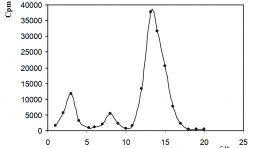
Điều chế Phosphorus-32 (P-32) từ bia chiếu xạ p2o5 cho mục đích điều trị trong y học hạt nhân
03/04/2020 10:59:25 | 0 binh luận
Preparation of phosphorus-32 (p-32) from irradiated target p2o5 for therapeutic purposes in nuclear medicine SUMMARY Phosphorus-32 is produced using the nuclear reaction 31P (n,γ) 32P by irradiation of the phosphorus peroxide (P2O5) target. Phosphoric acid is prepared by the dissolution of irradiated target in 40 ml of boiling chloric acid 0,1 N. When the dissolution of phosphor peroxide is completed, the beaker is allowed to cool. 8 ml of 30% H2O2 is added and refl uxed for 3h. Finally, the solution is fi ltered through a sintered glass fi lter, porosity G3 and passed into a column of cationic exchanger (Dowex-50 W-X4 preconditioned in hydrogen form) to remove metallic impurities. The effl uent is collected as the stock solution. Radiochemical purity is determined by paper chromatography (radiochemical purity control) in the solvent system: Whatman No. 1 paper and the mixture of isopropyl alcohol : water : 50% trichloracetic acid : 25% NH4OH (75:15:10:0.3 v/v.) as a mobile phase, developing time ranged from 12 to 17 h. Radiochemical purity of phosphoric acid (H3 32PO4) solution prepared by our method is obtained more than 99%. Key word : H3 32PO4, Phosphorus-32.
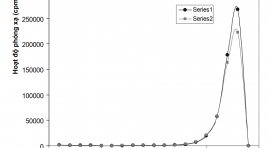
Khản năng sản xuất 177Lu từ bia Lutetium tự nhiên trên lò phản ứng hạt nhân Đà Lạt
03/04/2020 10:55:14 | 0 binh luận
Production ability of 177Lu from natural lutetium target on the Da Lat nuclear reactor SUMMARY 177Lu is presently being considered as a potential radionuclide, for use in in-vivo targeted radiotherapy, owing to its favorable nuclear decay characteristics. This paper presents some research fi ndings on the ability to produce 177Lu on the IVV-9 research reactor with thermal neutron fl ux of 1.8×1013.cm-2.s-1 at the Nuclear Research Institute to produce this radioactive isotope. Our products have specifi c activity of 17.7 mCi/mg Lu, radionuclide and radiochemical purities more than 99.9% of total radioactivity. Immediate products are used for the initial basic research of labeling capabilities with DOTATATE, and especially studying on the possibility preparing 177Lu-EDTMP used to treat pain palliation caused by bone metastases. Keywords: production of Lu-177, nuclear reactor IVV-9, 177Lu-EDTMP, pain palliation.

Ứng dụng kĩ thuật chụp PET/CT mô phỏng lập kế hoạch xạ trị ung thư
12/04/2020 21:31:25 | 0 binh luận
Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning SUMMARY Background: Application of PET/CT images for simulation in Radiation therapy planning is one of the most advantage techniques in cancer treatment. In 2009, Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center of Bach Mai Hospital was the fi rst place in Vietnam, where PET/CT simulation for radiation therapy planning has been conducted successfully for cancer patients. Objective: To build the PET/CT simulation process in radiation treatment planning for esophageal cancer. Subjects and methods: 50 esophageal cancer patients treated by radiation. Results: Simulation for radiotherapy in esophageal cancer: PET/CT has higher values than CT such as detecting lesions more precisely and more clearly. Patients in our study had good response and less complication: overall response (complete and partial) with improving clinical symptoms: 80%, size of tumor reduced in 83% patients. Common complication is depletion (in 34% patients). Most complications are mild and can be treated by medicine. Conclusion: Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center Bach Mai Hospital has standardized the PET/CT simulation process for esophageal cancer patients with initial good results.
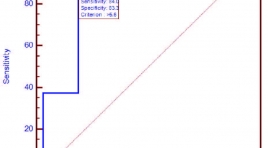
Đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị chẩn đoán của 18f-fdg PET/CT ở bệnh nhân ung thư tuyến giáp thể biệt hóa sau phẫu thuật có thyroglobulin cao và xạ hình toàn thân với 131i âm tính
17/03/2020 10:47:22 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics and diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in post-operative differentiated thyroid cancer patients with elevated serum thyroglobulin and negative 131I whole body scan SUMMARY To evaluate the imaging characteristics and diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in post-operative differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) patients with elevated serum thyroglobulin and negative 131I whole body scan. Materials and method : we performed a cross-sectional descriptive study on 109 post-surgical DTC patients. All patients underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT scan to look for recurrence/metastasis. PET/CT results were compared with hisopathology and clinical follow-up to determine its diagnostic values. Results: 294 lesions were identified in PET/CT with mean diameter and SUV were 14.0 mm và 9.3 g/ml, respectively. Lesions were most found in cervical lymphnode, mediastinum, thyroid bed and lung. PET/CT was positive in 78% of patients with true positive, false positive, true negative and false negative rates were 92.9; 7.1; 75 and 25%; respectively. Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of PET/CT in detecting recurrent/metastatic DTC were 92.9; 75 and 89%, respectively. SUVmax threshold of 5.9 ng/ml was the most suitable to determine recurrent/metastatic lesions in PET/CT. Conclusions: 18F-FDG PET/CT is a valuable imaging tool to diagnose recurrence/metastasis in DTC patient with elevated serum thyroglobulin and negative 131I whole body scan. Key words: 18F-FDG PET/CT, differentiated thyroid cancer, elevated thyroglobulin, negative131I whole body scan.
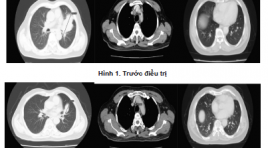
Đặc điểm cắt lớp vi tính ung thư phổi trước điều trị huốc ức chế tyrosin kinase và đánh giá đáp ứng theo tiêu chuẩn recist 1.1
05/12/2019 09:38:20 | 0 binh luận
Computed tomography features of lung cancer patients before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment and response assessment by recist 1.1 SUMMARY Objective: 1. Describe computed tomography features of non-small cell lung cancer before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. 2. Treament response assessment by RECIST 1.1. Patients and metho d: Cross-sectional, retrospective and prospective study of 36 non- small cell lung cancer patients, EGFR mutations positive, treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor from 08/2018 to 06/2018, having Computed Tomography image after 3 and 6 months treament. Results: Tumors located mainly in peripheral of the lung (77,8%). The most common position is the right upper lobe (30,5%), the least common position is the right middle lobe (5,6%). There are 83,3% of tumors with the size over 3cm. 100% of tumor have irregular and spicules magin. Solid mass accounted for 63,9%, partly solid mass (33,3%), one tumor is cavity form. Medium attenuation value is 27 HU in pre-contrast and 57,1 HU in post-contrast CT scan. Lymph node metastasis in 27 (61%) patients. Lymph node metastasis is mainly occured in paratracheal nodes [2,4(R,L), 3] (48%), A-Pwindow, paraaortic nodes (5,6) (12%), subcarinal nodes (7) (16%), supraclavicular nodes (1) (20%). After 3 months treament, partial response: 17 patients (52,8%), stable disease: 19 patients (47,2%). After 6 months treament, partial response: 14 patients (38,9%), stable disease: 20 patients (55,6%), progressive disease: 2 patients (5,5%). Conclusion: Computed TomographyFeatures can be used to diagnose lung cancer. 2. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment is effective inadvancednonsmall cell lung cancer. Keywords: lung cancer, computed tomography, tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment, Recist 1.1
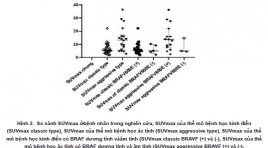
Mối liên quan giữa đột biến BRAV600E, mô bệnh học và khả năng bắt giữ 18F-FDG trên hình ảnh PET/CT ở bệnh nhân ung thư tuyến giáp kháng I-131
18/12/2019 10:32:39 | 0 binh luận
Relationships between BRAFV600E mutation, clinicopathologic factors and 18F-FDG avidity in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma patients SUMMARY Objectives: The BRAFV600E mutation is one of the prognostic factors in thyroid carcinoma related to GLUT-1 expression which increases 18F-FDG uptake. In this study, we investigated the relationship between BRAFV600E mutation, clinicopathologic factors and 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (18F-FDG) avidity in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Methods : Total 46 radioiodine-refractory DTC patients who underwent BRAFV600E analysis from the biopsy and 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography from 2011 to 2018. Semi-quantitative analysis of highest hypermetabolic lesion was accessed by automated polygonal regions of interest (ROIs) drawing on attenuation-corrected PET images the Workstation AW4.7(GE). The relationship between BRAF mutation, clinicopathologic factors, and 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (18F-FDG) avidity was investigated. Results : Patients with the BRAFV600E mutation present higher 18F-FDG uptake (median of SUVmax: 7,11) than those without mutation (median of SUVmax: 4,91) but the difference is not statisticcal significance (p=0,236). The tumor size (p = 0.006) and distant metastases (0,03) were significantly associated with 18F-FDG uptake in univariate analysis. Aggressive histopathologic type of DTC is only the factor (p = 0.01) related to FDG uptake significantly (p = 0.01) in both univariate and multivariate analysis. Conclusion : The aggressive and classic type of DTC were the factors significantly related to 18F-FDG avidity in both univariate and multivariate analysis. The effect BRAFV600E of mutation on glucose metabolism in radio iodine refractory patients needs further study in larger groups of patients. Key words : 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, Positron-emission tomography, BRAFV600E mutation, histopathologic type, radioiodine refractory.
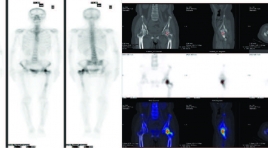
Mối liên quan giữa sUVMAX với hình thái tổn thương di căn xương trên 99MTC-MDP SPECT/CT ở bệnh nhân ung thư
18/12/2019 09:56:50 | 0 binh luận
The relationships between suvmax and morphologic features of bone metastatic lesions on 99mtc-mdp spect/ct in known cancer patients SUMMARY The aim of our study was to evaluate the relationships between SUVmax and morphologic features of bone metastasis on 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT in known cancer patients. Materials and Methods: This prospective study enrolled 90 known cancer patients (32 women and 58 men patients with aged average of 61.6 ± 10.4) underwent 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT scans from February 2018 to February 2019 at Nuclear Medicine Department, 108 central military hospital. Bone metastatic lesions were classified based on morphologic features on CT. The standadized uptake values (SUVmax) were measured at each morphologic features of bone metastasis and determining the relationships between SUVmax and those lesions in different primary cancer diseases. Results : The total of 264 lesions were found in 90 patients. Of which, 29% was osteolytic, 25% was osteoblastic, 23% was mixed and 23% was unclassified lesions on CT. SUVmax values at osteolytic lesions were significantly lower than other types of lesions (p<0.05). SUVmax values of bone lesions in thyroid cancer, liver cancer patients were lower compared to those in prostate cancer and lung cancer patients. This difference was statistically significant (p<0.05). Conclusions: The morphologic features of bone metastatic lesions on CT were found to be in correlation to metabolic bone changes on 99mTc- MDP SPECT/CT imaging. Keywords: SPECT/CT, bone metastasis, SUVmax
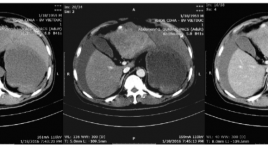
Đánh giá hình ảnh và kết quả nút mạch cầm máu cấp cứu ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan vỡ
25/03/2020 23:29:45 | 0 binh luận
Evaluate the imaging characteristics of ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma and the effectiveness of embolization for controlling hemorrhage SUMMARY Objects : Evaluate the effectivenes of transcatheter arterial embolization for controlling arterial hemorrhage due to spontaneous ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Methods: analyze retrospectively the outcomes of 22 patients who underwent abdominal CTscanner and urgent transarterial embolization for spontaneous ruptured HCC during the period from 01/2014 to 06/2016 in Viet Duc hospital. Results: Mean tumor size: 83.95mm (longest diameter). 7/22 patients (31.8%) exhibited contrast extravasation on angiography, 2/22 patients (9.1%) exhibited pseudoaneurysm, one patient (4.6%) showed arterioportal shunt, 12/22 (54.5%) showed no vascular injury. The embolization materials we used mostly was Spongel in 19/22 patients (86.4%), histoacryl 3/22 (14.6%). The success rate of embolization on angiography is 22/22. The average volume of blood tranfusion was 969ml. 1 patient die in one months after the procedure due to liver failure. 6/9 (66.7%) patients with thrombosis of portal vein die in less than 6 months after procedure. Conclusion: Transarterial embolization is a safe and effective method for controlling spontaneous rupture of HCC. Key words: angiography, embolization, hepatocellular carcinoma, spontaneous rupture.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












