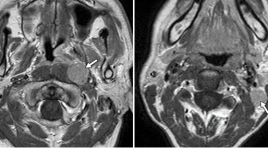
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ thường qui và cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán trong chẩn đoán ung thư vòm họng
25/12/2019 17:54:41 | 0 binh luận
Bệnh ung thư vòm họng (NPC - Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma) ở nước ta có tỷ lệ cao, đứng hàng đầu trong các bệnh ung thư đầu cổ, đứng hàng thứ 5 trong các bệnh ung thư nói chung. Nhưng các triệu chứng lại không điển hình hầu hết là các triệu chứng của các cơ quan lân cận.
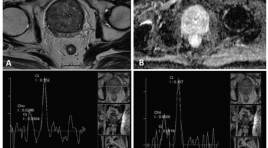
Gía trị cộng hưởng từ phổ trong chẩn đoán ung thư tuyến tiền liệt
25/03/2020 22:33:20 | 0 binh luận
T he value of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in diagnosis of prostate cancer SUMMARY Purpose: The aim of study was to determine the value of MRS in diagnosis of prostate carcinoma especially for differentiating begnin from malignant lesion of the prostate. Materials and methods : During a period of 4/2014 to 6/2016, 25 consecutive patients with elevated PSA level or clinical suspiciousness were evaluated with MRS of the prostate. The results were confirmed by TRUS-guided biopsy. We compare two groups (prostate carcinoma/PCa and prostate non-caricnoma/PNCa) by variant: mean of the choline plus creatine -to- citrate. Analyzing ROC curve to find the value of MRS in differentiating begnin from malignant tissue of the prostate. Results : Patients range in age from 40 to 89 years (mean 71 ± 12 year). 08 patients were confirmed to have PNCa (32%), whereas 17 patients had PCa (68%). The mean of (Cho+ Cr)/Ci values for PNCa and PCa were 0.50± 0.31 and 2.64± 1.22 respectively. The mean of (Cho+Cr)/ Ci value of PCa was significantly higher than PNCa (p<0.05). On ROC curve, using discrimination threshold of (Cho+Cr)/ Ci is 0.84, the MRS provided a sensitivity of 94.1%, specificity of 87.5% for differentiating NPCa from PCa. Conclusion : Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of the prostate can be use to differentiate begnin from malignant tissue with high accuracy. Key words: Prostatic carcinoma, non-carcinoma, Magnetic resonance spectroscopy, TRUS.
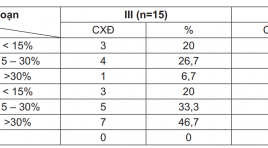
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ hoại tử vô khuẩn chỏm xương đùi ở những bệnh nhân có chỉ định thay khớp háng
01/04/2020 16:17:40 | 0 binh luận
Study the magnetic resonance imaging characteristics in patients with hip joint repiacement indicattion SUMMARY Objectives: 1) Characterization of magnetic resonance images aseptic necrosis of the femoral head in patients with hip replacement appointed. 2) Characterization of magnetic resonance images of the contralateral hip in patients people on. Objects and methods of research: Retrospective study of 60 patients with aseptic necrosis of the femoral head surgery during 2014- 2015 at a hospital in Hanoi Medical University and Hospital Vietnam Germany. Results: The patients having hip replacement appointed two phase III and IV. All patients had femoral head collapse and are mostly seen when patients have hip osteoarthritis secondary (75% stage IV). Hypointense region was 73.3% stage III, stage IV, 93.3%, in line with a high prevalence of bone marrow showing the progression of the disease is> 85%. Rate aseptic necrosis of the femoral head in the contralateral hip joint meeting with the high rate of 80%, occur in all phases. Photos CHT at an early stage (I and II) are more common form hypointense band (77.4%), bone marrow lesions form T1-weighted images are shaped ring (61.3%), lesions of the subclass A (74.2%). Late stage (III and IV) characteristic image is under the cartilage fracture and femoral head collapse, besides that other image: hypointense on T1-weighted images region (70.5%), the image of subclass D (52.9%). Conclusions: MRI allows an accurate assessment stage lesions of clinical help for prognosis and hip replacement decision at the right time, at the same time to detect aseptic necrosis of the femoral head in the contralateral hip though no clinical symptoms, so that early treatment measures or prevent the more severe complications. Keywords: Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
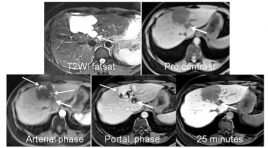
Chất tương phản MRI - PRIMOVIST: Vai trò trong chẩn đoán thương tổn gan
22/03/2020 19:18:01 | 0 binh luận
The role of hepatobiliary specific MR cantrast agent in the diagnostic focal liver lesion SUMMARY Purpose: Assessing the role of hepatobiliary - specific MR contrast Agent in the detection and differentiation of benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Maximizing accuracy of imaging in the context of focal liver lesions is paramount in avoiding unnecessary biopsies, which may result in post-procedural complications. Methods and Materials: Retrospectively evaluated the 200 patients cases, executed hepatic MRI at Medic Medical center wich hepatobiliary - specific MR contrast Agent. From on January 2013 to on January 2016, age range 28 - 72years. The lesion detected in liver: 65 cases HCC, 5 Metastasis, 2 cholangiocarcinoma, 2 Adenoma, 26 FNH, 24 Hemangiomas, 14 Regenerative nodules, 20 cysts, 5 Abscess, 37cases had normal liver. All the patients executed T2WI fatsat, Diffusion weighted imaging - MRI with three b values (0, 500, 800 sec/mm2) and Dynamic with Primovist contrast media on the Siemens Avanto 1,5T MRI. Results : In 65cases MRI HCC: 8 cases <1cm; 32 cases 1-2cm; 25 cases >25cm. 26 cases biopsic result: 24 cases HCC (92%), 2 cases cholangiocarcinoma, 39 cases TOCE or RFA no biopsy. 5 cases metastas detected primary tumor. 2 cases cholangiocarcinoma are right with biopsic result. 2 cases adenoma: 1case biopsic resulted in adenoma, 1 case follow up over 1year. 25 cases hemangiomas with contrast media from peripheral enhancement progressing to centre of lesion; 12 cases regenerative nodules is follow up over 1 year no change in nodule size; 20 cysts are high-signal intensity like fluid - signal on the T2WI, T1WI, Diffusion and no change of intensity is found after contrast injection; in 5 cases abscess: 3 cases recovered from an illness, 2 cases HCC after biopsy. Conclusion : Magnetic resonance imaging executed with hepatobiliary - specific MR contrast Agent, contributed to detect the small lesion and differential diagnosis between benign and malignant tumor of the liver.
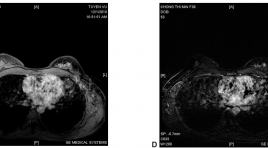
Cộng hưởng từ tuyến vú ở bệnh nhân ung thư vú thể ẩn có di căn hạch nách
03/04/2020 09:02:31 | 0 binh luận
Mr imaging of the breast in patients with occult primary breast cancer presenting as an axillary metastasis SUMMARY: Purpose: To access the value of MRI in the diagnosis of occult primary cancer with axillary metastasis. Methods and Materials: 12 patients occult breast cancer with malignant axillary adenopathy and negative on mammographic, echography and physical examination findings, were underwent contrast material-enhanced MR imaging in Hanoi medical university hospital. Results: The sensitivity of MRI in the diagnosis of occult primary cancer with axillary metastases was 83%. MR imaging depicted small cancers from 3 to 12mm diameter. Of the 12 patients, three patients were underwent mastectomy, five were underwent lobectomy, and four were underwent breast-conservation therapy. Conclusion: MR imaging is very sensitive for the detection of occult breast cancer with malignant axillary adenopathy. MR imaging offers potential not only for cancer detection but also for staging the cancer within the breast, which may be useful for treatment planning. Keywords: dynamic breast MRI, occult breast cancer
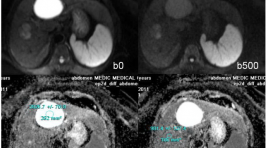
Vai trò của ADC trong chẩn đoán phân biệt giữa tổn thương lành tính và ác tính ở gan
31/03/2020 15:24:03 | 0 binh luận
summary Purpose : Assessing the role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) measurement in differentiation of benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions. Methods and Materials: Retrospectively evaluated the 248 patients cases, executed hepatic MRI at Medic Medical center, from on February 2011 to on February 2013, age range 41 - 78years, with 142 benign hepatocellular lesions (30 FNHs, 9 HCAs, 63 hemangiomas and 40 cysts) and 104 malignant lesions (76 HCC and 28 metastasis) diagnosed, 50 patients had normal liver. All the patients executed Diffusion weighted imaging - MRI with three b values (0, 500, 800 sec/mm2) on the Siemens Avanto 1,5T MRI. Results : We found difference between ADC of benign lesions compared with malignant lesions (mean ± standard deviation): ADC of normal liver (1.242 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.33), FNH-HCA (1.742 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.40), Hemangiomas (2.084 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.46), Cyst (2.861 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.34), HCC (1.093× 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.37), Metastasis (1.126 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.48). ADC of benign lesions: (2.327 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.41), compared with malignant lesions: (1.113 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.39). Conclusion: Mean value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) contribute to differential diagnosis between benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions.
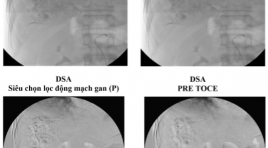
Ung thư gan vỡ, xuất huyết ổ bụng, được trị liệu hóa dầu thuyên tắc mạch qua catheter (TOCE) tai bệnh viện Hoàn Mỹ Đà Nẵng: Nhân một trường hợp
26/03/2020 22:18:24 | 0 binh luận
Ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc), bleeding in abdomen is treated by toce (transcatheter oily chemoembolization) at hoanmy DaNang hospita: a case report SUMMARY - HCC is the most common of cancer liver. - Nature progress, metastasis is complex, multiple organs. - Ruptured HCC, Bleeding in abdomen, hypotention, shock,...: is severe statement, progress is very rapid, complex, serious, dead rate is hight. - Diagnotic and treatment (TOCE) of ruptured HCC must rapid, exact. Doing everything possible to keep the patient alive !. - A report of a man patient 79 year olds, at emergency room of Hoan My Da Nang hospital, was diagnosted ruptured HCC, hypotention,…He hadbeen taken emergency abdoment CT and treatmented – TOCE. The doctors did everything possible to keep him alive. - Follow- up and consolidate TOCE, crux problem !\ Keyword: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Computed tomography, Digital Subtraction Angiography, Transcatheter Oily Chemoembolization, Gastrointestinal endoscopy surgery, laparoscopic surgery.
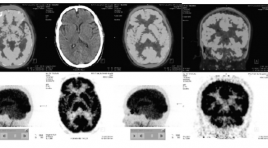
Đặc điểm hình ảnh 18F-FDG PET/CT não ở bệnh nhân Alzheimer và ở người lão hóa bình thường
25/03/2020 22:45:48 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics of brain 18f-fdg pet/ct in alzheimer’s disease patients and in normal elderly persons SUMMARY Purpose : Define 18F-FDG PET/CT cerebral imaging characteristics in Alzheimer’s Disease patients and in the normal elderly persons (Nls). Objects and Methods : From 2014 to 2015, 26 Alzheimer’s disease patients and 20 normal elderly persons undergone brain 18F-FDG PET/CT scans. Results: Mean age of Alzheimer’s disease patients is 66,3±8,2 years old and 64,2±8,1 in Nls. Homogenous 18F-FDG cerebral uptake in Nls. Most of cerebral regions in Alzheimer’s disease patients suffering from a reduction of mean SUV. Rate of 18F-FDG hypometabolism in medial temporo-hippocampal area in 96.2% of cases on left side, meanwhile 92.3% of cases having a hypometabolism in right medial temporo-hippocampal area as well as in bilateral posterior cingulate gyrus, 76.9% in temporo-parietal area on right side and 86.5% on left side. Cerebral metabolism in occipital lobes principally reserved. Hypometabolism affecting bilateral frontal lobe in a half of cases. Brain glucose metabolism partially reserved at primary moto-sensory cortices, cerebellum, as well as in anterior cingulate gyrus, especially reservation of glucose metabolism at basal ganglias in Alzheimer disease (96,2%). Rate of glucose hypometabolic Alzheimer like patterns in 92,3% of cases with 84,6% on both sides. Conclusion: No focal cerebral cortical hypometabolism in Nls. Evident reduction in 18F-FDG uptake of cerebral cortices in Alzheimer’s disease patients in compared with Nls. Imaging characteristics of hypometabolism in 18F-FDG PET/CT brain scan in Alzheimer’s disease patients are regional anatomically and specifically with high rate in medial temporo-hippocampal, posterior temporal, temporo-parietal and posterior cingulate areas, well correspondent to wellknown glucose metabolic patterns in Alzheimer’s disease. Key words: Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Brain 18F-FDG PET/ CT, imaging characteristics.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












