Đặc điểm siêu âm dị vật tiêu hóa trên ở trẻ em được can thiệp lấy dị vật tại Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng 1 báo cáo loạt ca
02/06/2020 09:16:09 | 0 binh luận
Ultrasound of foreign bodies in gastrointestinal tract removed at Children’s Hospital 1 case report SUMMARY Objectives : We reviewed ultrasound features of all cases of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract that underwent endoscopic or surgical removal at Children’s Hospital N1 from 1/2018 to 4/2019. Method : retrospective case. Results : From 1/2018 to 4/2019, 7 cases were included. Mean age was 7,9 years old. Boy to girl ratio was 5/2. 5/7 cases were radiolucent foreign bodies, toothpick mostly. The positions were one oesophageal, 2 gastric và 4 duodenal. All cases were diagnosed correctly by ultrasound before intervention. 4/7 cases underwent surgical removal, 3 cases underwent endoscopic removal. The signs of right-side retroperitoneal oedema and fluid collection surrounding right kidney on ultrasound were highly suspected of posterior D3 duodenal wall perforation due to foreign bodies. Conclusion: Foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract can cause dangerous complications in case of late diagnosis. Ultrasound can help find radiolucent as well as radiopaque objects. We should know typical ultrasound features of some foreign bodies and common sites of complication in order to predict the object and the location exactly to give proper management. Key words : foreign bodies, ultrasound, children.
Nghiên cứu so sánh siêu âm đàn hồi strain elastography (se) so với shearwave elastography (swe) trong bệnh lý u vú nữ tại Medic TPHCM 2019
01/06/2020 17:32:09 | 0 binh luận
A comparative study of strain elastography (se) and shear wave elastography (swe) in female breast tumor disease at medic medical center in HCMC in 2019 SUMMARY Objective: Combining B-mode US, BI-RADS classification and applying 2 types of elastography: Strain Elastography (SE) and Shear Wave Elastography (SWE) on RS85 ultrasound scanner (Samsung) in diagnosis of benign/ malignant breast tumors. Detecting diagnostic value for each method and when combining them. Materials and methods: Selecting female breast tumors that classified Birads 3,4,5 by B-mode US, examining elastography at the same time by 2 methods: SE and SWE using L2-9MHz probe on RS85 ultrasound scanner (Samsung) from August to October, 2019 at Medic Medical Center in HCMC. Collecting data of 2 types of Elastography: SE: collecting 3 values: (1) color mapped elastogram according to Tsukuba elasticity score, (2) E/B ratio (the largest transversal diameter that hardest color - coded on the color map / the largest transversal diameter of tumor on B-mode US) (<1 or >1), (3) ratio B/A (A= tumor lesion, B= normal fat tissue above the lesion). SWE: measuring the tissue stiffness (kPa) and shear wave velocity (m/s) (according to color-coded tumor stiffness map, selecting the hardest point that satisfied RMI (reability measurment index) ≥ 0.4. Measuring each method 3 times on the same tumor. Bi-rads 3-4-5 lesions undergone biopsy (FNAC and/ or core biopsy) to have determined diagnosis. Then calculating the diagnostic value of each method and when combining the 2 methods. Using the SPSS 20 software for statistics and analyzing. Results: The study has 84 breast tumors (51 benign and 33 malignant) that have determined diagnosis by cytology and histology. Strain Elastography value: 1.1. Choosing color map according to Tsukuba elasticity score from 1→5 in diagnosis has sensitivity (90%), specificity (88.2%), positive predictive value (83%), negative predictive value (93.8%), accuracy (8.3%)1.2. Choosing the E/B ratio (the largest transversal diameter that hardest color - coded on the color map / the largest transversal diameter of tumor on B-mode US) value (that <1 suspected benign tumor and ≥ 1 suspected malignancy) has sensitivity (87%), specificity (90.2%), positive predictive value (85.3%), negative predictive value (92%), accuracy (89.3%) 1.3. The ratio of mean strain elastography value of malignant and benignbreast tumor / fat tissue are (8.1+/- 3.7) and (2.4+/-1.3) (p<0,001).The ratio at cut-off value (3.2) has the highest sensitivity (97%) and specificity (84.3%) in diagnosing malignant breast tumors. Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.969). Positive predictive value (80%). Accuracy (89.3%). 2. Shear wave elastography (SWE) value: 2.1. Shear wave mean velocity of benign and malignant tumor groups are (3.9 ± 1.1) and (5.9 ± 1.3) (m/s) (p<0,001). Mean ratio at the cut-off value (4.2m/s) has the highest sensitivity (90.9%) and specificity (66.7%) in diagnosing malignant breast tumors. Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.873).Positive predictive value (63.8%). Negative predictive value (91.8%). Accuracy (76.2%). 2.2. Mean stiffness value of benign and malignant breast tumor groups are (49.7 ± 28.2) and (108±4.5) (kPa) (p<0,001). Mean ratio at the cut-off value (50.3 kPa) has sensitivity (90.9%), specificity (66.7%). Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.864), positive predictive value (61.2%), negative predictive value (91.4%), accuracy (73.8%) 3. Combination of SE and SWE value Combining the 2 types of elastography SE and SWE in diagnosing breast tumor by evaluating E/B of SE and shear wave velocity (m/s) of SWE increases the strongly sensitivity (100%), specificity (52,9%) and positive predictive value (57,9%), negative predictive value (100%), accuracy (71,4%), helps to reduce unnecessary biopsied cases. Conclusions: SE and SWE are useful in diagnosing breast tumor. Combining the 2 types of elastography SE and SWE have strongly sensitivity, helps to reduce unnecessary biopsied cases.
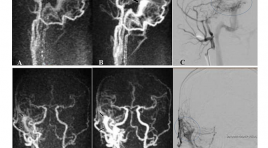
Vai trò của mra có tương phản động học với độ phân giải thời gian cao trong đánh giá rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng nội sọ
01/06/2020 17:09:26 | 0 binh luận
The role of Time-resolved CE-MRA in evaluation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas SUMMARY Objective: We evaluate the role of Time-resolved CE-MRA in diagnosis, localization, and detecting cortical venous drainage of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) in comparison with Digital Subtraction Angiography Subjects and methods : Prospective study between 1/2015 and 4/2019, 93 patients (35 male, 58 female), aged from 11 to 88 (mean 55), diagnosed of DAVF on conventional MRI, 55 of them had Time-resolved CE-MRA and then underwent DSA for confirming the diagnosis. Results: In our study (n=55), Time-resolved CE-MRA showed high sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value in diagnosis of DAVF (98%, 100%, 100%, 83,3%, 98,2% respectively) and in detecting cortical venous drainage (80%, 96,67%, 95,23%, 85,29%, 89,09% respectively). Kappa coefficient showed very good agreement between Time-resolved CE-MRA and DSA in detecting the location of DAVF. Conclusion: The use of Time-resolved CE-MRA is valuable in diagnosis, localization, and detecting cortical venous drainage of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF). This noninvasive examination would be helpful in choosing patients with DAVF, especially patients with high risk of complications for further cerebral angiography. Keywords: DAVF, dural arteriovenous fistula, cortical venous reflux, cortical venous drainage, Time-resolved CE MRA.
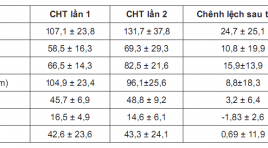
Vai trò cộng hưởng từ ngấm thuốc muộn trong dự báo khả năng phục hồi chức năng tim ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp được can thiệp tái thông động mạch vành thì đầu
01/06/2020 16:20:33 | 0 binh luận
Role of delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance Imaging to predict cardiacfunctional improvement after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for patients with acute myocardial infarction SUMMARY Objective: To access the transmural extent of hyperenhancement and infarct size at Delayed Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) on relating toleft ventricular (LV) functional improvement in reperfused myocardial infarction (MI) and to compare theLV morphology and function on MRI afterprimary percutanous coronary revascularization. Materialand Methods : Cine sequenceand Delayed Contrast- Enhanced MRIwere underwent in period of 9 days after percutanous coronary revascularization on29 patients suffering fromAcute MI at Bach Mai Hospital. Long term follow-up cardiac MRI was done to compare the change in LV morphology and function, infarct size. Myocardial wall thickening and left ventricular volumes were quantified on cine-images, and the transmural extent of infarction (TEI), infarct size was doned on delayed-enhancement images. Remodeling was defined as an increase in LV end-diastolic volume index of 20% or higher at follow up. Results: A decrease in myocardial mass (104,9 ± 23,4 to 96,1 ± 25,6 gram; p<0,05), mean SWT score (16,5 ± 4,9 to 14,6 ± 6,1; p<0,001) and increase the mean ejection fraction (45,7 ± 6,9 to 48,8 ± 9,2%; mean 3,2%; p<0,05), whereas mean end-diastolic volume(107,1 ± 23,8to131,7 ± 37,8 ml; p<0,0001) and mean end-systolic volume(58,5 ± 16,3 to 69,3 ± 29,3 ml, p<0,05) did not decrease. Segmental wall thickening did not change (42,6 ± 23,6to 43,3 ± 24,1%; p>0,5). The infarct size at DCE-MRI was related to LVEDVI (r=0,643, p<0,0001). Infarct size of 29% or more of LV area predicted remodeling with high sensitivity (100%) and specificity (89%). The extent of segments that was dysfunctional but viable was related to improvement in ejection fraction(r=0,56; p=0,002). Segmental wall thickening improved significantly in segments with<25% TEI(35 ± 7 to48 ± 7%, p<0,0001), tended to improve in segments with 25% to 75% TEI (32± 10to38 ± 11%, p<0,001), whereas segments with>75% TEI did not improve (22 ± 15to20 ± 14%, p<0,05). Conclusion :In patients with recent reperfused MI, functional improvement predicted by delayed contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Key word s: Cardiac Magnetic Resonace Imaging, delayed enhancement MRI, late gadolinium, Acute myocardial infarction, transmural extent of infarction (TEI), infarct size.
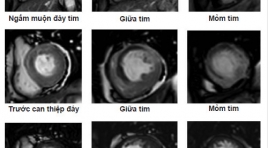
Vai trò của cộng hưởng từ ngấm thuốc muộn trong tiên lượng khả năng phục hồi chức năng thất trái sau tái tưới máu cơ tim ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp
17/03/2020 15:56:04 | 0 binh luận
Role of delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the prediction of functional improvement after reperfused acute myocardial infarction SUMMARY Objective : To access the transmural extent of hyperenhancement at delayed contrast enhancement MRI on relating to left ventricular functional improvement in reperfused myocardial infarction and to compare the left ventricular morphology and function on MRI before and post percutaneous coronary revascularization. Methods: Cine sequence and delayed Contrast-Enhanced MRI were underwent in period of 10 days just before or postpercutaneous coronary revascularization on 28 patients suffering from Acute Myocardial Infarction at Bach Mai hospital. Long term follow-up cardiac MRI was done to compare the change in left ventricular morphology and function. Myocardial wall thickening and left ventricular volumes were quantified on cine-images, and the transmural extent of infarction (TEI) was scored on delayed-enhancement images. Results : A decrease in myocardial mass (104,8 ± 23,89 to 95,83 ± 25,81, p<0,05), mean SWT score (16,75 ± 4,7 to 14,86 ± 5,98, p<0,001) and increase the mean ejection fraction (45,74 ± 7,25% to 49,12 ± 9,2%, mean 3,39%, p<0,05), whereas mean end-diastolic volume (109,49 ± 28,53 to 131,73 ± 39,37 ml, p<0,0001) and mean end-systolic volume (59,91 ± 19,13 to 69,19 ± 30,18, p<0,05) did not decrease. Segmental wall thickening did not change (42,12 ± 23,19 to 42,57 ± 23,99, p>0,5). The transmural extent of hyperenhancement at DCE-MRI was related to left ventricular remodeling (r=0,628, p-0,0001) and ejection fraction(r=0,583, p=0,001). Segmental wall thickening improved significantly in segments with<25% TEI(35 ± 7,39 to 48,86 ± 6,65, p<0,0001), tended to improve in segments with 25% to 75% TEI (32,88± 9,78 to 39,67 ± 10,7, p<0,001), whereas segments with>75% TEI did not improve (22,61 ± 14,62 to 19,71 ± 14,56, p<0,05). Conclusion : In patients with recent reperfused MI, functional improvement predicted by delayed contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Key words: Cardiac Magnetic Resonace Imaging, delayed enhancement MRI, late gadolinium, Acute myocardial infarction, transmural extent of infarction (TEI)

Nút phình hình túi với WEB: Thiết bị, kỹ thuật, mẹo và hiệu quả lâu dài
20/04/2021 10:50:34 | 0 binh luận
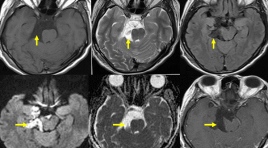
Đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ thường qui và khuếch tán của u nang thượng bì nội sọ
22/12/2019 13:07:55 | 0 binh luận
U nang thượng bì là một tổn thương bẩm sinh có nguồn gốc từ ngoại bì phôi. Bệnh chỉ chiếm 1% trong các khối u vùng nội sọ, là khối u lành tính tiến triển chậm và không có triệu chứng trên lâm sàng.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












