
Đặc điểm hình ảnh PET/CT sau xạ trị chiếu trong chọn lọc bằng hạt vi cầu gắn 90Y với hình ảnh 99MTC MAA mô phỏng trước điều trị ở bệnh nhân ung thư gan đối chiếu
06/04/2020 22:18:01 | 0 binh luận
Characteristics of Post- Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)90 Y Microsphere PET/CT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Comparison With 99mTc Macroaggregated Albumin (MAA) scan SUMMARY Purpose: 90Y microspheres are recommended for intra-arterial treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Before treatment,99mTc-labelled macroaggregated albumin (MAA) is injected intra-arterially to simulate the treatment and yttirum-90 (90Y PET/CT) images is performed to evaluate posttreatment. The aim of the study is to assess the correlation between the pretreatment planning and posttreatment images. Methods: Twenty patients with the intermediate and advanced stage of HCC were reviewed in this study. 99mTc-MAA was injected intra -arterially before treatment and whole body scintigraphy and abdominal SPECT was done after 60 min.Post-injection of 90Y microspheres (SIRTEX, Australia), the patients underwent posttreatment 90Y PET/CTwithin 24 h. The tumor to normal ratios (T/N ratios) on PET/CT and SPECT were analyzed and correlated using Spearman rank correlation test. Results : In 20 patients, the distribution of microspheres was consistently demonstrated in both 99mTc-MAA planar scintigraphy before therapy and posttreatmentPET/CT images. Agood correlation was observed between T/N on scintigraphy before treatment and T/N on PET/CT images after treatment (rho value=0.58, p<0.005). The TN on PET/CT (median 14.85) tends to show significantly higher values than T/N stimulated (median 11.2, p<0.05). The T/N post treatment showed good correlation with tumor volume (rho=0.69, p<0.05). Conclusions The 99m-Tc MAA planar imgaes showed a good correlation with 90Y PET/CT in T/N values, suggesting that it should be used as an adequate pretreatment evaluation method. 90Y PET/CT should be included routinely in the post-therapeutic evaluation. Keywords : resin microspheres 90Y, 99mTc-MAA, hepatocellular carcinoma
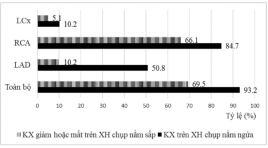
Đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị chẩn đoán bệnh động mạch vành của xạ hình SPECT tưới máu cơ tim chụp tư thế nằm ngửa kết hợp nằm sấp
06/04/2020 22:09:43 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics and diagnostic value of SPECT myocardial perfustion scintigraphy with combined supine - prone acquisition in diagnosis of coronary artery diseases SUMMARY Abstract: The aim of the study is to determine the imaging characteristics and diagnostic values of the combined supine - prone myocardial perfusion SPECT in comparison with supine alone acquisition. Methods : 59 CAD suspected patients were underwent Tc-99m sestamibi ECG - gated myocardial perfusion SPECT with combined supine - proneacquisition protocol to reduce attenuation defects in supine images. The results of MPI were compared with the coronary angiogram. Results: The sensitivity and specificity of the combined acquisitionprotocol were 76%, 94.1% respectively. There is no significant difference in the sensitivity between the two patient’s position acquisition. However, specificity was significantly improved in the combined acquisition (94.1% vs. 70.6%), especially in male (96.4% vs. 71.4%) and overweight patient’s groups (BMI> 23) (94.4% vs 61.1%). Conclusions : The combined supine - prone acquisitionprotocol did significantly improved the specificity ofmyocardial perfusion SPECT, especially in the overweight and males. Key words: combined supine - proneacquisition ,myocardial perfusion SPECT
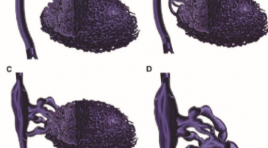
Đánh giá kết quả điều trị dị dạng tĩnh mạch nông bằng tiêm xơ dưới máy chụp mạch
06/04/2020 21:52:02 | 0 binh luận
Evaluation the result of flouroscopy-guided sclerotherapy in treating superficial venous malformation SUMMARY Purpose : Describe imaging characteristics of superficial venous malformation (VM) on flouroscopy and evaluate effectiveness of foam sclerotherapy. Method: Prospective cohort from november 2015 till may 2017 on 26 patients with VM treated by flouroscopy-guided sclerotherapy. Results: 26 patients with VM were involved in our study: 15,4% type I; 61,5% type II; 7,7% type III and 15,4% type IV. Malformation dimensionwere reduced by mean of 41,3%, VM type I had 62,5% size reduction; pain score were decreased by mean of 2,9 points (48,5%). VM type IV had 26,7% dimension reduction and 30,8% painful ease. No complication were noted. Conclusion: Flouroscopy-guided sclerotherapy is a safe procedure to reduce size and pain for patient with VM, particularly the most dimension reduction in type I, the most pain ease in type II . Keywords: venous malformation, sclerotherapy, flouroscopy-guided
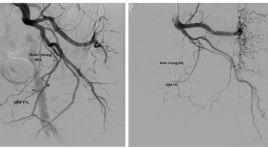
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm giải phẫu, biến thể của động mạch tuyến tiền liệt trên chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền
06/04/2020 21:18:37 | 0 binh luận
Studying anatomical characteristics and variants of prostatic artery on digital subtraction angiography SUMMARY Objectives : To describe anatomical features and variants of prostatic artery (PA) on digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Subjects and Methods: Descriptive statistic study. We reviewed the DSA of 58 patients, which had a PA embolization to reduce the benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms at radiology department of Bach Mai Hospitalfrom Oct - 2016 to June - 2017 Results: PA was found at 110 pelvic halves, of which 5 pelvic halves (4,5%) had two PAs, 105 pelvic halves had one PA. In terms of the type of origin of PA according to Francisco Carnevalle, in 115 PAs, the percentage of type 1 (was from a common trunk with the superior vesical artery - SVA), type 2 (anterior division of internal iliac artery), type 3 (obturator artery), type 4 (internal pudendal artery), type 5 (less common origins)was successively 33,9%, 13,9%, 18,3%, 23,9%, 10,4%. Atherosclerosis of PA observed in 20.9%.The “corkscrew” patern was found in 30.4%. The average diameter of PA was 1.5 ± 0.34mm. Anastomosis of PA with surrounding arteriesare common. PA may supply rectum (6.1%), seminal vesical(9.6%), bladder (5,2%), controlateral prostatic parenhyma (13%), surrounding soft - tissues (3.5%). Conclusion : The common trunk with SVA was the most common origin of PA. Anatomosis of PA with surrounding tissues is complex.... Therefore, profound knowledge ofthe PA anatomy and variants on DSA is necessary to treat BPH by prostatic arterial embolization. Key words: prostatic artery, digital subtraction angiography, Francisco Carnevalle classification.

Kết quả bước đầu sinh thiết xương qua da dưới hướng dẫn cắt lớp vi tính bằng hệ thống khoan xương ARROW ONCONTROL tại bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy
03/04/2020 16:57:33 | 0 binh luận
Initial results of ct-guided percutaneous bone biopsy using an arrow oncontrol bone access system at Cho Ray Hospital SUMMARY Background: Computed tomography (CT)-guided percutaneous bone biopsy has been widely performed at big hospitals in Vietnam, but these techniques were done by using bone biopsy handle needle. Procedural time was usually prolonged, pain level of patients increased, especially osteopetrosis lesion, risk of not receiving samples. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to assess the initial effectiveness of CT-guided percutaneous bone biopsy using Arrow Oncontrol bone access system. Materials and methods: All the patients were performed CT- guided percutaneous bone biopsy at Cho Ray hospital from February 2016 to June 2017, 58 patients using Arrow Oncontrol bone access system. The techniques include: local anesthesia, confirming accurate lesion by CT scan, inserting 11G needle and 13G coaxial needle with Arrow Oncontrol bone access system putting into lesion, checking again by CT scan, drilling to take core sample. The efficacy, safety, pain level and procedural time were evaluated by variants: technique success rate, accuracy of histopathology, pain level, procedural time and complications. Results : 58 patients were performed with CT-guided percutaneous bone biopsy using drilling Arrow Oncontrol system. Technique success rate was 96.5%, diagnostic accuracy histopathology was 87.9%, the correlation was strong (r = 0.95) between histopathological diagnosis and discharge diagnosis, low pain score (mild pain) 82.7%, technical median time 11 minutes, there were no complications. Conclusions: CT-guided percutaneous bone biopsy using Arrow Oncontrol drill-assisted system had high technique success rates, high diagnostic accuracy of histopathology, mild pain level, fast and safe procedure. Key words: CT-guided bone biopsy, Arrow Oncontrol bone access system.
Vai trò của X-quang cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán lồng ruột ở người lớn
03/04/2020 16:31:14 | 0 binh luận
Role of abdominal computed tomography in diagnosis of adult intussception SUMMARY Objective: To describe imaging characteristics of adult intussception (AI) on CT and to identify diagnostic values of them. Materials and methods : Case series report including patients: defined AI on CT, over 18 years of age, having been on surgery, with/ without histo-pathology. Patients are divided into two groups: those with enteroenteric intussusception (EI) and those with intussusceptions involving colon (IC), including enterocolic and colocolic lesions. Results: from 01/2014 to 01/2017 at University Medical Center, HCMC, there were 53 intussusceptions of 52 patients on CT (EI: 14_26%, IC: 39_74%). 33 of those have intussusception on surgery (EI: 10_3%, IC: 23_70%). Mean length of intussusceptions of both groups is 7,6±4,0cm (2,4-19,6). Mean diameter of intussusceptions is 4,7±1,1cm (2,2-7). Mean interposed fat thickness is 1±0,6cm (0,1-2,6). CT and surgery characteristics of patients in EI group are of minor differences. Ratio of AI on CT with obstruction and with ischemia_necrosis are both 3,8%. Outcome of diagnosing complications by CT and by surgery are comparable. Characteristics capable of predicting presence of insstususception on surgery are: in EI group: lead point, length > 6cm, interposed fat thickness > 0,5 cm; in IC group: length > 5.65 cm, interposed fat thickness > 0,75 cm. Conclusion: Characteristics capable of predicting presence of insstususception on surgery are: lead point, length, interposed fat thickness. Key words: Computerized Tomography (CT), Intussusception, obstruction, enteric ischemia, lead point.
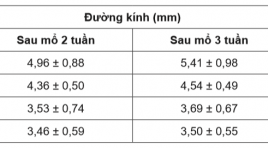
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm siêu âm đường thông động tĩnh mạch bên tận ở cẳng tay trên bệnh nhân suy thận lọc máu chu kỳ
30/03/2020 21:59:47 | 0 binh luận
Ultrasound characteristics of side-to-end arteriovenous fistula at forearm in chronic renal failureforperiodical hemodialysis SUMMARY Objective: To assess ultrasound characteristics of radiocephalic fistula at 2 and 3weeksafter operation in chronic renal failure with periodical hemodialysis. Methods: This study was conductedon 34 patients with indication of periodical hemodialysis due to chronic renal failure from April, 2016 to July, 2017 at Hemodialysis Department in Hue Central Hospital. These patients were operated to createside-to-end radiocephalic fistula at forearm and examed with ultrasound at week 2 and 3after operation. Results : The mean age was 45,79 ± 14,59 (mean ± SD); 47,10% male and 52,90% female patient. Diabetes was presented in 5,88% of the patients. The mean diameter of vein was 4,96 ± 0,88 mm at week 2 and 5,40 ± 0,99 mm at week 3 (p < 0,05);venous flow volume was 531,33 ± 162,40 ml/p and 666,56 ± 260 ml/p at week 2 and 3, respectively (p < 0,05). The rate of mature fistula at week 3 after operation was 82,35%. Most of the fistula complication was stenosis at the arterio-venous anastomosis and the draining veins. Conclusion : Ultrasound can assess the flow through arteriovenous fistula, detect several early complications which cause abnormal fistulas and help formanagement and treatmentof patients. Key word: radio-cephalic fistula, periodical hemodialysis.
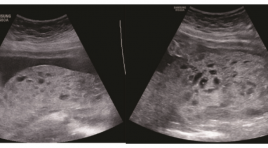
Loạn sản trung mô bánh nhau: Báo cáo trường hợp
30/03/2020 23:14:49 | 0 binh luận
Placental mesenchymal dysplasia: case report ABSTRACT: Introduction : Placental mesenchymal dysplasia (PMD) is a rare vascular anomaly characterized by mesenchymal stem villous hyperplasia. it is important to distinguish PMD from partial hydatidiform mole or a twin pregnancy with a normal fetus and coexistent complete mole and placenta mosacism due to the completely difference in prediction and prognosis. It is also crucial to manage PMD because the association between this problem and severe pregnancy outcomes. Case report : 02 outpatient PMD cases was diagnosed and monitored at Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Hue University Hospital during pregnancy. The placental histopathologic and grossly findings correspond to the diagnosis of PMD and the prenatal ultrasound findings. The results was similar with other publications worldwide. There was no severe pregnancy outcomes on two pregnant woman, but 1 of 2 fetus was suspected intrauterine growth restriction. Conclusion: It is necessary to evaluate morphology carefully to make a sutable diagnosis. Amniocentesis should be thought. PMD relates to some pregnancy outcomes, however it is a benign disease so we should evaluate carefully the fetal growth and pregnancy outcomes. Keywords : Placental mesenchymal dysplasia, fetal growth, pregnancy outcomes.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












