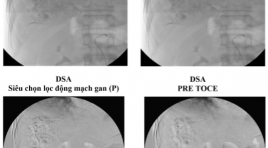
Ung thư gan vỡ, xuất huyết ổ bụng, được trị liệu hóa dầu thuyên tắc mạch qua catheter (TOCE) tai bệnh viện Hoàn Mỹ Đà Nẵng: Nhân một trường hợp
26/03/2020 22:18:24 | 0 binh luận
Ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc), bleeding in abdomen is treated by toce (transcatheter oily chemoembolization) at hoanmy DaNang hospita: a case report SUMMARY - HCC is the most common of cancer liver. - Nature progress, metastasis is complex, multiple organs. - Ruptured HCC, Bleeding in abdomen, hypotention, shock,...: is severe statement, progress is very rapid, complex, serious, dead rate is hight. - Diagnotic and treatment (TOCE) of ruptured HCC must rapid, exact. Doing everything possible to keep the patient alive !. - A report of a man patient 79 year olds, at emergency room of Hoan My Da Nang hospital, was diagnosted ruptured HCC, hypotention,…He hadbeen taken emergency abdoment CT and treatmented – TOCE. The doctors did everything possible to keep him alive. - Follow- up and consolidate TOCE, crux problem !\ Keyword: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Computed tomography, Digital Subtraction Angiography, Transcatheter Oily Chemoembolization, Gastrointestinal endoscopy surgery, laparoscopic surgery.
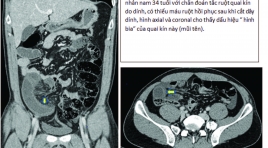
Các dấu hiệu chụp cắt lớp vi tính chẩn đoán thiếu máu và hoại tử ruột ở tắc ruột non quai kín
17/12/2019 10:30:16 | 0 binh luận
CT findings for diagnosis of bowel ischemia and necrosis in closed-loop small-bowel obstruction SUMMARY Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the imaging features of contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) to diagnosis for bowel ischemiaand necrosis in closed-loop small-bowel obstruction Materials and Methods: Thirty-three patients with CL-SBO confirmed by laparotomy. Based on the surgical findings, these patients were classified into three groups: necrosis group (n = 9), ischemia without necrosis group (n = 12), and no-ischemia group (n = 12). Two blinded radiologists retrospectively reviewed CECT including multiplanar reconstruction images and evaluated 11 CT findings. The sensitivity and specificity of each finding were compared among the three groups, and logistic regression analysis was performed. Results:Reduced bowel- wall enhancement, reduced enhancement of the mesenteric veins showed high specificities of 92%, 96% and sensitivities of 62% and 78%, respectively, for the prediction of bowel necrosis in CL-SBO. The target sign in the ischemia group were 83% and 76%, respectively, for sensitivities and specificities, compared with 22% and 46% of the necrosis group. We have included the data in a univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, but there is no correlation between imaging features and surgical findings. This can be explained by the interval between CT and laparotomy has altered bowel conditions. Conclusions : In our prospective patients, reduced enhancements of bowel wall and mesenteric veins were good indicators of bowel necrosis. On the contrary, target sign was a predictor of a viable bowel. Key words : intestinal obstruction, closed loop, ischemia, necrosis, computed tomography.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












