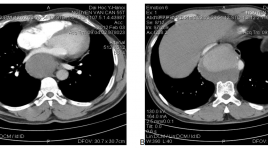
Điều trị phình động mạch chủ ngực bằng stent phủ tại bệnh viện trường đại học y Hà Nội: nhân ba trường hợp
02/04/2020 20:47:46 | 0 binh luận
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TE VAR) for the descending thoracic aortic aneurysm at the HaNoi Medical University Hospital:report three cases SUMMARY: Thoracic aortic aneurysm is a life threatening condition that needs to be treated urgently. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) for the descending thoracic aortic aneurysm was first reported by Dake et al in 1994 [4]. The advent of TEVAR was clinically relevant because descending thoracic disease repair had long been associated with operative mortality rates. The favorable results of TEVAR with reduction of operative mortality have led it to be used worldwide. Up to now, TEVAR has been initially used in Viet Nam. We report three cases with descending thoracic aorta aneurysms that were successfully treated by endovascular stent graft in HaNoi medical university hospital. Keywords: Thoracic aneurysm, stent graft, TEVAR.
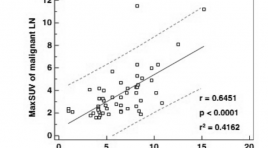
Tương quan cao về mức độ hấp thu 2-deoxy-2-F18-fluoro-D-glucose (FDG) qua trung gian glucose transporter type 1 giữa khối u nguyên phát và hạch di căn tại chổ tại vùng trong ung thư phổi không tế bào nhỏ
02/04/2020 18:02:52 | 0 binh luận
High correlations between primary tumours and locoregional metastatic lymph nodes in non-small-cell lung cancer with respect to glucose transporter type 1-mediated 2-deoxy-2-F18- fluoro-D-glucose uptake SUMMARY: The purpose of the study was to investigate whether glucose transporter type 1 (Glut-1) mediated 2-deoxy-2-F18- fluoro-D-glucose (FDG) uptake of primary tumour is related to the likelihood of malignancy involvement in loco-regional lymph nodes (LNs) in 126 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (M:F = 103:23, age = 65 ± 9.7 years). Maximum standardized uptake values (maxSUV) and Glut-1 expression levels (determined by PET and immunostaining, respectively) of primary tumours and PET positive loco-regional LNs were compared. Significant correlations were found between malignant LNs and primary tumours with respect to maxSUV (r = 0.6451, p < 0.0001), %Glut-1 expression (r = 0.8341, p < 0.0001) and Glut-1 staining intensity (p = 0.827, p < 0.0001). The areaunder- curve value for LN differentiation using lymph node maxSUV was significantly higher in patients with a primary tumour maxSUV of >6 (AUC = 0.775, p = 0.0001). High correlations between the primary tumours and metastatic LNs in NSCLC with respect to the Glut-1 mediated FDG uptake may be useful for mediastinal LN discrimination by FDG-PET. Keywords: Non-small-cell lung cancer, FDG-PET, Lymph node, Glucose transporter.
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm tổn thương xương trên xạ hình xương toàn thân 99mTc-MDP ở bệnh nhân ung thư vú, phổi và tiền liệt tuyến
02/04/2020 17:57:00 | 0 binh luận
Detection of bone metastases on breast cancer , lung cancer and prostate cancer patients by spect 99mTc – MDP inmaging SUMMARY: Background: Skeletal scintigraphy is a good modality for detecting bone metastasis. It can provide a whole view of skeletal system and has a high sensitivity. Method and Material: 99mTc – MDP bone scan for 108 patients with different stage cancer of Breast, Lung or Prostate, with or without clinical syndrome of bone metastases. Result: Bone metastases were detected on 73 studied patients (69.4%). Almost were multifoci asymmetric lesions, with increased uptake of radiophamatical activity (93.3%). The most common site of bone metastases were spine, pelvis (hip) and ribs. Conclusion: Almost imaging of bone metastases in bone scan were multifoci asymmetric lesions with increased uptake of radiophamatical activity (93.3%). The most common site of bone metastases are spine, pelvis (hip) and ribs. Key words: Bone metastases, Bone scan 99mTc- MDP.
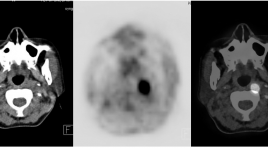
Bước đầu đánh giá vai trò của FDG-PET/CT trong chẩn đoán và lập kế hoạch xạ trị ung thư vòm mũi họng
02/04/2020 17:52:56 | 0 binh luận
Initial evaluation of the role of FDG -PET /CT in diagnosis and radiotherapy planification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) SUMMARY: NPC (cavum) is a common disease in the world (1% world population according to UICC) and one of leading causes of death in South China as well as in most of ASEAN countries. PET/ CT (Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography) is a modern imaging modality, playing an important role in management of NPC. Applications of FDG-PET/CT in NPC are diagnosis, staging, restaging for recurrence, monitoring therapeutic response and radiotherapy planning. Purposes: Initial evaluation of role of PET/CT in diagnosis and radiotherapy planning for 20 NPC patients (cavum tumor). Objects and research method: 20 patients with determined diagnosis of NPC with anapathological results, received PET/CT in Nuclear medicine and Oncology Center, Bach Mai hospital for diagnosing, staging and emulating radiotherapy plan from July 2010 to January 2011. Results: 1. FDG-PET/CT is very valuable in diagnosing and staging NPC including detection of primary tumor in metastasic patients with unknown origin; Importance of FDG uptake (SUV value) is high at cavum (mean SUV = 11.83), at metastatic ganglions (mean SUV= 8.37) helping detection, staging modified in 38.9% patients, modifying treatment way as well as better prognosing. 2. FDG-PET/CT is usefull in planning NPC radiotherapy by helping exactly BTV, without omission of regional ganglions, modifying volume of radiotherapy in 80% patients in compared with conventional emulation by CT, reducing volume of radiotherapy in 60% patients, limiting complications due to radiation. Mean GVT-PET volume is about 92.3 cm3 in compared with GTV-CT (128.4 cm3). Conclusion: Using FDG-PET/CT is a highly effective and safe technics in diagnosing and emulating radiotherapy plans for NPC patients. Key words: PET/CT, diagnosing, emulating, radiotherapy, NPC
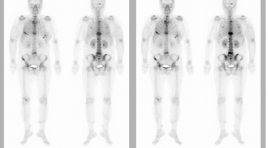
Kết quả xạ hình xương trên bệnh nhân ung thư
02/04/2020 17:48:03 | 0 binh luận
Result of Spect detection bone metastatic SUMMARY: Applying bone-scan radiation with Tc99m - MDP to 576 patients, who are in different stages of arch, breast, colon, ovarian, lung, prostate, lymphoma, thyroid, bronchial, cervical, tongue, lower throat… cancers. The result has been shown that the percentage of lesion detection is about 22,08% (20.22%) patients, in which the rate of multiple damage accounted for 34.7% of the entire metastatic bone lesions and even for patients, who have been diagnosed early, the common locations of lesions are: ribs, spine bone. This ability of bone lesions early detection has helped many clinical positioning for biopsy, dividing in phases, treatment course, test after treatment.
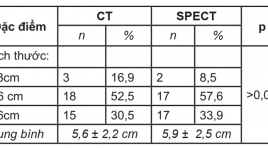
Xạ hình SPECT 99mTc-MDP phát hiện hạch trung thất và đánh giá đáp ứng với xạ trị ở bệnh nhân ung thư phổi không tế bào nhỏ
02/04/2020 17:43:48 | 0 binh luận
The role of 99mTc - MIBI SPECT in the identification of mediastinal lymph node and assesstment of radiotherapeutic response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer SUMMARY: 36 patients with non-small cell lung cancer underwent a 99mTc-MIBI SPECT studies before starting and after radiotherapy 4 weeks. For neoplastic lung lesions, the diagnostic sensitivity of MIBI SPECT were 100% (36/36 patients). Tumor size on SPECT 5,9 ± 2,5cm, was higher compared 5,6 ± 2,2 cm on CT. For mediastinal lymph node, MIBI SPECT identified 83 lesions in 35 patients, when CT showed only 42 lymph node in 29 patients. 99mTc-MIBI SPECT imaging may be useful to differentiate between necrotic tumor tissue and residual, recurrent lung lesions after radiotherapy. Key words: 99mTc-MIBI SPECT scan, non-small cell lung cancer.
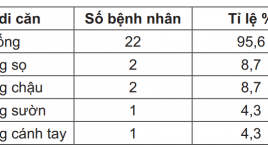
Điều trị giảm đau bằng chiếu xạ kết hợp Bisphosphonate trên 23 bệnh nhân ung thư di căn xương
02/04/2020 17:34:52 | 0 binh luận
Palliative treatment by gamma ray with bisphosphonate of 23 bone metastases cancer patients SUMMARY: 23 cancer patients with bone metastases 1-2 sites were treated by gamma rays of Cobalt-machine, daily dose 4Gy, total dose 20Gy in combination with bisphosphonates infusion (Zometa, 4mg, IV over 15 minutes). Good response bone pain relief 82.6% and partial response 17.4%. Bone pain relief time was longer 2 months. Improved quality of patient’s life. Key words: Palliative treatment, bone metastases
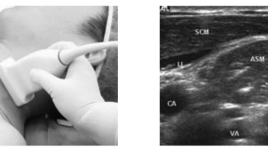
Bước đầu nghiên cứu đặc điểm giải phẩu siêu âm đám rối thần kinh cánh tay vùng cổ
02/04/2020 17:30:59 | 0 binh luận
Initial study of anatomical ultrasound imaging of neck region brachial plexus SUMMARY: Objective: To describe the sonographic appearance of the normal brachial plexus and to suggest the suitable region for brachial plexus blockade under the guidance of ultrasound. Subjects and methods: 15 patients whose age varies from 32 to 83, hospitalized at ultrasonography department in Hue Central Hospital from 3/2012 to 4/2012. The subjects had beenultrasound scanned to locate the brachial plexuses. Their sonographic appearances and relationship with surrounding structures then were described and cross- sectional description were studied. Results: Of all 15 subjects, brachial plexus appearances were well vizualized at interscalene and supraclavicular region. At infraclavicular region however, the same result occured in only 3 subjects, equaling to 20%. The brachial plexus was visualized as a chain of hypoechoic nodules representing the trunks at interscalene region, a cluster of hypoechoic nodules representing the divisions at the supraclavicular and hyperechoic nodules representing the cords of which diameters decrease from roots to nervous fiber. Brachial plexus’s location is nearer from skin at its roots and deeper towards the fiber end. Antomically, brachial plexus relates to stenocleidomastoid muscle, anterior scalene muscle, interscalene, subclavian artery at superior thoracic aperture and lung membrane at subclavian region. The brachial plexus that locates at interscalene region is the most suitable for brachial plexus desensitilization with ultrasound guide method for better efficiency and safety. Conclusion: Initial studies of anatomical ultrasound imaging of the brachial plexus in the neck region result in two conclusions. Firstly, high resolution ultrasound (7-10 MHz probe) allows clear description of brachial plexus from roots to divisions, and clear description of cords in about 20% of cases. Lastly, the interscalene region is the best place for neck region brachial plexus desensitilization with ultrasound guide method for its highest possibility of success and least complication.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












