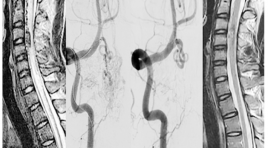
Nghiên cứu các đặc điểm hình ảnh và đánh giá kết quả điều trị dị dạng động - tĩnh mạch tủy bằng can thiệp nội mạch
22/03/2020 17:29:46 | 0 binh luận
The imaging characteristics and embolization treatment of spinal arteriovenous SUMMARY Purpose: to describe the imaging characteristics and the results of spinal arteriovenous shunt treated by endovascular intervention. Material and Methods: Descriptive and intervention study, patients were diagnosed and treated by endovascular intervention at the Bach Mai hospital from 2012 to 2016. Imaging features were evaluated on MRI and DSA, evaluated of effectiveness of treatment based on the comparison of clinical symtoms, MRI imaging before and after endovascular treatment. Result: Diagnosis and endovascular intervention of 20 patients. On MRI, the sign of spinal cord edema and dilated venous drainage were spotted in almost patients. The rate of complete angiographic obliteration was 60% patients and partial in 45.5% patients. After follow up of 3-6 months, spinal cord damage reduce accounted 88.23% and 11.77% patients remain unchanged, clinically significance improvement was achieved in 82.35% patients,17.65% patients do not improve (3 cases are continous following). Conclusion : MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow up patients with spinal arteriovenous shunt, DSA is the gold standard for diagnosis and to allow intervention treatment with high effective.
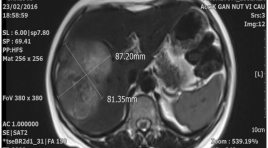
Đánh giá hiệu quả bước đầu trong điều trị ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan bằng phương pháp nút mạch sử dụng hạt vi cầu phóng xạ YTTRIUM-90
30/03/2020 14:45:16 | 0 binh luận
T he results of Y90 radioembolization in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma SUMMARY Background : Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is aggressive primary malignancy of the liver that most commonly presents late in the disease course. As a result, the majority of patients are not candidates for curative therapies. Locoregional therapies including Yttrium-90 (Y-90) radioembolization play an important role in management of the vast majority of patients with HCC. Methods : Patients with unnresectable HCC (n=41) treated with Y-90 radioembolization from 2013 to 2016 were evaluated retrospectively. Data was abstracted from medical records including patient charts, laboratory data, and imaging. Results : The most common clinical toxicity among all patients was fatigue (58.5%). A clinical benefit, defined as patients achieving PR was seen in 95.13% of cases; was seen complete reponse (CR) in 4.87%. The mean overall survival from the time of diagnosis was 18.4 months. Conclutions : For patients with HCC, Y-90 radioembolization is a safe and well-tolerated procedure. Our experience suggests that a significant percentage of patients achieve clinical benefit including many with PR. Prospective, randomized data is required to compare radioembolization with other therapies including chemoembolization and systemic therapy with sorafenib. Keywords : Radioembolization, Yttrium-90 microspheres, SIR-spheres, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Transarterial radioembolization, SIRT.
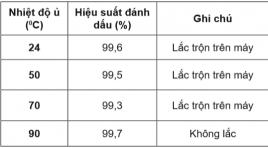
Ngiến cứu điều chế hạt ALBUMIN gắn đồng vị phóng xạ YTTRIUM-90
15/04/2020 20:38:47 | 0 binh luận
Study On Radiolabeling Of Albumin Particles With Yttrium-90 SUMMARY Objective: This report is intended to determine the optimum conditions of the radiolabeling of microaggregated albumin particles with Yttrium-90 radioisotope and the completion of the quality control procedures. Subjects and Methods: The albumin microsphere kit was prepared in sodium phosphate buffer. The original solution includes 2 mg albumin particle and 0.5 mg stannous chloride dihydrate. The albumin particles size was ranged from 5 mm to 30 mm. The mixture was washed three times with phosphate buffer saline, pH 7.2 by centrifugation and suspended in 0.5 M sodium acetate buffer, pH 6. Yttrium-90 in 1.0 M acetic acid was collected from 90Sr/90Y generator. The labeling of the particles with 90Y (185 MBq) was performed at pH 5.5 in acetate buffer with agitating for 60 min at room temperature. The labeled albumin suspensions were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min. Labeling yields was calculated using centrifugation, filtration and compared with paper chromatography, which is developed in the Tris Acetic EDTA. In this system, the unbound of Y-90 migrates to an Rf of 0.9-1.0 and the radiolabeled albumin particles remains at the point of origin (Rf = 0). The size of 90Y-albumin particles was compared with the albumin particles in the original solution to be sure that they didn’t change during the labeling treatment Results : The radiolabeling yields were more than 80% at pH 5,5, the labeled compound was dialysis in phosphate buffer. The radiochemical purity was 98%, the reaction time marked 60 minutes, at room temperature (about 240C). The labeled compound was dialysis in phosphate buffer. The product has a radioactivity of more than 98%. The product has been tested and the quality requirements of radioactive drugs. Conclusion: The subject has achieved the goal of producing conjugate 90Y-albumin and quality control, which is the ideal radioactive substance for the treatment of malignant cancer such as radiation therapy. In the future it is necessary to continue the study of high-activity radiolabeled albumin particles and study on laboratory cancer animals. Key words: 90Y-albumin microspheres, radiopharmaceuticals, brachytherapy
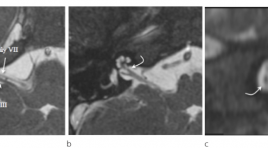
Hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính và cộng hưởng tử bất thường dây thần inh ốc tai trên 22 bệnh nhân điếc tiếp nhận bẩm sinh
07/04/2020 21:04:15 | 0 binh luận
CT scanner and MRI imagingof cochlear nerve deficiency in 22 patients with bilateral congenital sensorineural hearing loss SUMMARY Objective: To describe CT scanner and MRI imagingof cochlear nerve deficiency (CND) and cochleovestibular nerve abnormality in association with cochlear aperture, internal auditory canal (IAC) and labyrinthine malformations. Material and Methods : 22 patients with CNDin 43 ears. Aplasia or hypoplasia of the cochlear branch was evaluated on high resolution 3D gradient-echo MRI. Cochlear aperture, IAC and bony labyrinthine malformations was evaluated on high resolutionCT scanner. Results : 22 patients with CNDin 43 ears. Cochlear nerve aplasia in 20 ears (46,5%), cochlear nerve hypoplasia in 2 ears (4,7%), presence of vestibulocochlear nerve with no cochlear branch in 21 ears (48,8%). Labyrinthine malformation in 25 ears (58,1%).The mean IAC diameter 3,03 ± 1,03mm.Cochlear aperture stenosis and atresia 76,7%. Conclusion :CND frequently associated with labyrinthine malformations, cochlear aperture stenosis or atresia and IAC stenosis. Key words : Cochlear nerve deficiency, CT scanner and MRI.
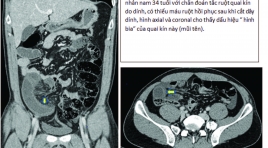
Các dấu hiệu chụp cắt lớp vi tính chẩn đoán thiếu máu và hoại tử ruột ở tắc ruột non quai kín
17/12/2019 10:30:16 | 0 binh luận
CT findings for diagnosis of bowel ischemia and necrosis in closed-loop small-bowel obstruction SUMMARY Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the imaging features of contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) to diagnosis for bowel ischemiaand necrosis in closed-loop small-bowel obstruction Materials and Methods: Thirty-three patients with CL-SBO confirmed by laparotomy. Based on the surgical findings, these patients were classified into three groups: necrosis group (n = 9), ischemia without necrosis group (n = 12), and no-ischemia group (n = 12). Two blinded radiologists retrospectively reviewed CECT including multiplanar reconstruction images and evaluated 11 CT findings. The sensitivity and specificity of each finding were compared among the three groups, and logistic regression analysis was performed. Results:Reduced bowel- wall enhancement, reduced enhancement of the mesenteric veins showed high specificities of 92%, 96% and sensitivities of 62% and 78%, respectively, for the prediction of bowel necrosis in CL-SBO. The target sign in the ischemia group were 83% and 76%, respectively, for sensitivities and specificities, compared with 22% and 46% of the necrosis group. We have included the data in a univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, but there is no correlation between imaging features and surgical findings. This can be explained by the interval between CT and laparotomy has altered bowel conditions. Conclusions : In our prospective patients, reduced enhancements of bowel wall and mesenteric veins were good indicators of bowel necrosis. On the contrary, target sign was a predictor of a viable bowel. Key words : intestinal obstruction, closed loop, ischemia, necrosis, computed tomography.
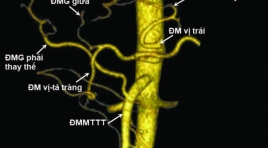
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm giải phẫu động mạch thân tạng và hệ động mạch gan ở người trưởng thành bằng X quang cắt lớp vi tính
05/12/2019 09:11:06 | 0 binh luận
Anatomical study of celiac artery and hepatic arterial system in adults: an analysis using multidectector computed tomography SUMMARY Objectives : The aim of the present study was to evaluate the anatomical chacracteristics of celiac artery (CA) and hepatic arterial system (HAS) in Vietnamese adults by using multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Materials and Methods : Retrospective, cross-sectional and predominantly descriptive study based on the analysis of arterial phase contrast-enhanced CT images of 600 patients between July 2016 and November 2016, at the Radiology Department, University Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City (UMC HCMC). Results : The CA arises variably from the aorta at the level between lower 1/3 11th thoracic and upper 1/3 2nd lumbar vertebrae with more than 70% at the level of lower 1/3 12th thoracic, T12 – L1 junction and upper 1/3 1st lumbar vertebra. The celiac trunk anatomy was normal (Uflacker type 1) in 87.7% of cases and variation of CA was observed in 12.3% with the form of hepatosplenic trunk (Uflacker type 2) was the most common type (4.0%). Ambiguous celiac axis anatomy was seen in 3.1% of patients. CHA originated from celiac axis in 92.7% of cases, followed by SMA (4.0%) and aorta (1.2%). The HAS was described as normal (Michels type 1) in 73% of patients and several variations were noted in 23%. The most common variation was Michels type 2 (7.0%), followed by type 3 (5.7%), type 9 (3.8%) and others. Type\ 10 was not observed in our series. We have noted additional, unclassified variations in 19 cases (3.2%). Mean length and diameter of CA were 28.29 ± 6.68mm and 7.33 ± 1.15mm. Mean distance between CA and SMA was 20.51 ± 4.17mm. Normal measures of CA in women were smaller than in men (p<0.05). Mean length and diameter of CHA were 32.43 ± 8.49mm and 5.40 ± 1.04mm. Mean diameter of PHA was 4.45 ± 0.87mm. Normal measures of hepatic artery in women were smaller than in men (p<0.05). In the presence of anatomical variations, there was a decrease in the arterial diameters of the CA and HAS, decrease in the CA length, but increase in CHA length (p<0.05). In addition, a significant correlation was observed between CA diameter and length; CA diameter and distance to SMA; CHA diameter and length; and CHA diameter and PHA diameter (p<0.05). Conclusion: The knowledge of anatomic characteristics of the celiac artery and hepatic arterial system, including the most common variations of these arteries in population may assist in the selection of treatmen options và surgical planning. As a reliable non invasive method, MDCT can accurately provide detailed information of celiac artery and hepatic arterial system. Keywords: Anatomical variations; Celiac artery (CA); Hepatic arterial system (HAS); Common hepatic artery (CHA), Proper hepatic artery (PHA); Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT).

Các tiến bộ kỉ thuật cộng hưởng từ trong hình ảnh u não và ứng dụng tại bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy
31/03/2020 17:07:38 | 0 binh luận
Advanced MR techniques in brain tumor imaging and the application at Choray hospital SUMMARY MRI is the imaging modality of choice for brain tumours. Advanced MRI techniques have significantly developed and used clinically in imaging of brain tumor such as: diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Conventional MR imaging (MRI) provides mainly anatomic or structural information about the brain and tumor. Unlike conventional imaging, advanced MR techniques also provide physiological information concerning tumor cellularity, white matter invasion, metabolism and hemodynamics.These techniques can be used to diagnosis, differential diagnosis, grading, surgical planning, and monitoring of therapeutic response of brain tumors. A principles of the physiology, techniques, and clinical applications of these techniques is provived. Some experience of using these technique in the domain of brain tumor at Choray Hospital were also presented in this article. Key words: Advanced MR techniques, brain tumor, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), conventional MRI.
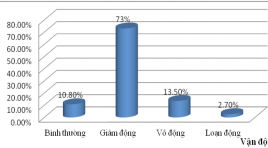
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ 1.5 Tesla trong đánh giá sống còn cơ tim ở bệnh tim thiếu máu cục bộ
31/03/2020 16:00:33 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics on and value MRI of myocardial viability in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease summary Purposes: 1. To describe the imaging characteristics on CMR of myocardial viability in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease; 2. To define the relationship between myocardial viability on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with the stenosis degree of coronary artery on invasive coronary angiography (IVA). Materials and Methods: 37 patients with chronic ischemic heart disease were enrolled in this cross-sectional prospective study. All patients were performed cardiac MRI and IVA during a period from 12/2011 to 8/2012 at Bach Mai Hospital. The data analysis by using the SPSS 18.0 (Chicago, United States). Results: 37 patients/ 27 males (73%) with mean age: 60.11 ± 11.74 year (35 - 81). Mean left ventricular systolic function (EF): 45.83 ± 12.83% (ranged 16.6 - 72%). 64.9% had EF decreased moderate to severe. 73% had reduction of ventricular contraction. 35 patients (94.6%) had late enhancement, of which 67.6% segments supplied by LAD, 64.8% had extent myocardial scar > 50%. Sensitivity and specificity of late enhancement at coronary artery stenosis ≥ 50% were 97.1%, 33.3% respectively. Conclusion: The extent of myocardial scar had good relationship with the stenosis degree of coronary artery. Key word: Cardiac MRI, Chronic ischemic disease, coronary artery.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












