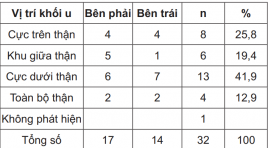
Nghiên cứu vai trò của siêu âm, cắt lớp vi tính đánh giá xâm lấn và di căn trong ung thư tế bào thận
01/04/2020 09:10:58 | 0 binh luận
Role of ultrasonography, computed tomography estimating abdominal invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma SUMMARY Object: Describe the ultrasonography and computed tomography features of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and investigate the role of ultrasonography, computed tomography in estimating RCC invasion and metastasis in abdomen Research design : Including 32 RCC diagnosed patients who underwent surgical treatment at Hue Central Hospital and Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy from April 2013 to August 2014. Results : The ultrasonographic features: The average size of tumor was 6.2 ± 2.4 cm; One case wasn’t found by ultrasound. The computed tomographic features: the size of tumors within 7 to 10cm occupied the highest rate at 43.8 percent (43.8%). Postoperatively, according to the pathological results, the tumor in T1 stage occupied the highest rate at 37.5 percent (37.5%). Compared the result of ultrasonography and computed tomography in finding calcification, vein thrombosis, located invasion and abdominal metastasis had p < 0.05 meant significant statistic. Conclusion : Ultrasonograph is a useful method to detect early tumor. Besides, computed tomography, especially spiral computed tomography with the multi planar reconstruction ability, indicated many advantages in estimation located invasion and vicinage organs metastasis in abdomen. That is also the most important criterion to classify the stage of kidney cancer in order to determine the best treatment plan for patients. Key word: Renal cell carcinoma, metastasis
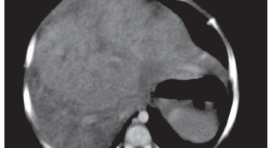
Gía trị của chụp cắt lớp vi tính hai dãy đầu thu trong chẩn đoán u nguyên bào gan trẻ em
01/04/2020 09:07:14 | 0 binh luận
Value of 2 detectors computed tomography in diagnosis o f hepatoblastoma SUMMARY Purpose: to evaluate the diagnostic value of 2 detector CT in pediatrichepatoblastoma (HB). Materials and methods: 69 patients 0-15 year old with clinical diagnosis of liver tumor, had 2 detectors CT-Scaner result of hepatoblastoma or not, all of them had pathology results, from 1/2010 to 5/2014 in National Hospital of Pediatric. Result: these is no single characteristic of HB on CT-Scaner wich had high value in diagnosis of HB. The characteristic of calcification within the tumor had highest specificity of 90% but with low sensitivity of 34.7%. The value of diagnosis that combine the characteristic of solid tumor on computedtomography with the age under 3 year old has specificity of 55%, sensitivity of 85.7%, when combining the characteristic of solid tumor on computedtomography, age under 3 year old and AFP higher than normal limit has specificity of 80%, sensitivity of 85.7%. CT- Scaner had high value in evaluating the tumor location with very high Kappa score of 0.856 and high in staging PRETEXT of 0.65. Conclusion : the diagnosis of HB should combine the characteristic of CT- Scaner with the age and value of alfa fetoprotein, wich had high sensitivity and high specificity. CT-Scaner had high value in evaluating tumor location, staging PRETEXT, and infiltration of tumors. Keywords: hepatoblastoma, liver tumors in children, liver mass in children, hepatoblastoma imaging.
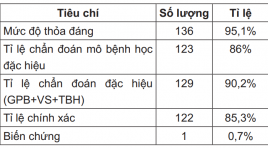
Đánh giá hiệu quả của phương pháp sinh thiết cột sống qua da dưới hướng dẫn cắt lớp vi tính bằng kim sinh thiết tủy xương kết hợp với kim sinh thiết phần mềm bán tự động
01/04/2020 08:58:13 | 0 binh luận
The role of percutaneous CT-guided vertebral biopsy using bone marrow biopsy needle combine with semi-automatic soft tissue biopsy needle SUMMARY Introduction : The bone biopsy instruments were improved regularly to increase successful rate and reduce complication but accompany with increasing of cost price. Our research purpose to assess the role of percutaneous CT-guided vertebral biopsy using bone marrow biopsy needle combine with semi-automatic soft tissue biopsy needle. Method: This is a retrospective study involving 143 patients who underwent percutaneous CT-guided vertebral biopsy in Radiology department, Bach Mai hospital. Biopsy needle included: bone marrow biopsy needle 13 and 11G, Surelock, TSK, Japan combined with soft tissue biopsy needle Stericut 16 and 14 G, TSK, Japan. Result: Adequacy 95.1%, pathologic specific diagnosis rate 86%, accuracy 85.3% and complication rate 0.7%. Conclusion: The adequacy of technique is not lower than most recent researches as so as open vertebral biopsy, the complication rate is not higher than most recent researches but significant lower than vertebral open biopsy. Keywords: Percutaneous, vertebra, biopsy, CT scanner, adequacy, complication.
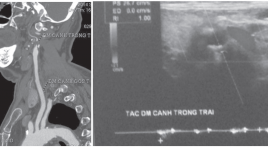
Đối chiếu hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính 64 dãy và siêu âm doppler động mạch cảnh trên bệnh nhân nhồi máu não hệ cảnh
01/04/2020 08:51:10 | 0 binh luận
The diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in patients with cerebra l infarction caused by atherosclerotic plaques of carotid system SUMMARY To compare the diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in patients with cerebral infarction caused by atherosclerotic plaques of carotid system. Objectives : (1) Describing that cause image findings of 64-slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in patients with cerebral infarction caused by atherosclerotic plaques of carotid system. (2) Comparison image findings of 64-slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in patients with cerebral infarction caused by atherosclerotic plaques of carotid system. Method: we studied 34 patientswith the diagnosis of ischemic stroke admitted to Huu Nghi Hospital from 11/2013 to 9/2014. All patients’s carotid arterial system were evaluated by US and then by 64-slice CT. Results : Average age: 76.5 ± 8.5. Hypertension: 80%. Diabetes: 37.1%. High blood cholesterol: 20%, previous stroke history: 45.7%. More than 2 Risk Factors: 60%. Carotid artery stenosis: Normal: 35.3% by 64 slice ct and 32.3% by Ultrasound. Up to 69%: 47.2% by 64 slice ct and 44.3% by Ultrasound. 70-100%: 20% by 64 slice ct and 18.6% by Ultrasound. This study showed almost perfect agreement between 64-slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in detection of stenosis with kappa value of 0,804. Conclusions: Good correlations were observed between 64 slice computed tomography and Doppler sonography in evaluating carotid artery system in cerebral infarction caused by atherosclerotic plaques of carotid system. Keywords: 64 slice CT, carotid artery, doppler sonography, ischemic stroke.
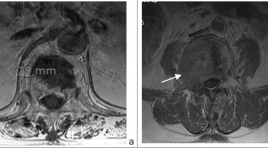
Nghiên cứu các dấu hiệu cộng hưởng từ thường quy trong chẩn đoán phân biệt xẹp đốt sống do loãng xương và xẹp đốt sống do nguyên nhân ác tính người cao tuổi
01/04/2020 08:35:48 | 0 binh luận
The conventional MRI features in different benign and malignant vertebral collapse SUMMARY Purpose: To points out the MRI important features in different benign and malignant vertebral collapse. Method: Retrospective research bases on the conventional MRI with enhancement of 40 patients who were more than 50 year old (20 patients with osteoporosis vertebral collapse and 20 patients with malignant collapse) in Ajou university hospital, Suwon, Korea from 01-01-2010 to 01-01-2012. Using Chi-square test to evaluation the significant different in frequency of MRI features of two group. Result: Lesion with wedge symmetric sharp, posterior wall intact or concave, no or less of paravertebral soft tissue, isointence on T1W, isointence or heterogenous on T2W, no enhance after contrast were favored as benign collapse; lesion with crush asymmetric collapse, big paravertebral mass, include posterior arch lesion, posterior wall convex were favored as malignant collapse. Conclusion: Conventional MRI enables differentiate between osteoporosis vertebral collapse and malignant collapse. Key word: osteoporosis vertebral collapse, malignant vertebral collapse.
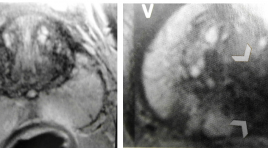
Phân loại PI-RADS của cộng hưởng từ( CHT) tuyến tiền liệt
31/03/2020 19:50:16 | 0 binh luận
Classification of Prostatic cancer with PI-RADS
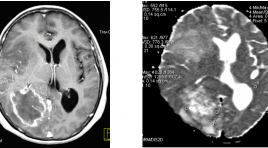
Các tiến bộ kỉ thuật cộng hưởng từ trong hình ảnh u não và ứng dụng tại bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy
31/03/2020 16:19:05 | 0 binh luận
Advanced MR techniques in brain tumor imaging and the application at Choray hospital SUMMARY MRI is the imaging modality of choice for brain tumours. Advanced MRI techniques have significantly developed and used clinically in imaging of brain tumor such as: diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Conventional MR imaging (MRI) provides mainly anatomic or structural information about the brain and tumor. Unlike conventional imaging, advanced MR techniques also provide physiological information concerning tumor cellularity, white matter invasion, metabolism and hemodynamics.These techniques can be used to diagnosis, differential diagnosis, grading, surgical planning, and monitoring of therapeutic response of brain tumors. A principles of the physiology, techniques, and clinical applications of these techniques is provived. Some experience of using these technique in the domain of brain tumor at Choray Hospital were also presented in this article. Key words: Advanced MR techniques, brain tumor, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), conventional MRI.
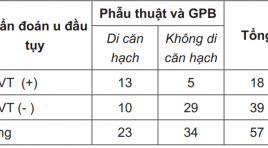
Gía trị của cắt lớp vi tính 64 dãy trong chẩn đoán u đầu tụy
31/03/2020 15:49:48 | 0 binh luận
The value of CT- Scanner 64 multi-detector in diagnosis of pancreatic head tumor summar y Objectives : Evaluating the role of CT scanner 64 multidetector in diagnosing of pancreatic head tumor. Subjects and methods: 57 patients were diagnosed of pancreatic head tumor on MSCT 64 multi-detector and were operated with pathology result confirmed from January 2012 to December 2012 in Viet Duc hospital. Results: The sensitivity, specificity, fault negative rate, accurate diagnosis and positive predictive value of MSCT 64 detectors in definite diagnosis were 96%, 100%, 3.4%, 98%, and 100% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, fault negative rate, accurate diagnosis and positive predictive value of MSCT 64 detectors in local invasive diagnosis were 74%, 87%, 26%, 86%, and 94% respectively. The evaluation vascular invasion were with the Se of 75%, Sp of 95%, FNR of 25%, ACC of 85%, PPV of 88%. The value of metastasis diagnosis were with Se of 57%, Sp of 85%, FNR of 43%, ACC of 71%, PPV of 72%. Accuracy of surgery technique proposing was 87.7%. Conclusion: CT scanner 64 multi-detector has high sensitivity and specificity in definitive diagnosis, evaluating the invasion and proposing the diagnosis possibilities. Key words : CT scanner 64 multi-detector, pancreatic head tumor.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












