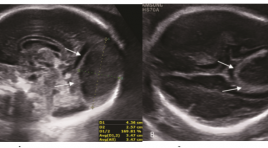
Huyết khối nội lưu các xoang tĩnh mạch màng cứng tổng quan và báo cáo ca
30/03/2020 23:06:20 | 0 binh luận
Dural venous sinus thrombosis: an overview and case report ABSTRACT: Torcular herophili is the site of the confluence of superior sagittal sinus, tranverse sinus, straight sinus and occipital sinus [1]. Anatomy of torcular herophili is highly variable. Dilatation of torcular herophili is presented as an anechoic triangular structure, with venous flow communicated with other sinuses and cerebral veins. Torcular herphili thrombosis is a rare cerebrovascular disorder[9, 11, 13, 15], and the prenatal diagnosis of this condition is difficult. This condition can be caused by the abnormalities that produce prothrombotic states, such as acute fetal distress, and congenital deficiency of anticoagulants such as antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S[8]. Prenatal ultrasound is the firs-line modality for diagnosing and monitoring thrombosis of the torcular herophili. In addition, color-Doppler ultrasound helps to differentiate this disorder from other cerebrovascular malformations such as vein of Galen aneurysmal dilatation[5] and identify the presence of collateral vessels and its relationship with other dural sinuses[6, 7]. As a complementary technique, MRI can provide additional information to rule out secondary cerebral damages and associated brain malformations. Prognosis of this disorder is highly variable, ranging from spontaneous resolution with a normal neurologic outcome to severe neurologic deficits and death. We present 1 case of thrombosis of ectatic torcular herophili with serial sonographic and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations, along with review of literature of this condition. Besides, we have a routine follow-up of the new-born mental development until now. Keywords : thrombosis, torcular herophili, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Method: case-report, prospective study from July 2017 until now.
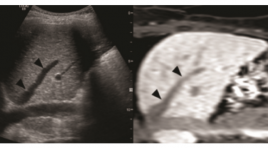
Kỹ thuật kết hợp hình ảnh siêu âm với hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính hoặc cộng hưởng từ
30/03/2020 22:56:08 | 0 binh luận
Fusion imaging of ultrasonography with CT or MRI ABSTRACT: Fusion imaging of ultrasonography with CT or MRI is the technique that creates hybrid images of two imaging modalities and combines advantages of ultrasound such as dynamic real-time imaging with advantages of CT of MRI such as high spatial and contrast resolution. The fusion imaging of ultrasound with other imaging modalities is a recently developed technique of this decade and expected to establish new and useful application in clinical practice. Key word: Fusion imaging of ultrasonography with CT or MRI
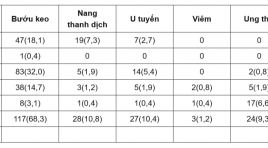
Đánh giá các thương tổn dạng nốt tuyến giáp theo phân độ TIRADS 2017
30/03/2020 22:45:43 | 0 binh luận
Research value of ultrasonographic and TIRADS 2017 classification as ACR (American College of Radiology) SUMMARY Purposes : Describe imaging characteristics and stratify TIRADS 2017 as ACR. Materials and methods : There are 259 consecutive patients with thyroid nodules on ultrasound. All of them were undergone operation with pathology after surgery. Results : The average age is 42,8 ± 12,2 years old and female/ male=10/1. Histopathology results after surgery, thyroid cancer 9,3%. The solitary nodules are the highest ratio (65,8%). Most lesions are over 25 mm in size. TIRADS 3 is the highest (40,2%) and the least is TIRADS 2 accounts for 0,4 %. TIRADS 2017 classification and pathology indicates strong evidence with p < 0,05. Conclusion :TIRADS 3 is the highest (40,2%) and TIRADS 2017 classification and pathology indicates strong evidence with p < 0,05. Key word: Thyroid nodule, TIRADS classification
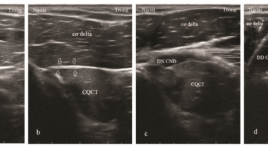
Siêu âm với tần số cao khảo sát phân nhánh thần kinh vận động của thần kinh cơ bì chi phối cơ nhị đầu cánh tay: Từ vị trí tách nhánh đến phân bố trong cơ
30/03/2020 22:19:02 | 0 binh luận
High-frequency ultrasonography for the motor branchesof the musculocutaneous nerve innervating biceps brachii: from the branching location to the distribution in the muscle SUMMARY Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the ability of high-frequency ultrasonography in examing the motor branches of the musculocutaneous nerveinnervating biceps brachii in the correlation with anatomical and histological knowledge. We analysed the location where they exit the main nerve trunk, penetrate the muscle epimysium and distribute inside the muscle. Methods: Sixteen healthy volunteers (eight males and eight females, ages 20-60, mean age 35) were examined on both sides of the musculocutaneous nerves and their branches innervating biceps brachii. The 5-18 MHz and 16-23 Mhz multi-frequency transducers along with the latest high-resolution ultrasound systems were used to examine the musculocutaneous nerves slowly and continuously in cross section from the coracoid process of the scapula to the elbow. By analyzing the nerve bundles inside the musculocutaneous nerve and the epimysium of biceps brachii, we observed the position where one nervebranch separated from the main trunk of the nerve, penetratedthe epimysium and distributedinside the muscle.Blood vessels were distinguished with nerves by Doppler ultrasound and compression method. Results: One right arm of a 28-year-old womanwas found with the absence of the musculocutaneous nerve and the median nerve give the motor branches to the biceps brachii. Thirty one musculocutaneous nerves and their motor branches to biceps brachii muscles were detected on ultrasound. Inside the muscle, the nerve branches were located in the hyperechoic bands while the surrounding muscular tissue was hypoechoic. In these hyperechoic bands, the nerves were identified because of hypoechoic structure and thicker than the thickness of the bands. The blood vessels were also foundin these bands. The minimum diameter of the nerve branches inside the muscles can be seen as 0.3 mm. Conclusion: High-frequency ultrasonography can examine very small nervestructure, detemine the position where the motor branches exit from the maintrunk of the nerve, penetrate the muscle epimysium and branching inside the muscle. Keywords : ultrasound, motor branch of the nerve, intramuscular nerve distribution, musculocutaneous nerve, biceps brachii muscle
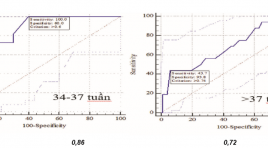
Nghiên cứu giá trị của siêu âm doppler trong tiên lượng tình trạng sức khỏe của thai ở thai phụ tiền sản giật
30/03/2020 22:11:27 | 0 binh luận
Value of doppler ultrasonography in predicting fetal well-being in pregnant women with preecclampsia SUMMARY Background: .Study on the value of some ultrasound explorations in predicting fetal well-beingin pregnant women with preeclampsia and to compare the effectiveness of different Doppler indices in predicting fetal well-being in pregnant women with preeclampsia. Methods : Study on153 patients with pre-eclampsia at Obs. & Gyn. Department - Hue Central Hospital were taken by an prospective cohort study from 12/2012 to 2/2016,. Results: Cut-off value of UTA RI for IUGR and fetal distress prediction at gestational age of 34-37 weeks was 0.6. The UTA S/D ratio cut-off value of 2.6 for fetal distress prediction at gestational age of 34-37 weeks had the sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 60%. Fetal distress prediction using UMA RI at gestational age of 34-37 weeks with cut-off value of 0.64 had the sensitivity of 90.9%, at gestational age above 37 weeks with cut-off value of 9.75 had the sensitivity of 100%. Cut-off values for UMA RI for IUGR prediction at gestational age of 34-37 weeks was 0.74 and at gestational age above 37 weeks was 0.76. Conclusion :The study found the cut-off values of PI, RI, S/D ratios of the UTA, UMA andMCA to predict fetal distress, IUGR in preeclampsia to help clinicians determine the most appropriate management to reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality rates.The study also compared the effectiveness of different Doppler indices in predicting fetal well-being. Key words : Doppler ultrosound,uterine Doppler, fetal distress, preeclampsia, IUGR
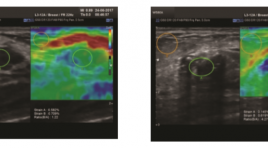
Nghiên cứu giá trị siêu âm đàn hồi bán định lượng (SEMI-QUANTITATIVE) trong chẩn đoán u vú
30/03/2020 22:04:54 | 0 binh luận
Research Value of Strain Elastography (Semi-quantitative) in Breast Tumor Diagnosis. SUMMARY Objective : Combined B-mode ultrasound and Strain Elastography Imaging (Semi-quantitative) which calculates the cutoff value of Strain Elastography in diagnosis of benign /malignant breast tumor. Method : Patients with breast tumors were combined B-mode breast ultrasound, using the WS80A equipment (Samsung), and Strain Elastography (Semi-quantitative), followed by Tsukuba-score and Ratio (B/A) (A= tumor lesion, B = fatty tissue above the lesion). From that, evaluated the accuracy, specificity, positive predictive value, accuracy and cut-off values of the Strain Elastography for diagnosis of benign/malignant breast tumors. Results : 93 women with breast tumors (67 benign tumors, 26 breast cancers), diagnosed by cytology and histopathology. The average rate of semi-quantitative in malignant and benign tumors compared to fat tissue respectively was (4.73 +/- 2.45) and (1.85 +/- 0.92). The area under the ROC curve is 0.92. The cut-off value was (2.43) has the highest sensitivity (88.5%) and the specificity (82.1%) in the diagnosis of malignant tumors. Positive predictive value (92.8%), accuracy (82.3%). Conclusion : Using Strain Elastography to measure the elasticity ratio of the breast tumor compared to fat tissue, with a cutoff values (2.43), with high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosis of benign /malignant breast tumor, which complements the breast Birads categories classification. Key words: Strain Elastography (SE), Semi-quantitative, benign /malignant breast tumor, Tsukuba-score , Ratio (B/A).
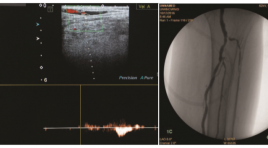
Đặc điểm hình ảnh siêu âm doppler và giá trị bổ sung của chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền trong chẩn đoán hẹp, tắc động mạch chi dưới
30/03/2020 21:49:42 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics of doppler ultrasound and complementary value of digital subtraction angiography in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial occlusive disease of lower extremity SUMMARY Objectives: Describe imaging characteristics of doppler ultrasound (DUS) and evaluate the complementary value of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) of lower extremity. Materials and Methods: The study is a cross sectional one and was carried out at the hospital of Hue university of medicine and pharmacy. 40 patients diagnosed with PAOD of lower limbs went through arterial assessment with DUS and DSA. The image findings of both technique were used to evaluate the diagnosis accuracy of DUS and the complementary value of DSA. Results: The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of DUS in PAOD is 80,65%, 92,83%, 86,21% and 89,61% respectively. DSA complemented for DUS with 6,36% additional cases of >50% stenosis or complete occlusion and 5,49% cases of low flow in occlusion suspected arteries. DSA revealed an additional of 81% collaterals in occluded arteries compared to DUS. Conclusion: DUS has high diagnostic value in PAOD of lower extremities. DSA has high complementary value for DUS in the diagnosis of PAOD of lower extremities, with the highest value at below-knee arteries. Keywords: peripheral arterial occlusive disease, doppler ultrasound, digital subtraction angiography.
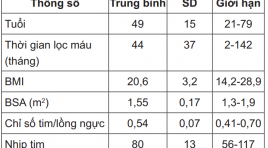
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm siêu âm tim ở bệnh nhân lọc máu chu kỳ tại bệnh viện 175
01/04/2020 16:26:53 | 0 binh luận
The evaluation of cardiac morphology and function on echocardiography of patients post dialysis at 175 Hospital SUMMARY Studies in 101 patients with these degree of kidney failure and dialysis several times, we can see the changes occurring in heart can see when echocardiography: The morphologic changes of heart, showing the dilate slight of left ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle wall thickening, increased heart muscle mass. There are signs of diastolic dysfunction on doppler ultrasound, that saw earlier by tissue doppler imaging (Em, Em / Am ...) but not affecting systolic function. There are changes in cardiac morphology and function between the dialysis groups over time towards improving. Keywords: Renal failure, dialysis, echocardiography.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












