Đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ 1.5T trong phân loại giai đoạn ung thư cổ tử cung
06/05/2021 16:59:10 | 0 binh luận
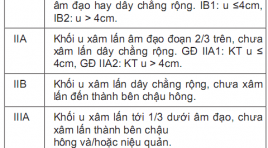
SUMMARY A prospective descriptive study of 47 cervical cancer patients, were taken 1.5T MRI before surgery, and has result pathology after surgery in the Ha Noi Oncology hospital. Results: The min and max ages are 32 and 69, the average age is 52,1 ± 10,0. Squamous-cell carcinoma 89,4%, Adenocarcinoma 10,6%. 100% mass shows a slightly hyperintense in T2-weighted MR image, 94,2% shows a isointense in T1W, 97,1% shows a hyperintense in Diffusion (b800), 97,1% T1FS-weighted MR image shows poorly absorbed drugs for muscle fiber uterus after injection, 61,8% heterogeneous infiltration strong enhancement of the tumor. Assess tumor size has Acc 85,3%. The rating invasive vaginal has Se 100%, Sp 100%, Acc 100%, PPV và NPV 100%. Invasive parametre has Se 95,2%, Sp 96,2%, Acc 95,7%, PPV 95,2% và NPV 96,2%. Diagnosed lymph node metastases with Se 100%, Sp 97,8%, Acc 97,9%, PPV 66,7% và NPV 100%. Staging of the MRI 1.5T has Acc 95,7% Conclusion: Image 1.5T MRI on observable clarity T2WI, DWI before the injection and T1FS after the injection contract. 1.5T MRI has high value for staging Cervical cancer. MRI should be used routinely for staging Cervical cancer. Keyword: Cervical cancer, MRI of cervical, staging cervical cancer.
Đánh giá kết quả điều trị rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng nội sọ ngoài vùng xoang hang bằng can thiệp nội mạch có sử dụng bóng chẹn bảo vệ
06/05/2021 16:21:45 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: To evaluate the apply the transvenous balloon protection in endovascular intervention of non - cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Material and methods: The uncontrolled interventional study was conducted in Radiology center at Bach Mai hospital from January 2017 to August 2020. 15 patients with non - cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula underwent endovascular treatment using transvenous balloon protection. Results: 15 patients were treated in 18 procedures. Among these, there were 7 males and 8 females, mean age was 48.2 ± 14.82 years. Most non - cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas were located at the transverse - sigmoid sinus (76,5%). According to the Cognard classification, Cognard IIa accounted for 47%, Cognard IIb accounted for 17,6%, Cognard IIa+b accounted for 29,4%, and Cognard IV accounted for 5,9%. Most fistulas presented with multiple feeding arteries, the most common artery was middle meningeal artery. With 18 procedures underwent tranvenous balloon protection, the sinus protection was achieved in 17 out of 18 patients. 86,7% of these patients had complete occlusion of fistula, whereas partial occlusion occurred in 13,3% of these patients. After treatment, 86,7% of these cases didn’t have complication, complete symptom remission rate was 53,3%, 26,7% showed symptom relief. Only 1 case had severe complication, accounted for 5,6%. Conclusion : Endovascular intervention using transvenous balloon protection is a safe and effective technique in the treament of non - cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Key words: dAVF, endovascular intervention, transvenous balloon protection.
Nghiên cứu giá trị của cộng hưởng từ với thuốc đối quang từ primovist trong chẩn đoán ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan
06/05/2021 14:48:38 | 0 binh luận
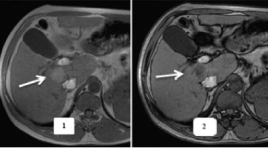
SUMMARY Aim: Evaluate the value of MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA (Primovist) in the detection of HCC comparison with the pathological results Methods : Descriptive cross-sectional research, performed on 28 patients consist of 2 groups: Group I includes 18 patients with HCC and group II includes 10 non-HCC patients (7 patients with focal nodular hyperplasia. 3 patients with liver metastasis). The patients whose liver lesion were detected on diagnostic imaging modalities undergone MRI with hepatiobillial specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA (Primovist). Thereafter, definite diagnosis was based on histopathological results of biopsy or surgery. Results: Hepatobiillial phase hypointense was the most sensitive diagnostic criteria of HCC(94.4%), however, specificity is only 70%. For liver cancer diagnosing, arterial enhancement followed by washout on portal venous or late phase had the sensitivity, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy were 61.1%, 58.8% and 75%, respectively. When combining with hepatobillial phase hypointense, these values increased to 72.2%, 67.7%, and 82.1%, respectively; while, the specificity and positive predictive values were unchanged. Conclusion: Hepatobiillial phase hypointense is a good diagnostic criteria on detection of HCC than differential diagnosis with other hepatic lesions. The addition of hepatobiillial phase on MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA (Primovist) increases the likelihood of detecting HCC lesions.
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm búi giãn tĩnh mạch dạ dày ở bệnh nhân xơ gan trên hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính đa dãy để chỉ định can thiệp PARTO
06/05/2021 12:58:38 | 0 binh luận
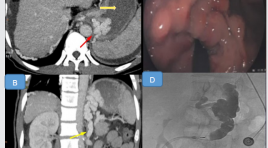
SUMMARY Esophageal varicose veins are the main cause of high GI bleeding in cirrhotic patients. Plug – assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration (PARTO) is a safe, minimally invasive, effective hemostasis technique and prevent recurrence in gastric variceal hemorrhage/ gastric varices that has been widely deployed in many countries such as Japan and Korea. Multislice Computer Tomography (MSCT) that provides complete information about the features of gastric varicose buns is the method that should be performed prior to PARTO intervention. Objectives: 1. Characterization of gastric varicose buns on multiseries computed tomography and Kiyosue classification. 2. Comparing multi-sequence computed tomography with DSA image of gastric varicose tufts in patients with PARTO retrograde intervention. Methods : The study was conducted retrospectively and with crosssectional descriptions of 91 patients with cirrhosis and gastric varices admitted to the hospital because of gastrointestinal bleeding were taken MSCT in the period from April 2018 to July 2020. Conclusion : Among 91 cases of gastric varices; the majority of gastric veins dilated to an average of 5-10 mm (51 patients), supplied mainly from the left gastric vein (84 patients) and drained to the esophageal veins (60 patients). The diameter of the dilated gastric vein measured on the MSCT was correlated with the number of afferent portal venous feeders and not with the number of efferent systemic venous drainage. The major gastric varicose tufts fall under the type 2B classification (~ 22%). Out of 91 cases, there were 58 cases with gastrorenal shunt, 2 cases with gastrocaval shunt, of which 21 cases of severe gastrointestinal bleeding required PARTO intervention; There were 2 cases where there was no renal shunt but had severe gastrointestinal bleeding, PVTO. For the PARTO intervention group, the renal shunt diameter measured on CLVT and measured on the DSA did not differ with p = 0.083. Results: The gastric varicose buns is mainly supplied with blood from the left gastric vein, and drained by the esophageal vein and the kidney shunt. Examination of imaging of gastric varicose buns is necessary to determine whether PARTO is indicated, to select the right materials and to effectively predict of PARTO interventions. Keywords: xơ gan, giãn tĩnh mạch dạ dày, can thiệp ngược dòng qua shunt vị thận bằng dù /cirrhosis, gastric varices, Plug – assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration.

Giá trị của thang điểm EU-TIRADs 2017 và ACR-TIRADS 2017 trong đánh giá nhân tuyến giáp
06/05/2021 12:41:10 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective : Characteristic of thyroid nodules according to EU-TIRADS 2017 and ACR-TIRADS 2017 classification. Comparison among EUTIRADS and ACR-TIRADS in the diagnostic efficiency of thyroid nodules. Subject and methods : descriptive cross-sectional study was performed on 233 patients with thyroid nodule who were diagnosed with ultrasound and performed FNA at Dien Quang Center, Bach Mai Hospital from 8/2019 to 8/2020. Results: 233 patients in study with 233 thyroid nodules, 79 nodules with malignant cells (33.9%), 154 nodules had no malignant cells (66.1%). Malignant nodule are mainly solid nodule (97.5%), 100% sponges and follicles do not have malignant cells. Hypoechoic solid and irregular margins had high sensitivity and specificity (>70%) in diagnosing malignancies. Very hypoechoic solid and microcalcification has a 100% specificity in diagnosing malignancies. There is a statistically significant difference in malignancy between the nuclear group of thyroid with height> = width and height <width. ACR-TIRADS classification has sensitivity 96.2%, specificity 53.9%, PPV 51.7%, NPV 96.5%, accuracy 68.2% . EU-TIRADS classification sensitivity 87.3%, specificity 71.4%, PPV61.1%, NPV 91.7%, accuracy 76.8%. Conclusion: ACR-TIRADS and EU-TIRADS classification are well diagnostic efficiency in the diagnosis of malignant and benign thyroid nodules. The ACR-TIRADS classification has a higher sensitivity but less specificity than the EU-TIRADS classification. Key words: thyroid ultrasound, EU-TIRADS classification, ACRTIRADS classification.
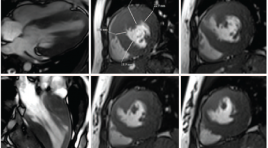
Khảo sát đặc điểm hình ảnh bắt thuốc thì muộn trên cộng hưởng từ của bệnh cơ tim phì đại
06/05/2021 11:33:36 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To describe the characteristics of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy on Magnetic resonance imaging; to evaluate the loacation, pattern and extent of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE); to evaluate the relationship among left ventricular function, end diastolic wall thickness and LGE about pattern and extent. Materials and Methods: Cine imaging and delayed enhancement imaging were performed in 27 patients with HCM on a 3 Tesla MRI unit (Siemens Verio) at the University Medical Center Hospital between January 2016 and June 2020. Global left ventricular function was quantified, using a Argus function software of Siemens Healthineers. The location, pattern, and extent of DE were evaluated. Results: Global left ventricular function and mass calculations yielded a mean ± SD for ejection fraction of 64.8 ± 11.7%, an end-diastolic volume of 111.5 ±27.2ml, and a left ventricular mass of 181.4 ± 96.2g. Diffuse hypertrophy was present in 12 patients (44.5%), asymmetric septal hypertrophy in 11 patients (40.7%), and apical hypertrophy in 4 patients (14.8%). LGE occurred in 24 patients (88.9%) and in 164 segments (33.7%), most commonly in the anteroseptal and inferoseptal segments. LGE was detected in an ill-defined patchy pattern in 61.6% and in a focal nodular pattern in 38.4% enhanced segments. LGE with an extent ≥ 50% was observed in 61 segments (37.2%), and that with an extent < 50% was observed in 103 segments (62.8%). There were significant difference in EF between the LGE-positive patients and the LGE-negative patients (p = 0.03). The myocardial wall was thicker in the enhanced segments than in the non-enhanced segments (p < 0.001). No significant difference was found in wall thicker of segments between ill-defined patchy pattern and focal nodular pattern in our study. The enhanced segments with the transmural extent ≥ 50% were thicker than non-enhanced segments and the enhanced segments with an extent < 50% were thicker than nonenhanced segments at end-diastole and at end-systole (p < 0.01). Conclusion: Cardiac MR imaging is beneficial in making a diagnosis and determining the phenotype of HCM because it can observe the cardiac morphology clearly and evaluate its function comprehensively. It is possible to accurately measure the wall thickness, detect high-risk phenotypes and determine myocardial fibrosis based on late myocardial enhancement. Therefore, it is necessary to perform cardiac MR imaging in patients with HCM or suspected HCM on clinical examination. Keywords: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, late gadolinium enhancement

Bài giảng trực tuyến khóa học Cắt Lớp Vi Tính Hai Mức Năng Lượng ứng dụng và thực hành T8-T10.2020
05/11/2020 15:58:31 | 0 binh luận
Ban tổ chức chương trình đào tạo trực tuyến xin gửi tới quý bạn đọc các video buổi học của khóa "Ứng dụng CLVT hai mức năng lượng ứng dụng và thực hành "
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"













