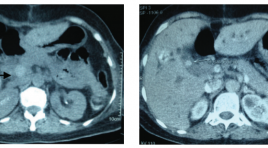
Chẩn đoán và điều trị giả phình động mạch gan sau phẫu thuật cắt túi mật nội soi nhân 1 trường hợp
02/06/2020 10:57:51 | 0 binh luận
Diagnosis and management of hepatic artery pseudoaneuryms following a laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a case report SUMMARY Hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm is a rare and potentially fatal complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy that often presents with abdominal pain, anemia, hemobilia, and liver function elevations. The authors report a case of hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm diagnosed by abdominal computed topography in a 64-year-old woman who had undergone laparoscopic cholecystectomy the previous month. Definitive treatment was angiography with embolization. Key words: Hepatic artery pseuaneurysm, embolization
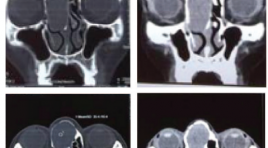
Báo cáo ca lâm sàng schwannoma mũi xoang bên phải- một trường hợp hiếm gặp và tổng kết trên y văn
02/06/2020 11:02:21 | 0 binh luận
Sinonasal Schwannoma: Case report and review in literature SUMMARY Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumours, that may occur throughout the body. Paranasal schwannomas are uncommon lesion representing less than 4% of all head and neck schwannomas. We report a case of Right Sinonasal Schwannoma in a 61-year-old woman. She admited Bach Mai hospital because of swelling of the right paranasal and bloody mucus for about 4 months. Patients underwent laparoscopic surgery, the mass was removed successfully without any postoperative complication, there was no recurrence within 8 months of follow up. Key word: Paranasal schwannomas.
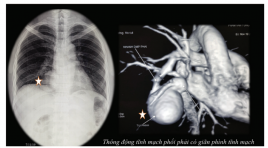
Dị dạng rò động tĩnh mạch phổi lưu lượng lớn: ca bệnh hiểm được chẩn đoán và điều trị can thiệp nội mạch
02/06/2020 11:07:52 | 0 binh luận
Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula case report: diagnosis and endovascular treatment SUMMARY Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (PAVM) are rare pulmonary vascular anomalies. Although most patients are asymptomatic, PAVMs can cause dyspnoea from right-to-left shunt. Because of paradoxical emboli, various central nervous system complications have been described including stroke and brain abscess. There is a strong association between PAVM and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Chest radiography and contrast enhanced computed tomography are essential initial diagnostic tools but pulmonary angiography is the gold standard. Contrast echocardiography is useful for diagnosis and monitoring after treatment. Most patients should be treated. Therapeutic options include angiographic embolisation with metal coil or balloon occlusion and surgical excision. We present a clinical case in a 33-year-old male patient, diagnosed with a large, single PAVM in the right lower lung with X-ray and CT scan. Patients treated with pulmonary angiography embolisation with 2 metal coil and plug14, rechecked after 6 months by magnetic resonance, computerized tomography and pulmonary angiography, complete loss of shunt stream. Clinically improved, blood gas test before intervention: pO2 64.7mmHg and SatO2 89.9% and 6 months after intervention: pO2 91.3mmHg and SatO2 96.2% . Key word: arteriovenous fistula, embolization, pulmonary vascular malformation
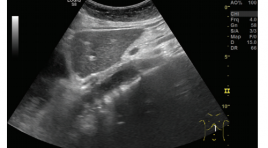
Siêu âm phát hiện giãn thực quản trong co thắt tâm vị báo cáo 3 trường hợp
02/06/2020 09:55:31 | 1 binh luận
Ultrasound imaging the dilate esophagus in achalasia reported 3 cases SUMMARY The esophagus can be divided into four sections: the neck, the thoracic, the diaphragm, and the abdominal segment. During the ultrasound examination of patients at the Department of Functional Ultrasound, we found that the sonographer could observe the images of the diaphragmatic esophagus with normal and dilated images. weirdo. Through the study of 3 cases of patients with esophageal dilatation in pathological spasms, we found that the image of esophageal dilatation on the ultrasound is: size> 20 mm, the last segment has a image that can be called "bird beak”, patients who drink water observe that the fluid in their esophagus swirling can be called a “washing machine”sign.
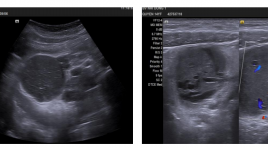
Bệnh castleman vùng bụng ở trẻ em, đặc điểm lâm sàng và hình ảnh siêu âm - báo cáo ca lâm sàng và hồi cứu y văn
02/06/2020 09:52:07 | 0 binh luận
Castleman’s disease in the abdomen in children Clinical and sonographics findings: Case report and review of literature SUMMARY Castleman’s disease, also known as angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia, is a rare benign disease, has two principal histologic types are hyaline-vascular and plasma cell types, can be unicentric or multicentric. The disease is usually detected by imaging diagnostic tools, but difficult to diagnose accurately before surgery and is easily confused with malignant disease. We present 5 cases of hyaline vascular unicentric Castleman disease in the abdomen, had been operated at Children's Hospital N01, we investigated the ultrasound characteristics and reviewed literature. Keywords : Castleman’s disease, ultrasound, in children
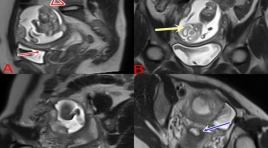
Thai 18 tuần ở sừng chột của tử cung 1 sừng
15/06/2020 11:19:35 | 0 binh luận
A 18 WEEK OF GESTATIONAL AGE IN A NONCOMMUNICATING RUDIMENTARY HORN OF A UNICORNUATE UTERUS
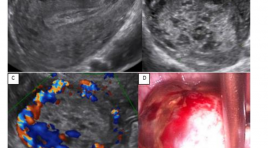
Thai ngoài tử cung ở buồng trứng
15/06/2020 10:31:59 | 0 binh luận
Thai ngoài tử cung (TNTC) ở buồng trứng được mô tả đầu tiên bởi by Saint Maurice de Perigot vào năm 1682. TNTC ở buồng trứng là loại hiếm gặp nhất trong các thể TNTC với tần suất khoảng 1:3000-40.000 ca sinh sống và <3% các trường hợp TNTC [2]. TNTC ở buồng trứng có thể là thứ phát, do phôi làm tổ ở buồng trứng hoặc do thất bại trong việc thoát noãn. Bệnh cảnh lâm sàng của TNTC ở buồng trứng cũng tương tự như TNTC ở tai vòi: trễ kinh, đau bụng, ra huyết âm đạo bất thường, khối cạnh tử cung đau… Siêu âm chẩn đoán TNTC ở buồng trứng hiện nay vẫn là một thách thức vì hình ảnh trùng lấp khó phân biệt với TNTC ở tai vòi hay xuất huyết nang hoàng thể. Nội soi ổ bụng được xem là tiêu chuẩn vàng cho chẩn đoán và điều trị bệnh lý này. Từ khóa: Thai ngoài tử cung (ectopic pregnancy), thai ngoài tử cung ở buồng trứng (Ovarian ectopic pregnancy), nang hoàng thể (corpus luteum cyst)
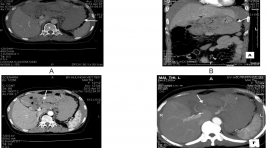
Nhân một trường hợp chảy máu ổ bụng tự phát do tổn thương động mạch vị phải được chẩn đoán bằng chụp cắt lớp vi tính
31/03/2020 16:24:54 | 0 binh luận
Acute abdominal hemorrage by gastric atery aneurysm rupture- Case report SUMMARY We show the case of acute abdominal hemorrhage by gastric atery aneurysm rupture that was diagnosed and treated in Viet Tiep Hospital, Hai Phong. The female patient who was attended to hospital in acute lost blood volume. The patient was examined by US and abdominal CT scanner. The diagnosis was gastric atery aneurysm rupture. The patient was treated by surgery 4/5 gastroectomy because of gastric necrosis. In our experience, the large blood clot in lesser sac, increase arterial diameter and leak of contrast agent were suggested of diagnosis.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












