
Case lâm sàng: nhân một trường hợp chụp và can thiệp bạch mạch đái dưỡng chấp tại trung tâm điện quang bệnh viện Bạch Mai
20/04/2021 13:30:28 | 0 binh luận
Đang cập nhật

Case lâm sàng: Tràn dịch màng ngoài tim do dò dưỡng chấp, nhân một trường hợp được điều trị tại bệnh viện Nhi Trung Ương
20/04/2021 13:28:35 | 0 binh luận
Đang cập nhật
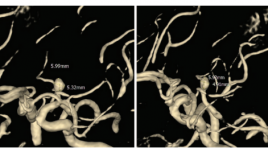
Can thiệp điều trị phình động mạch não cổ rộng vị trí đỉnh thân nền bằng web: báo cáo ca lâm sàng
06/05/2021 17:44:59 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY A basilar tip artery bifurcation aneurysm was diagnosed incidentally in a 69-year-old female patient. She was a normal her medical history. The MRI revealed a non-ruptured aneurysm with a maximum fundus diameter 4.9mm. Selective cerebral angiography confirmed the presence of a wide-necked aneurysm with a mean transverse diameter of 5mm and a mean height of 3mm; the neck width was 4.9mm. With this complex anatomy, the multidisciplinary team recommended endovascular treatment of the aneurysm with the WEB device. The procedure was performed with dual antiplatelet therapy (75 mg aspirin PO daily 3 days and 180 mg ticagrelor PO daily 2 days prior to the intervention). Immediately after placement of the WEB device, DSA showed complete occlusion of the aneurysm but has thromboembolic event in P3 posterior cerebral artery and no deficit. Postoperatively the patient received dual antiplatelet therapy for 5 days and continued 75 mg aspirin PO for 2 weeks, ticagrelor was discontinued. The patient was discharged 2 days after the intervention without any neurological symptoms. Follow-up by MRI at 3, 6, by MRI and DSA 12 months after treatment confirmed the stable obliteration of the aneurysm without recurrence or reperfusion. The value of the WEB device in the endovascular treatment of wide-necked basilar tip artery bifurcation aneurysms is the main topic of this chapter.
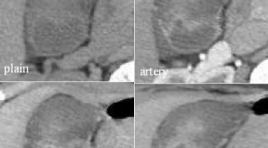
Trường hợp lâm sàng: U cơ tuyến túi mật
20/11/2019 16:01:17 | 0 binh luận
Bệnh nhân nữ 37 tuổi, đi kiểm tra sức khỏe. Tiền căn: không có tiền căn bệnh lý Các xét nghiệm SGOT, SGPT, bilirubin, CTM, chức năng thận trong giới hạn bình thường
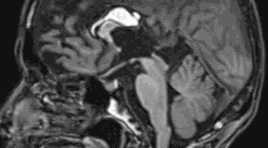
Lipoma of Corpus Callosum A case report in Quang Tri General Hospital
22/11/2020 19:13:47 | 0 binh luận
Intracranial lipomas represent rare congenital malformations, accounting for less than 1% of intracranial tumours. Lipoma of corpus callosum, the commonest variety of all intracranial lipomas (40%-50%), is associated with varying degrees of dysgenesis of corpus callosum and generally remains asymptomatic.
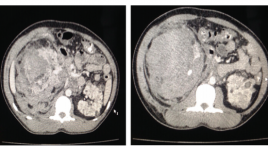
U thận trong bệnh cảnh phakomatosis, những điều cần lưu ý: nhân hai trường hợp lâm sàng
02/06/2020 10:35:14 | 0 binh luận
Renal tumors in the Phakomatosis disease, what to note: two case report SUMMARY Phakomatosis are a group of neurocutaneous disorders characterised by involvement of structures that arise from the embryonic ectoderm , consist of central nervous system, skin ,eyes and others: kidney, heart, lung… In this article we focus on the incidence of renal tumors in Tuberous sclerosis, one of the common diseases in Phakomatosis. Tuberous sclerosis is a rare neurocutaneous disorder (phakomatosis) characterized by the development of multiple benign tumours in various organs, including the kidneys. Tuberous sclerosis complex has several renal manifestations including angiomyolipomas (AML) and renal epithelial neoplasms. Angiomyolipomas is found in 40% of patients with tuberous sclerosis, and its most common complication is ruptures due to aneurysms. We present two cases was diagnosed with bilateral angiomyolipomas in tuberculosis and emphasizes the importance of the diagnosis and choice of appropriate treatment for each patient. Key words : Phakomatosis, renal tumor
Nhân một vài trường hợp điều trị viêm gân vôi hóa bằng chọc hút vôi dưới hướng dẫn siêu âm
02/06/2020 10:39:12 | 0 binh luận
Report of several cases of treatment of calcific tendonitis by aspiration under ultrasound guidance SUMMARY Calcific tendonitis is a common disease caused by the deposition of canxi hydroxyapatite crystals in the tendons. The disease can occur in all tendons in the body and also in the ligaments, but the most common sites are the tendons of rotator cuffs , tendons around great trochanter, tendons around elbow joints, wrists... Normally, there is no pain. However, as calcification resorption occurs because the body releases enzymes that resolve calcification, patients develop severe and persistent pain. In terms of diagnosis, clinical symptoms are quite difficult to distinguish from other causes of musculoskeletal pain, but diagnostic imaging is easy with methods such as radiography, ultrasound, computer tomography, resonance imaging... On the treatment side, medical therapy is the first-line treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers. However, in fact, we found that there are many cases of persistant pain that resistant to NSAIDS drugs, because the calcific deposits are quite large (size up to 1-2 cm) so that the calcification resorption process persists for a long time. Percutaneous aspiration of calcification under ultrasound guidance is a minimally invasive treatment that reduces the progression of the disease due to nearly completely calcific aspiration. This technique is quite easy to implement and can be widely disseminated. We have also performed this technique for some patients diagnosed with calcific tendonitis at Hanoi Medical University Hospital and had achieve good clinical efficacy.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"













