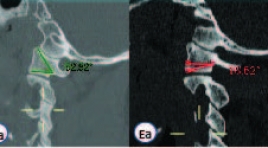
Đánh giá chỉ số giải phẫu C1, C2 trên cắt lớp vi tính phục vụ phẫu thuật chấn thương cột sống cổ cao
18/12/2019 09:37:47 | 0 binh luận
A computed tomographic study of C1, C2 morphology for atlantoaxial screw fixation techniques SUMMARY Purpose : This study is aimed to define the ethnic differences in the radiological measurements on C1 and C2 in Vietnamese population in order to determine the feasibility of implement C1-2 fixation techniques. Study design: Retrospective study. Methods : From October 2017 to April 2018, 120 thin-slide (1 to 3 mm) computed tomography scans of the cervical spine were reviewed. Various dimensions of C1 and C2 were analyzed on axial, sagittal reconstructed CT images. The differences between the right and left sides and between males and females were statistically analyzed using t-test, with a p-value of < 0.05 considered significant. Results: Mean anteroposterior dimension and transverse width of C1 lateral mass were 19.7±2.1 mm and 12.2±1.7 mm, respectively. Mean angle of the screw directed to maximal medial, lateral, cranial and caudal were 36.6±2.80, 28.2±3.00, 49.6±4.10 and 26.4±5.50 respectively. Average isthmus height, internal height and pedicle width of C2 were 5.8±1.0 mm, 4.8±1.3 mm and 5.0±1.3 mm. No significant differences between the right and the left side of C1, C2 parameters and between sex variations. The prevalence of high-riding vertebral artery was 13.8% and narrow pedicle was 17.9%. Conclusions: this study shows that the morphology of C1 and C2 is variable between Vietnamese and other populations. Due to several cases may not be relevant for C1-2 fixation techniques, preoperative anatomy evaluation based on CT data need to be performed for screw placement and trajectory planning. Key word: atlanto-axial trauma, C1 lateral mass dimension, high-riding verebral artery, C2 narrow pedicle.
Đánh giá hiệu quả can thiệp nội mạch trong điều trị phình mạch tạng sau chấn thương
17/12/2019 09:40:53 | 1 binh luận
To evaluate the effectiveness of endovascular intervention for treatment of traumatic visceral pseudoaneurysms SUMMARY Background: Visceral pseudoaneurysm was rare condition, its complication of bleeding led to severe clinical scenario, causing blood loss shock and death. Surgery was an invasive treatment and had high rate of morbidity and mortality; therefore, endovascular intervention has gradually becoming an alternative treatment nowadays. Objectives: To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of endovascular treatment in patients with traumatic visceral pseudoaneurysms. Materials and Methods : All patients were diagnosed of traumatic visceral pseudoaneurysm and treated by endovascular intervention at Cho Ray Hospital from October 2017 to February 2019. Results: Thirty (30) patients were enrolled in this study. Locations of pseudoaneurysm were as follows: hepatic arteries (22.2%), gastroduodenal arteries (5.6%), renal arteries (55.5%), splenic arteries (8.3%), superior mesenteric arteries (5.6%) and left gastric arteries (2.8%). The embolic agents included Histoacryl glue (NCBA) (6%), coils (82%), PVA particles + coils (6%) and gelfoam + coils (6%). 94.4% of pseudoaneurysms were completely embolized, and 90% of patients recovered of clinical status at discharge. No severve complications were reported and the most common complication was hematoma (5%) at puncture site. Conclusion : Endovascular treament is an effective and safe method in the management of traumatic visceral pseudoaneurysms. Keywords: traumatic visceral pseudoaneurysm, endovascular treatment, safety, effectiveness
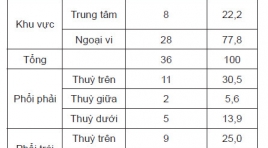
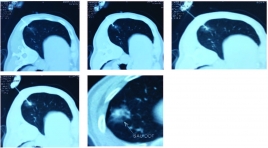
Đặc điểm cắt lớp vi tính ung thư phổi trước điều trị thuốc ức chế tyrosin Kinase và đánh giá đáp ứng theo tiêu chuản Recist 1.1
17/03/2020 10:29:02 | 0 binh luận
Computed tomography features of lung cancer patients before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment and response assessment by recist 1.1 SUMMARY Objective: 1. Describe computed tomography features of non-small cell lung cancer before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. 2. Treament response assessment by RECIST 1.1. Patients and method : Cross-sectional, retrospective and prospective study of 36 non- small cell lung cancer patients, EGFR mutations positive, treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor from 08/2018 to 06/2018, Results: Tumors located mainly in peripheral of the lung (77,8%). The most common position is the right upper lobe (30,5%), the least common position is the right middle lobe (5,6%). There are 83,3% of tumors with the size over 3cm. 100% of tumor have irregular and spicules magin. Solid mass accounted for 63,9%, partly solid mass (33,3%), one tumor is cavity form. Medium attenuation value is 27 HU in pre-contrast and 57,1 HU in post-contrast CT scan. Lymph node metastasis in 27 (61%) patients. Lymph node metastasis is mainly occured in paratracheal nodes [2,4(R,L), 3] (48%), A-Pwindow, paraaortic nodes (5,6) (12%), subcarinal nodes (7) (16%), supraclavicular nodes (1) (20%). After 3 months treament, partial response: 17 patients (52,8%), stable disease: 19 patients (47,2%). After 6 months treament, partial response: 14 patients (38,9%), stable disease: 20 patients (55,6%), progressive disease: 2 patients (5,5%). Conclusion : 1. Computed TomographyFeatures can be used to diagnose lung cancer. 2. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment is effective inadvancednonsmall cell lung cancer. Keywords : lung cancer, computed tomography, tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment, Recist 1.1
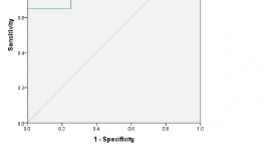
Giá trị của cộng hưởng từ phổ và cộng hưởng từ tưới máu trong chẩn đoán phân bậc u sao bào
05/12/2019 09:27:25 | 0 binh luận
Value of mr spectroscopy and perfusion in the grading of astrocytomas SUMMARY Objectives : The purpose of this study was to determine the value of MR spectroscopy and perfusion in the grading of astrocytomas. Methods: A descriptive study, retrospective and prospective study, MR spectroscopy and perfusion in 27 patients with histopathological findings of astrocytomas from 01/2016 to 07/2018 at the Viet Duc University Hospital. Evaluate the relationship between concentration of metabolics Cho, Cr, NAA, Cho/NAA, Cho/Cr, NAA/Cr; rCBV and grading of astrocytomas. Results : The Cho/NAA and Cho/Cr ratios of the high-grade astrosytomas and low-grade astrocytomas were statistically significant (p <0.05). The Cho/NAA ratio is useful in the diagnosis grade of astrocytomas. At the cutoff point of 2.22 for Cho/NAA ratio, MRS has sensitivity of 95%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value of 100%, negative predictive value of 80% for grading of astrocytomas. The rCBV index is valuable in the differential diagnosis grade of astrocytomas with the mean value of rCBV in the high-grade astrocytomas is higher than low-grade astrocytomas, there is a statistically significant difference of rCBV between the two groups. At the cutoff point of2.55 for rCBV, perfusion has sensitivity 81%, specificity 100%, positive predictive value 100%, negative predictive value 50%for grading of astrocytomas. Conclusion : MR spectroscopy and perfusion are valuable for grading of astrocytomas. Key words : MR spectroscopy,
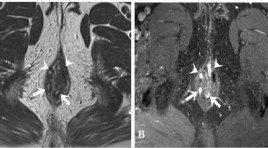
Đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ của rò hậu môn
05/12/2019 09:17:02 | 0 binh luận
M agnetic resonance imaging characterization of perianal fistula SUMMARY Background: Perianal fistula is a common disease in the anorectal region, just after hemorrhoids. The disease often recurs because of missed lesions at surgery, especially internal openings and secondary tracts, which can be identified by MRI. Surgery guided by Magnetic Resonance imaging (MRI) significantly reduces the recurrence of fistula. Aims : To describe the MRI features of perianal fistula and study the role of T2W TSE, post- contrast FS T1W TSE Gadolinium sequences in detecting the characterizations of the fistula tract. Subjects and methods : 367 patients with perianal fistulae, diagnosed and treated at University medical center hospital, between 1/1/2016 and 1/31/2018, were included in this study. This study is a retrospective analysis. We compared the imaging features with the surgical findings. Results : The mean age was 39.3 years (range, 12 – 84 years), male/ female = 9/1. A total of 411 fistulas were found at surgery. Agreement between the surgical findings and MR imaging for classification of the primary track, detecting secondary track was very good with kappa = 0.89 (0.84,0.93), 0.94 (0.90,0.97), respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of MRI in correctly detecting internal openings was found to be 99% and 85.2% respectively; for abscess, it was 100%. Both T2W TSE, post-contrast FS T1W TSE Gadolinium sequences have high sensitivity and specificity for the depiction of primary tracts, internal openings, and secondary tracts. Post- contrast FS T1W Gadolinium sequence was very good in detecting abscess; differentiating between abscess and inflammation, active inflammatory components with scars. Conclusions : Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) was highly accurate in assessment of surgically important parameters of perianal fistulae. With the very good agreement between the surgical findings and MR imaging for classification of the primary track, detecting secondary tract, high accuracy in detecting internal openings and abscess as well, MRI was considered the reliable technique of choice for establishing preoperative fistula map. If no contraindications exist, administration of contrast material is necessary for detecting abscess and secondary tracts, differentiating active inflammatory components with scars, especially in case of complex or recurrent fistula or having surgery around the anus before. Keywords: fistula, anal, MR imaging.
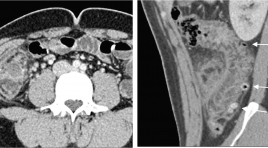
Đặc điểm hình ảnh X quang cắt lớp vi tính của viêm túi thừa đại tràng
05/12/2019 08:53:52 | 0 binh luận
The computed tomography scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis SUMMARY Purpose: Describe the computed tomography (CT) scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis (CD). Classification of colonic diverticulitis the World Emergency Surgery Society (WSES), and to compare computed tomography findings of right vs. left colonic diverticulitis. Methods: Retrospective studies described case series of patients diagnosed Colonic Diverticulitis at University Medical Center hospital and there was CT scan between January and December 2018. Clinical features, treatmentwere collected and assess the characteristics CT scan of Colonic diverticulitis Results : There were 104 patients, 75 right CD and 29 left CD. Mean age 46, ratio male/female 1,6. Inflamed diverticulum 89,4%; pericolic air bubbles19,2%; pericolic fluid 51,9%; abscess 1,7%; fistula 1,9%; bowel obstruction 1%. The classification of acute diverticulitis by the WSES, uncomplicated acute diverticulitis and complicated acute diverticulitisstage 1a, 1b, 2 a, 2b respectively of 48% and 39,2%; 6,9%; 4,9%; 1%. None of the complicated diverticulitis stage 3,4. Compare CT findings of right vs. left CD: Mean age (41 vs. 61), inflamed diverticulum (96% vs. 72,4%), pericolic air bubbles(8% vs. 48,3%), pericolic fluid (45,3% vs. 69%), abscess(4% vs. 31%), they differed significantly between the two groups (P < 0,05). Conclusions : Diverticulitis is often right-sided, mild in severity. Most are uncomplicate and complicated diverticulitis stage 1a by the classification of WSES. Right CD occurs in younger and lower complications compared to left CD Key words : Colonic diverticulitis,pericolic air, abscess,computed tomography findings, WSES.

Đặc điểm hình ảnh x quang cắt lớp vi tính của viêm túi thừa đại tràng
16/04/2020 16:14:17 | 0 binh luận
The computed tomography scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis SUMMARY Purpose : Describe the computed tomography (CT) scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis (CD). Classification of colonic diverticulitis the World Emergency Surgery Society (WSES), and to compare computed tomography findings of right vs. left colonic diverticulitis. Methods: Retrospective studies described case series of patients diagnosed Colonic Diverticulitis at University Medical Center hospital and there was CT scan between January and December 2018. Clinical features, treatmentwere collected and assess the characteristics CT scan of Colonic diverticulitis Results: There were 104 patients, 75 right CD and 29 left CD. Mean age 46, ratio male/female 1,6. Inflamed diverticulum 89,4%; pericolic air bubbles19,2%; pericolic fluid 51,9%; abscess 1,7%; fistula 1,9%; bowel obstruction 1%. The classification of acute diverticulitis by the WSES, uncomplicated acute diverticulitis and complicated acute diverticulitisstage 1a, 1b, 2 a, 2b respectively of 48% and 39,2%; 6,9%; 4,9%; 1%. None of the complicated diverticulitis stage 3,4. Compare CT findings of right vs. left CD: Mean age (41 vs. 61), inflamed diverticulum (96% vs. 72,4%), pericolic air bubbles(8% vs. 48,3%), pericolic fluid (45,3% vs. 69%), abscess(4% vs. 31%), they differed significantly between the two groups (P < 0,05). Conclusions: Diverticulitis is often right-sided, mild in severity. Most are uncomplicate and complicated diverticulitis stage 1a by the classification of WSES. Right CD occurs in younger and lower complications compared to left CD Key words : Colonic diverticulitis,pericolic air, abscess,computed tomography findings, WSES.
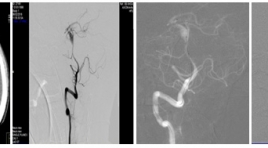
Điều trị phình động mạch não vỡ sau chấn thương bằng can thiệp nội mạch tại Bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy
04/12/2019 21:40:31 | 0 binh luận
Endovascular treatment of reptured traumatic cerebral aneurysm after brain injury in choray hospital SUMMARY Background: Traumatic intracranial aneurysms are rare, comprising 1% or less of all cerebral aneurysms. They can occur after even mild or severe head trauma, and are associated with significant morbidity and a mortality rate as high as 50%. Causes of pathogenesis, pathology and treatment methods differ from other cerebral aneurysms. So, the purpose of endovascular treatment is to prevent rebleeding and progressive cerebral dissecting anurysms. Materials and methods : Endovascular treatment of ruptured traumatic cerebral artery aneurysms performed at Department of Radiology, Choray Hospital, from 01/2017 to 05/2018, the technique as follows: digital subtraction angiography, inserting of microcatheter over the aneurysm neck and other microcatheter insert to aneurysm, deploying stent over the aneurysm neck and coiling into aneurysm. The efficacy and safety were evaluated by variants: complete and partial occlusion rates, procedural success rate, clinical improvement, procedural complication. Results: 33 cases of ruptured traumatic cerebral aneurysms treated by endovascular treatment, technical success rate 31/33 (93.9%) with stent assisted coiling (72.7%), parent artery occlusion (15.2%) and alone coiling (6.1%). Good outcome m-RS (0-2) were 25/33 cases (75.7%) , 5/33 cases (15.2%) reruptered and progressive cerebral dissecting anurysm cause mortality rates 3 cases (9.1%), morbidity rate (15.2%). Conclusion : Endovascular treatment of ruptured traumatic cerebral aneurysms after brain injury were high safety and efficiency, improve good outcomes, low mortality complication rates. Key words: Traumatic cerebral aneurysms, Stent assisted coiling, endovascular treatment.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












