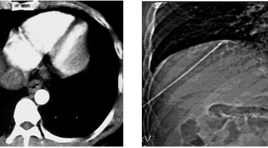
Kĩ thuật và kết quả bước đầu điều trị ung thư gan bằng đốt sóng cao tần tạ khoa chẩn đoán hình ảnh - Bệnh viện Bạch Mai - Hà Nội
03/04/2020 11:15:46 | 0 binh luận
Technique and early outcome of RFA in treating HCC at the Radiology Department Bach Mai, Hanoi summa ry Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) management has become varied with different ways, which are applicable for different stages of the disease. Hepatic resection forms part of the conventional treatment for patients with the disease; however, the majority of primary liver cancers are not suitable for curative treatment at the time of diagnosis. Local curative therapy is getting more and more used. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the first line indication for inoperable patients. Objective : To describe techniques and early outcomes of RFA in treating HCC patients at Radiology Department, Bach Mai Hospital, Hanoi. Method: descritive, retrospective, from 4/2010 to 12/2012 on 43 patients; image-guided techniques were used to treat the patients and evaluate results. Findings : male/female=35/8, average age = 54.5 (36-76), commonest tumor size is 3-5 cm (80%), majority of the patients had Child A (95%) and infected with HBV (98%); ultrasound imaged and cluster needles were performed on 77% and 80% respectively; post-intervention status was stable and without complication on 100% of the patients; 1-year and 2-year suvival rates were 95% and 88% correspondingly, of whom local recurrence appeared in two cases after five months and one case after one year. Conclusion : RFA in HCC management is safe and effective at the Radiology Department at Bach Mai Hospital, even in complicated cases.
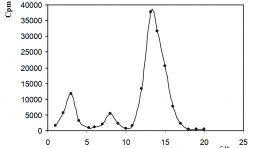
Điều chế Phosphorus-32 (P-32) từ bia chiếu xạ p2o5 cho mục đích điều trị trong y học hạt nhân
03/04/2020 10:59:25 | 0 binh luận
Preparation of phosphorus-32 (p-32) from irradiated target p2o5 for therapeutic purposes in nuclear medicine SUMMARY Phosphorus-32 is produced using the nuclear reaction 31P (n,γ) 32P by irradiation of the phosphorus peroxide (P2O5) target. Phosphoric acid is prepared by the dissolution of irradiated target in 40 ml of boiling chloric acid 0,1 N. When the dissolution of phosphor peroxide is completed, the beaker is allowed to cool. 8 ml of 30% H2O2 is added and refl uxed for 3h. Finally, the solution is fi ltered through a sintered glass fi lter, porosity G3 and passed into a column of cationic exchanger (Dowex-50 W-X4 preconditioned in hydrogen form) to remove metallic impurities. The effl uent is collected as the stock solution. Radiochemical purity is determined by paper chromatography (radiochemical purity control) in the solvent system: Whatman No. 1 paper and the mixture of isopropyl alcohol : water : 50% trichloracetic acid : 25% NH4OH (75:15:10:0.3 v/v.) as a mobile phase, developing time ranged from 12 to 17 h. Radiochemical purity of phosphoric acid (H3 32PO4) solution prepared by our method is obtained more than 99%. Key word : H3 32PO4, Phosphorus-32.
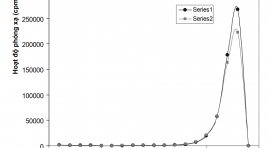
Khản năng sản xuất 177Lu từ bia Lutetium tự nhiên trên lò phản ứng hạt nhân Đà Lạt
03/04/2020 10:55:14 | 0 binh luận
Production ability of 177Lu from natural lutetium target on the Da Lat nuclear reactor SUMMARY 177Lu is presently being considered as a potential radionuclide, for use in in-vivo targeted radiotherapy, owing to its favorable nuclear decay characteristics. This paper presents some research fi ndings on the ability to produce 177Lu on the IVV-9 research reactor with thermal neutron fl ux of 1.8×1013.cm-2.s-1 at the Nuclear Research Institute to produce this radioactive isotope. Our products have specifi c activity of 17.7 mCi/mg Lu, radionuclide and radiochemical purities more than 99.9% of total radioactivity. Immediate products are used for the initial basic research of labeling capabilities with DOTATATE, and especially studying on the possibility preparing 177Lu-EDTMP used to treat pain palliation caused by bone metastases. Keywords: production of Lu-177, nuclear reactor IVV-9, 177Lu-EDTMP, pain palliation.
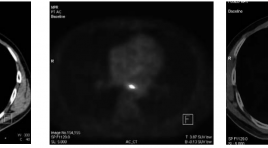
Ứng dụng kĩ thuật chụp PET/CT mô phỏng lập kế hoạch xạ trị ung thư thực quản
03/04/2020 10:44:54 | 0 binh luận
Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning SUMMARY Background: Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning is one of the most advantage techniques in cancer treatment. In 2009, Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center of Bach Mai Hospital was the fi rst place in Vietnam, where PET/CT simulation for radiation therapy planning has been conducted successfully for cancer patients. Objective : To build the PET/CT simulation process in radiation treatment planning for esophageal cancer. Subjects and methods: 50 esophageal cancer patients treated by radiation. Results: Simulation for radiotherapy in esophageal cancer: PET/CT has higher values than CT such as detecting lesions more precisely and more clearly. Patients in our study had good response and less complication: overall response (complete and partial) with improving clinical symptoms: 80%, size of tumor reduced in 83% patients. Common complication is depletion (in 34% patients). Most complications are mild and can be treated by medicine. Conclusion: Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center Bach Mai Hospital has standardized the PET/CT simulation process for esophageal cancer patients with initial good results.

Ứng dụng kĩ thuật chụp PET/CT mô phỏng lập kế hoạch xạ trị ung thư
12/04/2020 21:31:25 | 0 binh luận
Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning SUMMARY Background: Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning is one of the most advantage techniques in cancer treatment. In 2009, Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center of Bach Mai Hospital was the fi rst place in Vietnam, where PET/CT simulation for radiation therapy planning has been conducted successfully for cancer patients. Objective: To build the PET/CT simulation process in radiation treatment planning for esophageal cancer. Subjects and methods: 50 esophageal cancer patients treated by radiation. Results: Simulation for radiotherapy in esophageal cancer: PET/CT has higher values than CT such as detecting lesions more precisely and more clearly. Patients in our study had good response and less complication: overall response (complete and partial) with improving clinical symptoms: 80%, size of tumor reduced in 83% patients. Common complication is depletion (in 34% patients). Most complications are mild and can be treated by medicine. Conclusion: Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center Bach Mai Hospital has standardized the PET/CT simulation process for esophageal cancer patients with initial good results.
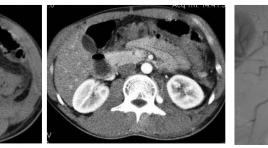
Điều trị giả phình động mạch thắt lưng sau chấn thương bằng phương pháp can thiệp nội mạch
03/04/2020 10:41:20 | 0 binh luận
Post-traumatic lumbar pseudo-aneurysm treatment by endovascular intervention SUMMARY Pseudo-aneurysm of the lumbar artery is a rare lesion at the abdominal injury though these arteries have small dimension and retro peritoneal localization. Ruprture of the aneurysm can infl uence to the patient life. Diagnostic imaging and deciding to early treatment play an important role.We present a case of the affection being treated sucessfully by endoluminal intervention.
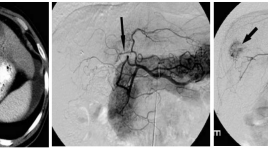
Đánh giá hệ thống tuần hoàn bàng hệ ngoài gan trong điều trị ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan bằng nút hóa chất động mạch qua catheter
03/04/2020 10:37:53 | 0 binh luận
Evaluation of extrahepatic colateral vessel supply in treatment of HCC by TACE SUMMARY Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, ranking fi fth for men and eighth for women as a source of primary malignancy. The highest incidences of HCC are found in sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia, Southeastern Asia with incidence rates of 17.43 and 6.77 per 100,000 in men and women of developing countries compared with 8.71 and 2.86 per 100,000 in men and women of developed regions of the world [2],[6]. The three curative options of resection, liver transplantation, and percutaneous ablation compete as fi rst-line treatment modalities for early HCC, achieving 5-year survival rates of 50-70% [18]. At these advanced stages of HCC, arterial embolization techniques combined with intra-arterial chemotherapy has been shown to be an effective palliative therapy that can also improve patient survival [19],[20]. HCC chemoembolization is based on the fact that the normal liver parenchyma receives a dual blood supply from the hepatic artery and the portal vein, whereas HCCs are supplied exclusively by the hepatic artery. In practice, many HCCs are supplied by extrahepatic collateral arteries even when the hepatic artery is patent [13],[19]. Detect these extraheparic colateral vessel supply as well as ways in which to improve the effective and avoid complications of TACE of the collateral vessels.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"