Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán chảy máu não thất
01/04/2020 15:50:40 | 0 binh luận
The role of CT-Scanner in diagnosis of intraventricle hemorrhage SUMMARY Objective : To describe the feature of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) image in CT scanner and beginning describe some reasons related to IVH in adults. Methods: In a cross - sectional using quantitative methods, we chose 52 patients who definitive diagnosed IVH by CT scan in Bach Mai hospital from August/2014 to September/2015. Results: The most common location hematoma in primary parenchyma is hippocampal central gray (55.55%), the most common location of IVH is occipital horn ventricular, the more greater hematoma size, the more high risk of poor prognosis, the more higher level of IVH, the high risk of poor prognosis. In people over 50 years old, the most common causes of IVH is hypertension and hypertension coordinate with other causes (51%),while people under 50 years old, they usually caused by vascular abnormalities (30%), the main causes of thalamus lobe bleeding and hippocampal central gray bleeding is hypertension (25%), lobe of brain bleeding caused by aneurysm (42.86%). Conclusion: When patients are diagnosed stroke, they must be take CT scanner image immediately, when the results showed IVH image, they must be take cerebrovascular CT scanner with multiple array receiver, with intravenous injection of contrast dye to initially find the causes. Key words: CT scanner, intraventricular hemorrhage, cause.
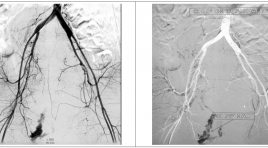
Chảy máu sau đẻ do tổn thương động mạch thẹn trong nguyên nhân hiếm gặp: báo cáo nhân 1 trường hợp
01/04/2020 14:18:39 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY A secondary postpartum hemorrhage may occur between 24 hours and 6 weeks after the birth. Secondary postpartum hemorrhage may be caused by endometritis, damage to an artery in caesarean, possible as a result of abscess from puerperal infection that causes damage to blood vessel. The urterine artery lesion is the most common, the internal pudental artery lesion is very rare. We report a case of a 36 year old patient, bleeding 12 days in postpartum due to damage to the internal pudendal artery, successful embolization of the internal pudendal artery. Keyword: Secondary postpartum hemorrhage, embolization, uterine artery, internal pudendal artery.
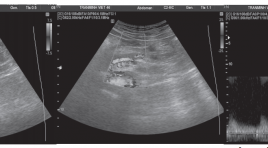
Bóc tách động mạch mạc treo tràng trên đơn độc chẩn đoán và điều trị
01/04/2020 14:15:33 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARRY Isolated superior mesenteric artery (SMA) dissection, with no other abnormality or aortic dissection, is unusual. Diagnosis base on the aid of Doppler and 64-slice multidetector CT. We report two cases of isolated spontaneous SMA dissection without aortic involvement in two patients who had presented with epigastric pain that was especially worse after food intake. Examen on 64-slice multidetector CT show an isolated SMA dissection, not involving the aorta. These patients were managed conservatively with anticoagulants. Keyword: Isolated superior mesenteric artery.
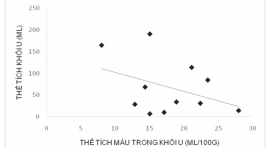
Đánh giá các chỉ số tưới máu trong ung thư phổi trên chụp cắt lớp vi tính tưới máu
01/04/2020 14:06:24 | 0 binh luận
Assessement changing in haemodynamics and contrast enhancement pattern of lung cancer lesions on perfusion CT SUMMARY Introduction : Lung tumour perfusion CT may help to evaluate characteristics and haemodynamics of lung cancer. This research was carried out to assess changes in haemodynamics and contrast enhancement pattern of lung cancer lesions. Methods: 12 patients were enrolled to the study underwent perfusion CT of lung tumour. Perfusion paramerters were obtained from perfusion CT maps. Results: perfusion paramerters increased in malignant tumour with measured blood flow of 33.15 ±15.7 ml/100g/min, blood volume of 17ml/100g and tumour volume ranged from 7 – 577ml. blood volume in small tumours was higher than that in larger lesions. The higher homogeneity in blood flow was found in small tumours. Conclusion : Lung tumour perfusion CT could be used to assess changes in tumour haemodynamics that may help in pretreatment of unresectable lung cancers. Keyword: Lung cancer, perfusion.
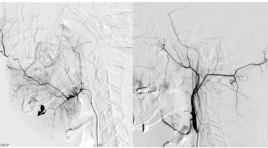
Điều trị ho ra máu cấp tính bằng nút động mạch phế quản và ngoài phế quản sử dụng phối hợp 2 loại vật liệu nút mạch
01/04/2020 14:01:43 | 0 binh luận
Bronchial artery charateristics and patient outcome in patients with acute hemoptysis treated using dual embo-agents SUMMARY Objectives : This study was carried out to describe angiographic charateristics and patient outcome in patients with acute hemoptysis treated using dual embo-agents Methods: 28 patients with acute hemoptysis were included in this study. All abnormal vessels were occluded using microsphere then re-enforced with N-butyl cyanoacrylate (NBCA). Patients were followed-up one year from procedure date. Results: Technical success rate accounted for 96.4%. Almost all patients presented with bronchial artery dilatation while 46% of patients had abnormal feeding vessels arising from subclavian artery, 39% from intercostal arteries. Postprocedural complications included chest pain (4 cases, 14.3%), infection (1 patient, 3.6%), unexpected vessel occlusion (1 case, 3.6%) and bronchial artery dissection (1 subject, 3.6%). Recurrent rate calculated in one year of following up was 7.14%. Conclusion: Major angiographic abnormalities were dilatation of the bronchial artery to lung lesions and its colaterals. Dual-material embolization is an effective treatment method with significantly high rate of technial and clinical success. Keyword : Hemoptysis, bronchial artery, embolization.
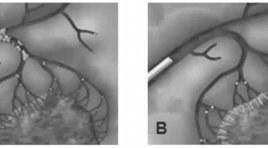
Đánh giá hiệu quả nút mạch điều trị chảy máu hàm mặt do chấn thương
01/04/2020 13:55:36 | 0 binh luận
Evaluation the effectiveness of arterial embolization in the treatment of maxillofacial trauma SUMMARY Purpose: This study was designed to characterize image of vascular lesions on DSA and evaluate the effectiveness of arterial embolization in the treatment of maxillofacial trauma. Materials and Methods: 44 patients with bleeding after jaw injury, did not meet with the local hemostatic measures who were taken to the angiography for embolization from April 2011 to September 2015. Results: 13.6% of the internal carotid artery injury with 4.5% of dissection and 9.1% of carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. 90,1% of the external carotid artery injury, the (internal) maxillary artery is the most vulnerable (in 88.6%) that the maxillary artery injury merely in 56.8% or combination in 31.8%. The external carotid artery injury of a side in 59.1%, 40.9% of two side. Active bleeding is the most common of injury morphology (88,6,6%), with 63.6% merely, and associated with other forms 25%, (pseudoaneurysms, arteriovenous malformation, the internal carotid artery injury), pseudoaneurysm merely is a rare lesions in 2.3%. Hystoacryl is the most common embolization material (86.3%), 59.1% of Hystoacryl merely and coordinate 13.6%. PVA embolization merely in 13.6%; Spongel in 13.6%; no circumstances used to try Coil. Technical success was 95.4%, 4.6% failed. Successful hemostasis was achieved in 95.4% after the first intervention and 100% after 2nd intervention. Clinical success was achieved in 79.6%. Clinical non-success included 7 patients died of severe traumatic brain injury (15.9%) and 2 patients (4.5%) had complications, including 1 patient with face necrosis and 1 patient with tongue necrosis. Conclusion : Arterial Embolization in the Treatment of Maxillofacial Trauma was effective and quick to control bleeding. Keywords: bleeding, maxillofacial trauma, Embolization.
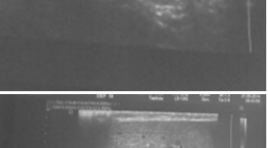
Đặc điểm hình ảnh siêu âm Triplex trong chẩn đoán xoắn tinh hoàn tại bệnh viện Việt Đức
01/04/2020 13:52:07 | 0 binh luận
Describe the characteristics of the Triplex ultrasound images of testicular torsion at Viet Duc hospital SUMMARY Purpsose: Describe the Triplex ultrasound imaging characteristics of testicular torsion Object and methods: Patients who have acute scrotum going to Viet Duc Hospital Emergency Sonography Department between March 2014 and September 2005, were diagnosed testicular torsion and operated. Results : 32 cases were diagnosed as testicular torsion, diagnosis after surgery is correct 100% of the cases. The mean age 19,2 ± 5,1. Sign “whirlpool” is found in 75% of cases, the common position is above the testicles 91.7%. Sign of losing the pulse signal at testicular torsion 31/32 (96.9%). Increased testicular size 27/32 (84.4%). 28/32 heterogeneous parenchyma, normal 3/32, 1/32 hypoechoic. Epididymis morphology change 25/32 cases (78.1%), of which the most common are sphere 76%. Conclusions: Triplex Ultrasonography has value in the different diagnosis of testicular torsion with other diseases causing scrotal pain. Keywords : Triplex sonography, testicular torsion.
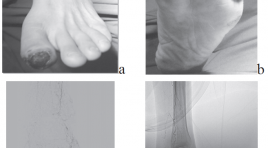
Nghiên cứu tương quan tổn thương động mạch trên chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền với vị trí, mức độ thiếu máu bàn chân trầm trọng
01/04/2020 13:49:07 | 0 binh luận
The correlation between arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography with location and level of critical foot ischemia SUMMARY Purpose: Description characterization critical ischemia and foot arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography. Description correlation between arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography with location and level of critical foot ischemia. Meterials and methods : 44 patients (28 male and 16 female) with the mean age of 69.3 years, with critical foot ischemia taken DSA from 8/2015 to 8/2012. Description research with prospective and retrospective. The correlation coefficient r and p significance is calculated by Spearman’s method. Results : In 111 critical ischemia regions: 45.95% belong to the posterior tibial artery, 33.33% anterior tibial artery, 20.72% peroneal artery. In 111 critical ischemia regions: 63.97% in the toes, 5.4% feet, 30.63% heel and lateral- anterior ankle. In 44 limbs: 22.7% having 1 critical ischemia regions alone; 34.1% with 2 region and 43.2% with ≥ 3 regions. In this number: 25% limbs with heaviest stage in rest pain, 61.36% in minor tissue loss and 13,64 % in major tissue loss. In 264 arteries: 46.05% with stenosis < 50% and 26.14% total stenosis with ≥ ½ in length. In 129 arteries with stenosis ≥ degree of 3: 28.68% belong to dorsal pedis artery, 48.06% branches from posterior tibial artery, 23.26% branches from peroneal arteries. The correlation coefficient r and significance p between foot arterial lesion and the level of critical foot ischemia, respectively: r from 0.755 to 0.891, all significance p <0.001. Keywords: Critical lower limb ischemia, angiosome of foot, variant anatomy foot artery.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












