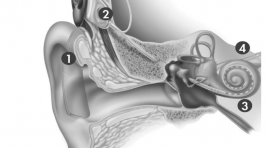
Tổng kết về đặc điểm hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính và cộng hưởng từ của 35 trường hợp thực hiện bilan trước đặt điện cực ốc tai
02/04/2020 17:22:26 | 0 binh luận
Assessment of scannographic and magnetic resonance caracteristics of 35 cases as bilan before cochlear implant SUMMARY: Objective: Bilan of scannographic and magnetic resonance imaging features for 35 candidates of cochlear implant (CI). Materials and methods: 35 cases suffering from profound deafness, undergone screening for CI from Jan 2011 to April 2012. Temporal CT scanner, Brain and inner ear MR imaging were performed. Results: 35 patients, Male/female is 18/17, average age is 8. None has outer ear abnormality. Six cases (17.1%) have malformation of middle ear. Ten cases (28.6) suffer from acute otitis media. Two cases with inner malformation and three cases with labirynthitis. Conclusions: CT scanner and MR imaging play an important role in bilan of CI.
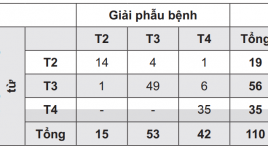
Đánh giá giai đoạn ung thư trực tràng bằng cộng hưởng từ: kết quả 3 năm
02/04/2020 15:12:16 | 0 binh luận
Preoperative staging of rectal cancer by pelvic mr imaging: results after 3 years SUMMARY: Introduction: Colorectal cancer is the most common cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. Rectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Vietnam. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer has an important role to select the most appropriate treatment. Purpose: To access the role of pelvic MR imaging in preoperative staging of rectal carcinoma. Materials and methods: Preoperative pelvic MRI of 110 patients with rectal cancer was performed in University Medical Center at HCMC for 3 years. Staging was made by evaluating images obtained and compared with postoperative histopathologic staging. Results: The accuracy of pelvic MR imaging for defining the T stage of rectal cancer was 89%. The accuracy rate to detecting lymph node metastases was 92.5%. Conclusions: Pelvic MR imaging is a promising technique for accurate preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Keywords: Rectal cancer, MR Imaging, colorectal carcinoma
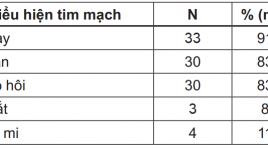
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm lâm sàng hình ảnh, siêu âm và xạ hình bệnh nhân nhiễm độc giáp
02/04/2020 15:01:37 | 0 binh luận
Study on clinical features, ultrasound imaging and scintigraphy of thyrotoxicosis patients SUMMARY: The cross section study on 36 patients at the Endocrinology - Neurology - Respiratory Department of Hue Central Hospital, from May 2010 to September 2011. The main clinical symtoms: palpitation, heart rate >90bpm, finger and hands tremors, weight loss, thyroid gland enlargement, systolic murmur at thyroid gland. Thyroid Scintigraphy: The major signs are irregular margins, thyroid gland enlargement, and high iodine-131thyroid imaging. Thyroid Ultrasonography: Most patients have enlargement thyroid volume, hypoechogenicity, irregular margins and hypervascularity. An increased mean peak systolic velocity of the thyroid artery is significantly charateristic.There was tied correlation between thyroid weight on Scintigraphy and thyroid volume on Ultrasonography, between peak diastolic velocity and T3 level, between peak systolic velocity and TSH level (p<0,05).
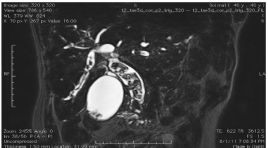
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ trong chẩn đoán sỏi ống mật chủ
02/04/2020 16:49:58 | 0 binh luận
imaging characteristic and evaluation of MRI on the diagnosing of extra hepatic biliary stone SUMMARY: Objective: Study of MR imaging characteristic of the extrahepatic CBD & its value about the stone finding. Objet and Method: Retrospectiv of 56 patients having open operation, endo and retrograde endoscopy from 10/2010 - 8/2011 at Bach mai hospital. Means: USG of Philips HD11, MRI units of Siemens Advanto and Essenza 1.5T. Results: Among 56 operated patients for CBD stone, 6 free of stone (4 Oddi stenosis, 1 vater ampulla tumor, 1 unknown cause). MRI detected 49/50, missing 2% . In 49 positiv, 1 having 10 stones (2%), almost 3 (38%), the greatest 20 x 30mm, mainly localized at the III extrahepatic CBD portion (85/153 stones). 1 missing 5mm is at the IV portion, 49% inhomogenous mosaic form,79 strongly hyposignal on T2W. 22 patients (44.9%) associated with lithiasis in right bile duct, left 27 (55.1%), GB 13 (26.5%). Bile duct dilatation up and downward of the stone 23 (46.9%), hepatic abcess 3 (6.1%) Compare USG/MRI. USG: Se 96%, Sp 16.1%, PPV 48%, PPV 48%, Acc 52%. MRI: Se 98%,Sp 83,3%, PPV 98%, NPV 83.3%, Acc 96.4%. Conclusion: MRI is a good means for detecting low CBD stone also for predicting its number, dimension, location and complication also Se, Acc evidently higher than USG.
Ứng dụng sinh thiết( ST) lõi trong chẩn đoán ung thư (UT) gan dưới hướng dẫn siêu âm
02/04/2020 14:54:27 | 0 binh luận
Core biopsies for focal hepatic lesions by ultrasound guidance SUMMARY: All percutaneous US-guided biopsies for focal liver lesions performed in 37 patients. Among the 54 lesions for which the 18- gauge cutting needle was used, core biopsy was performed once in 23 lesions (62.2%), twice in 11 lesions (29.7%), and three times in 3 lesions (8.1%). The length of tissue cores was above 1cm in 44 lesions (81.5%). Three of the 54 specimens (5.6%) fragmented when placed in formalin. The common complications were 2.7%. No major complications were observed. The core biopsy specimen was sufficient for diagnosis in 36 patients (97.3%) and was insufficient in one. Histologic examination revealed various types of H.C.C (62.2%), peripherial cholangiocarcinoma (2.7%), secondary malignant tumors (8.1%), benign tumors (24.3%). There was high concordance between the histologic and cytologic results (Kappa = 0.579, p < 0.05); and very high concordance between the core biopsy and post surgery histologic results (Kappa = 0.942, p < 0.05). Key words: core biopsy, focal hepatic lesions, HCC, cholangiocarcinoma.

Gía trị của phương pháp nút mạch bằng chọc trực tiếp qua da trong điều trị dị dạng thông động tĩnh mạch
02/04/2020 14:50:08 | 0 binh luận
Value of direct percutaneous puncture in the AMV treatment SUMMARY: Purpose: We present our experience in four cases using embolization technic by percutaneous direct puncture and injection of n-Butyl-2 Cyanoacrylate to embolize high flow fistula arteriovenous malformations having multiple feeding arteries. Materials and methods: 3 patients with high flow arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) of the head, neck region and one patient’s AVM in arm were treated with direct percutaneous injections of Histoacryl. Results: There were no major complications after the embolization procedure. The arteriovenous shunts were completely eliminated in three cases. The embolization was incomplete in one patient who required a surgical procedure to remove the residual AVM lesion and also for esthetic reason. Conclusion: Embolization by percutaneous direct puncture with n-BCA injection appears to be a good treatment for the high flow arteriovenous malformations having multiple feeding arteries and large nidus.
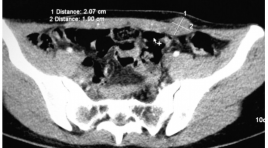
Lạc nội mạc tử cung vào cơ thành bụng sau mổ lấy thai và u tiểu khung được phát hiện tại trung tâm chẩn đoán hình ảnh AMTIC
02/04/2020 14:33:01 | 0 binh luận
7 BN nữ độ tuổi từ 26-41 đã có mổ lấy thai trước đó, 1 sau mổ u nang buồng trứng. BN đến khám vì đau ở dưới vết mổ thành bụng có liên quan tới chu kì kinh nguyệt. Khám lâm sàng thấy khối dưới sẹo mổ, một vài BN có thể tự sờ thấy. Siêu âm thấy khối giảm âm không đồng nhất trong thành bụng bên trái dưới sẹo mổ, chụp cắt lớp vi tính (CLVT) thấy khối giảm tỉ trọng so với cơ, chụp CHT thấy khối tăng tín hiệu trên T1W-T2W-FAT SAT và ngấm thuốc đối quang từ. Chẩn đoán giải phẫu bệnh xác nhận là lạc nội mạc tử cung

Tổng quan điện quang can thiệp các bệnh lý thần kinh bài 1
02/04/2020 14:29:25 | 0 binh luận
Lĩnh vực điện quang can thiệp nói chung và can thiệp các bệnh lý dị dạng mạch não nói riêng đang khẳng định ưu thế vượt trội trong điều trị các bệnh lý dị dạng mạch phức tạp, cùng với sự phát triển các máy móc hiện đại, vật liệu dùng trong can thiệp nội mạch liên tục phát triển và đổi mới. Trên thế giới, lĩnh vực can thiệp bệnh lý dị dạng mạch não đã được tiến hành từ cách đây 30 năm. Ở Việt Nam, can thiệp bệnh lý dị dạng mạch não được tiến hành từ năm 2000, đi đầu là Khoa Chẩn đoán hình ảnh, Bệnh viện Bạch Mai. Đến nay, các bệnh lý can thiệp mạch não được điều trị có kết quả rất tốt.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












