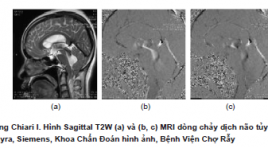
Ứng dụng lâm sàng kỹ thuật cộng hưởng từ tương phản pha (PC-MRI) trong đánh giá động học dòng chảy dịch não tủy
05/12/2019 09:46:10 | 0 binh luận
Clinical application of phase contrast mri technique in the evaluation csf flow dynamics SUMMARY Phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI) recently used as a reliable method for evaluating both qualitative and quantitative CSF flow. Phase-contrast MRI has often been used for the evaluation of normal pressure hydrocephalus, communicating and non-communicating hydrocephalus, arachnoid cyst, Chiari I malformations and syringomyelia, response to endoscopic third ventriculostomy and ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VP-shunt). This review introduces: the PC MRI technique, CSF physiology and cerebrospinal space anatomy, to describe a group of congenital and acquired disorders that can alter the CSF dynamics. Keywords: Phase contrast MRI, CSF flow, hydrocephalus, Chiari I malformation, syringomyelia
Tiến bộ kỹ thuật cộng hưởng từ trong đánh giá u tế bào đệm
04/12/2019 20:45:31 | 0 binh luận
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of glioma SUMMARY Glioma is the most common primary cerebral tumor which has a poor prognosis, high disability and fatalityespecially in high grade gliomas. The current standard of imaging technique for evaluating glioma is conventional MRI. Basic cMRI sequences are T1W, T2W, FLAIR, T1W+Gd. Conventional MRI provides critical clinical information about gliomas. Unfortunately, conventional MRI is nonspecificity, not reflect the complicated biology, has a limited capacity to grading and differentiate gliomas from other pathologies such as: inflammation,MS… Recently, there is a development of many new MRI techniques and these application have increased such as diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion-tensor, tractography, perfusion, spectroscopy and functional MRI. These techniques provided complementary information to cMRI for assessing tumor in cellularity, white matter invasion, hypoxia, necrosis, vascularization, permeability and relation tumor with functional areas. They give more accurate in diagnosis, planning pre-surgery and monitoring post-therapy. This lecture introduces an principle and clinical application of these advanced MRI techniques in cerebral gliomas which were performed at Choray hospital. Keywords : Glioma, conventional MRI, diffusion-weighted, diffusion-tensor, tractography, perfusion, spectroscopy, functional MRI.
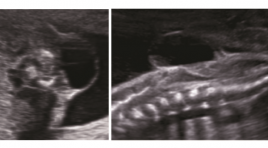
Chẻ đôi đốt sống thể kín: Báo cáo loạt ca
30/03/2020 22:50:48 | 0 binh luận
Closed spina bifida: Case series report ABSTRACT: Introduction : Imaging of closed spina bifida is very multiform, can diagnose in utero. Objective: Describe the imaging features of closed spinal bifida, classify the usual closed spina bifida. Methods: case series report, prospective study Conclusions: The important role of ultrasound in prenatal closed spinal bifida diagnosis. Identify the cranial sign and spinal defection to classify the type of closed spina bifida, to make fetal prognosis , to orientate in antenatal counseling Key words: Closed spina bifida, Spinal dysphaphism
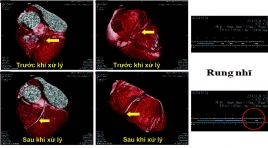
Cập nhật chụp cắt lớp vi tính trong bệnh lý tim mạch
17/03/2020 10:59:11 | 0 binh luận
CT scan of cardiovascular disease: An update SUMMARY Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, in developing countries, coronary artery disease is rising rapidly. It’s been projected that by 2020, chronic diseases will account for almost three-fourths all deaths, 71% deaths due to ischemic heart disease. Early detection of coronary artery lesion helps to reduce mortality and improve quality of life by risk factors control and stabilize atherosclerotic plaques. The newest commercially available MDCT scanners offer the greatest degree of spatial and temporal resolution owing to multidetector channels, fast gantry rotation times and thinner collimation. These parameters are important to creation of high definition coronary artery MDCT imaging. In the case of acute chest pain, CT also proved safe, effective, low-cost, reduced the number of emergency visits and hospitalization. In addition to the accurate diagnosis, CT of coronary artery disease also evaluated other heart diseases such as congenital heart disease, pericardium, cardiomyopathy, heart valve New developments such as FFR-CT, iFR-CT or Myocardial perfusion assessment show that computed tomography for cardiovascular disease diagnosis will be more potential in the future. Keywords: coronary computed tomographic angiography, cardiac computed tomography, multi-detector computed tomography for cardiovascular disease diagnosis.
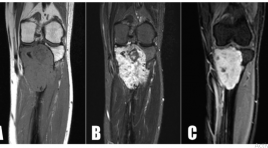
U tế bào quanh mạch nguyên phát ở xương chày - Báo cáo một trường hợp hiếm và tổng kết trên y văn
26/03/2020 22:33:38 | 0 binh luận
Primary haemangiopericytomas of tibia - a rare case report and review in litterature SUMMARY Hemangiopericytomas (HPCs) are rare vascular tumors arising from pericytes. Therefore HPCs have a wide distribution in both soft tissue and skeletal system, with the latter being the most unusual occurrence. Currently, there are about 74 cases of osseous HPC have been reported in the available English literature, only five of them located in the tibia. Primary hemangiopericytomas of bone usually occurs in pelvis, vertebrae and long bones of lower extremities. The prognosis of the tumor behaviour is still not feasible and it has the potential to demonstrate a highly malignant course. We introduce a case of primary HPCs of bone located in tibia, which received a treatment by widen resection and bone transportation. Keywords: u tế bào quanh mạch, u xương/ hemangiopericytoma, bone tumor.
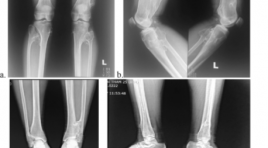
Đặc điểm hình ảnh XQUANG của tổn thương đa chồi xương có tính chất di truyền: Nhân một trường hợp
26/03/2020 22:26:41 | 0 binh luận
Imagings of hereditary multiple exostosis (hme): A case report SUMMARY Osteochondromatosis or Hereditary Multiple Exostoses (HME) is a rare disease which is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, there are many osteochondromas at the appendicular skeleton. This report presents the patient who had typical clinical and radiologic features of the disease. Female patient, 24 years old, she has a pain both lower limbs, there are slight deformity both upper and lower limbs on the examination. On the X-rays of the limbs present many osteochondromatosis at the meta-physeal regions of long tubular bone, it may be pedunculated or broad-based form, the pedunculated appearance follow the direction away from the epiphysis and towards the diaphysis follow-ing the tendon pill. With characteristic features on the plain radiology: the final diagnosis is hereditary multiple exostosis.
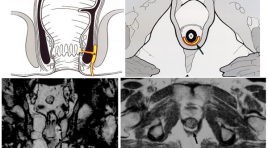
Vai trò của hình ảnh học trong nhiễm trùng quanh hậu môn
03/12/2019 14:22:51 | 0 binh luận
Áp xe và rò hậu môn là một trong các bệnh lý nhiễm trùng vùng hậu môn trực tràng khá phổ biến. Đây bản chất là 2 giai đoạn của ổ nhiễm trùng vùng hậu môn mà ở đó rò hậu môn hình thành từ những ổ áp xe cạnh hậu môn.
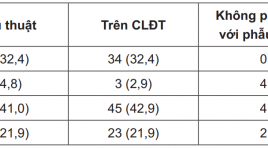
Vai trò của X quang cắt lớp điện toán trong chẩn đoán và phân giai đoạn ung thư tế bào thận
30/03/2020 15:18:30 | 0 binh luận
Role of computed tomography in diagnosing and staging of the renal cell carcinoma SUMMARY Background : Early diagnosis and accurate preoperative staging of the renal cell carcinoma are necessary to select the most appropriate treatment. Purposes : This study aims to describe the imaging characteristics and define the value of CT in preoperative staging of renal cell carcinoma. Subjecs and methods : Retro - and prospective cross section descriptive study of 105 patients in Binh Dan hospital from Dec 2012 to Apr 2015, with histologically verified renal cell carcinoma and using CT preoperatively. Imaging characteristics and staging were made by evaluating imaging obtained and compared with the operative and postoperative histopathologic results. Results : The most common location was upper 1/3 kidney (32.4%). Tumor size 41-70mm (52.4%) had the highest percentages. Tumors had constrast enhancement (100%), unsmooth margins (55.2%), intra-tumoral necrosis (91.0%), calcification (16.2%). Tumor detection in the nephrographic phase were 100%. Tumors had renal sinus fat invasion (34.3%), extension beyond Gerota’s fascia (17,1%); involvements of ipsilateral renal vein (6.7%), inferior vena cava above diaphragm (4,8%) and below diaphragm (5.7%), invasion of ipsilateral adrenal gland (1%), local lymph nodes (13.3%) and distant metastases (5.7%). Tumors had the surgical stages I, II, III, IV and then the mean tumor sizes increased 40.50mm, 63.60mm, 67.58mm, 97.01mm, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of CT to evaluate the perinephric fat invasion were 88.52%, 68.18%, 80.0%, 80.0%, 79.41%, respectively. Percentages of CT staging correlating with operative staging was 90%, in which stage I was 100%, stage IV was 91%. Conclusions : CT is still the principle basis for preoperative staging of renal cell carcinoma. Keywords : Computed tomography (CT), renal cell carcinoma.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












