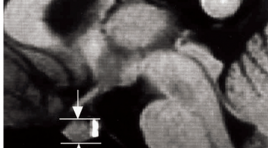
Chiều cao tuyến yên của người Việt Nam trên MRI
03/04/2020 11:34:54 | 0 binh luận
The height of the Pituitary Gland in Vietnamese summa ry Purpose: To clarify the normal Pituitary Gland in Vietnamese with the age and sex related changes. Methods: Reviewed Sagittal T1WI MRI in 1000 subjects, > 10 yaer olds, Head MRI with GE 1.5 T machine, to analyse the size of the Pituitary Gland. Results: The data were analyzed for different age ranges, sex related differences were statistically significant only in the 10 - 19, 20 - 29, 30 - 39, 40 - 49, 50 - 59, 60 - 69 and more 70 year old age groups. There are the differences between male and female. The pituitary height in male subjects maen 4.74 and 5.24 for female. The pituitary height peaked in the 20 - 29 year old age groups and tended to decline with age. Conclusion : The Pituitary gland height may reflect differences between younger and older subjects and between male and female subjects. Keywords: Pituitary gland, MRI of the pituitary grand.
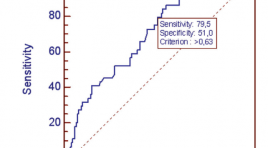
Khảo sát kĩ thuật tạo hình xung lực bức xạ âm ARFI trong chẩn đoán hạt giáp
03/04/2020 11:30:35 | 0 binh luận
Ttudy the feasibility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules summa ry Purpose : To assess the feasibility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging (VTQ and VTI) for differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Materials and methods: A total of 130 thyroid nodules underwent conventional ultrasound, including Color Doppler ultrasound using a 7.5MHz linear transducer; ARFI imaging was performed at 4MHz using Siemens Acuson S2000 B-mode- ARFI combination transducer; and FNAC (Fine needle aspiration cytology) assessment of thyroid nodule as reference criteria. Results: 130 nodules were analysed. 103 nodules were benign, 23 nodules were malignant and 4 follicular lesions. The median velocity of ARFI imaging in the normal nodule-free thyroid gland, as well as benign and malignant thyroid nodules was 1.41m/s (range 0.84 - 3m/s); 2.15m/s (range 0.8 - 4.04m/s) and 3.2m/s (range 0.9 - 9.22m/s), respectively. At cut-off 2.16m/s, a sensibility of 79.4% and specificity of 53.7% of VTQ could be achieved (AUROC = 0.731). The difference between VTQ of normal thyroid tissue and thyroid nodule (benign, malignant) has the sensibility of 79.5% and specificity of 51% at the cut-off of 0.63 (AUROC = 0.72). A significant difference was found between VTI on the one hand and benign or malignant thyroid nodules on the other hand, a = 0.001. Conclusions: VTQ and VTI of ARFI can be useful in the assessment of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. These novel quantitative and qualitative elastography method should be combined to give a more reliable result. Further investigations are needed to compare these baseline findings in thyroid nodules in healthy thyroid tissue with those in thyroid diffuse diseases.
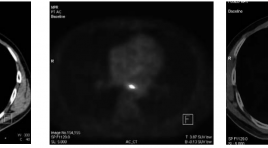
Ứng dụng kĩ thuật chụp PET/CT mô phỏng lập kế hoạch xạ trị ung thư thực quản
03/04/2020 10:44:54 | 0 binh luận
Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning SUMMARY Background: Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning is one of the most advantage techniques in cancer treatment. In 2009, Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center of Bach Mai Hospital was the fi rst place in Vietnam, where PET/CT simulation for radiation therapy planning has been conducted successfully for cancer patients. Objective : To build the PET/CT simulation process in radiation treatment planning for esophageal cancer. Subjects and methods: 50 esophageal cancer patients treated by radiation. Results: Simulation for radiotherapy in esophageal cancer: PET/CT has higher values than CT such as detecting lesions more precisely and more clearly. Patients in our study had good response and less complication: overall response (complete and partial) with improving clinical symptoms: 80%, size of tumor reduced in 83% patients. Common complication is depletion (in 34% patients). Most complications are mild and can be treated by medicine. Conclusion: Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center Bach Mai Hospital has standardized the PET/CT simulation process for esophageal cancer patients with initial good results.
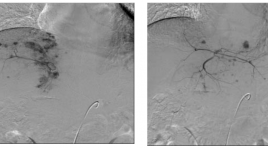
Giải phẩu hệ thống động mạch gan trên hình ảnh chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền ứng dụng trong điều trị ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan bằng nút hóa chấn động mạch qua catheter
03/04/2020 10:18:00 | 0 binh luận
Anatomy of hepartic artery on DSA images for treatment HCC by TACE SUMMARY Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common malignant tumor of the liver. This is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, ranking fi fth for men and eighth for women as a source of primary malignancy. The highest incidences of HCC are found in sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia, Southeastern Asia with incidence rates of 17.43 and 6.77 per 100,000 in men and women of developing countries compared with 8.71 and 2.86 per 100,000 in men and women of developed regions of the world [2],[6]. Although several therapeutic options have been advocated in international lectures, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in particular has been widely performed in the treatment of advantage HCC (nonsurgical patients). Otherwise in surgicalable patients, TACE has important role in presurgical stage. One of the most important factors which affect to TACE results is detection of tumor feeding arteries and nontarget arteries (supply the normal organs). Then, considerations of anatomy and variants of hepatica arterial system on (digital subtraction angiography) DSA images are very important in improvement of TACE effective and avoid complications.
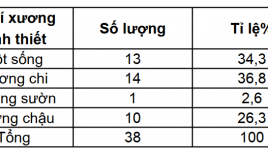
Đánh giá hiệu quả và tai biến của kĩ thuật sinh thiết xương dưới hướng dẫn của chụp cắt lớp vi tính
03/04/2020 10:01:14 | 0 binh luận
Effect and side effect evaluation of CT guided bone biopsy SUMMARY Objective: Study effect and side effect of CT-guided biopsy technique. Patients and method: 35 patients (38 times of biopsy) are biopyed under CT guiding at Radiology department, Bach Mai hospital from October 2011 to July 2012. Results: Successful rate 100%, adequacy 60,5%, complication 2,6%, using small size needle (14 và 13 G) and large size needle (11 và 10G) gots the same adequacy, the specimen >10mm is more effective than specimen <10mm. Conclusion: CT-guided biopsy is safe and effect.

Đặc điểm hình ảnh x quang cắt lớp vi tính của viêm túi thừa đại tràng
16/04/2020 16:14:17 | 0 binh luận
The computed tomography scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis SUMMARY Purpose : Describe the computed tomography (CT) scan characteristics of colonic diverticulitis (CD). Classification of colonic diverticulitis the World Emergency Surgery Society (WSES), and to compare computed tomography findings of right vs. left colonic diverticulitis. Methods: Retrospective studies described case series of patients diagnosed Colonic Diverticulitis at University Medical Center hospital and there was CT scan between January and December 2018. Clinical features, treatmentwere collected and assess the characteristics CT scan of Colonic diverticulitis Results: There were 104 patients, 75 right CD and 29 left CD. Mean age 46, ratio male/female 1,6. Inflamed diverticulum 89,4%; pericolic air bubbles19,2%; pericolic fluid 51,9%; abscess 1,7%; fistula 1,9%; bowel obstruction 1%. The classification of acute diverticulitis by the WSES, uncomplicated acute diverticulitis and complicated acute diverticulitisstage 1a, 1b, 2 a, 2b respectively of 48% and 39,2%; 6,9%; 4,9%; 1%. None of the complicated diverticulitis stage 3,4. Compare CT findings of right vs. left CD: Mean age (41 vs. 61), inflamed diverticulum (96% vs. 72,4%), pericolic air bubbles(8% vs. 48,3%), pericolic fluid (45,3% vs. 69%), abscess(4% vs. 31%), they differed significantly between the two groups (P < 0,05). Conclusions: Diverticulitis is often right-sided, mild in severity. Most are uncomplicate and complicated diverticulitis stage 1a by the classification of WSES. Right CD occurs in younger and lower complications compared to left CD Key words : Colonic diverticulitis,pericolic air, abscess,computed tomography findings, WSES.
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính đa dãy đầu thu và phân loại LUNG-RADS các nốt mờ phổi
30/03/2020 14:36:19 | 0 binh luận
MDCT images and The ACR Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS™) of Pulmonary nodules - Research in Hue National Hospital and Hue Medic Clinic SUMMARY Objective: Solitary pulmonary nodule may be benign or malignant. The purposes of this study is to illustrate the clinical characteristics, describe the images characteristics of chest X-ray and MSCT, classification of lung nodules by The ACR Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS™) then offer management and monitor strategies for this disease at Hue National Hospital and Hue MEDIC clinic. Methods: The study design was cross-sectional descriptive. Describe the clinical characteristics and images of lung nodules on chest X-ray and MSCT with LungCAD software to determine the nodular lesions during 1 year (5 / 2015-5 / 2016), in 2 centers (Hue National Hospital and Hue MEDIC clinic). Results : In our study, there was 49 patients with pulmonary nodules. Male was 38/49 (77.6%), more than female. Mean age was 57 ± 2 years old. Smallest nodule is 5mm, average size is 18.7 ± 9mm. There was 31/49 (63.3%) patients with lung size 15-30mm. MSCT has higher sensitivity than X-ray in detecting nodules <6mm and ground glass nodule. Base on The ACR Lung RADS classification, Lung - RADS 4B was seen most with 19/49 (38,8%) patients. Number of patients with Lung - RADS 4X was 8 (16.3%), including 5 patients who underwent surgeries, 3 of them had malignant pulmonary nodules. Conclusions : Patients with pulmonary nodules should be evaluated by estimating the probability of malignancy, be performed imaging tests to characterize the lesions better, be assessed the risks and benefits of different management strategies (biopsy, surgery and observation with serial imaging tests). Lung - RADS classification is simple, easy to apply and make appropriate recommendations for the management of solitary pulmonary nodules. Keywords : Solitary pulmonary nodule. Lung - RADS.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"