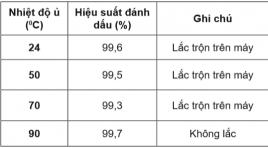
Ngiến cứu điều chế hạt ALBUMIN gắn đồng vị phóng xạ YTTRIUM-90
15/04/2020 20:38:47 | 0 binh luận
Study On Radiolabeling Of Albumin Particles With Yttrium-90 SUMMARY Objective: This report is intended to determine the optimum conditions of the radiolabeling of microaggregated albumin particles with Yttrium-90 radioisotope and the completion of the quality control procedures. Subjects and Methods: The albumin microsphere kit was prepared in sodium phosphate buffer. The original solution includes 2 mg albumin particle and 0.5 mg stannous chloride dihydrate. The albumin particles size was ranged from 5 mm to 30 mm. The mixture was washed three times with phosphate buffer saline, pH 7.2 by centrifugation and suspended in 0.5 M sodium acetate buffer, pH 6. Yttrium-90 in 1.0 M acetic acid was collected from 90Sr/90Y generator. The labeling of the particles with 90Y (185 MBq) was performed at pH 5.5 in acetate buffer with agitating for 60 min at room temperature. The labeled albumin suspensions were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min. Labeling yields was calculated using centrifugation, filtration and compared with paper chromatography, which is developed in the Tris Acetic EDTA. In this system, the unbound of Y-90 migrates to an Rf of 0.9-1.0 and the radiolabeled albumin particles remains at the point of origin (Rf = 0). The size of 90Y-albumin particles was compared with the albumin particles in the original solution to be sure that they didn’t change during the labeling treatment Results : The radiolabeling yields were more than 80% at pH 5,5, the labeled compound was dialysis in phosphate buffer. The radiochemical purity was 98%, the reaction time marked 60 minutes, at room temperature (about 240C). The labeled compound was dialysis in phosphate buffer. The product has a radioactivity of more than 98%. The product has been tested and the quality requirements of radioactive drugs. Conclusion: The subject has achieved the goal of producing conjugate 90Y-albumin and quality control, which is the ideal radioactive substance for the treatment of malignant cancer such as radiation therapy. In the future it is necessary to continue the study of high-activity radiolabeled albumin particles and study on laboratory cancer animals. Key words: 90Y-albumin microspheres, radiopharmaceuticals, brachytherapy

Đặc điểm hình ảnh PET/CT sau xạ trị chiếu trong chọn lọc bằng hạt vi cầu gắn 90Y với hình ảnh 99MTC MAA mô phỏng trước điều trị ở bệnh nhân ung thư gan đối chiếu
06/04/2020 22:18:01 | 0 binh luận
Characteristics of Post- Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)90 Y Microsphere PET/CT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Comparison With 99mTc Macroaggregated Albumin (MAA) scan SUMMARY Purpose: 90Y microspheres are recommended for intra-arterial treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Before treatment,99mTc-labelled macroaggregated albumin (MAA) is injected intra-arterially to simulate the treatment and yttirum-90 (90Y PET/CT) images is performed to evaluate posttreatment. The aim of the study is to assess the correlation between the pretreatment planning and posttreatment images. Methods: Twenty patients with the intermediate and advanced stage of HCC were reviewed in this study. 99mTc-MAA was injected intra -arterially before treatment and whole body scintigraphy and abdominal SPECT was done after 60 min.Post-injection of 90Y microspheres (SIRTEX, Australia), the patients underwent posttreatment 90Y PET/CTwithin 24 h. The tumor to normal ratios (T/N ratios) on PET/CT and SPECT were analyzed and correlated using Spearman rank correlation test. Results : In 20 patients, the distribution of microspheres was consistently demonstrated in both 99mTc-MAA planar scintigraphy before therapy and posttreatmentPET/CT images. Agood correlation was observed between T/N on scintigraphy before treatment and T/N on PET/CT images after treatment (rho value=0.58, p<0.005). The TN on PET/CT (median 14.85) tends to show significantly higher values than T/N stimulated (median 11.2, p<0.05). The T/N post treatment showed good correlation with tumor volume (rho=0.69, p<0.05). Conclusions The 99m-Tc MAA planar imgaes showed a good correlation with 90Y PET/CT in T/N values, suggesting that it should be used as an adequate pretreatment evaluation method. 90Y PET/CT should be included routinely in the post-therapeutic evaluation. Keywords : resin microspheres 90Y, 99mTc-MAA, hepatocellular carcinoma
Xạ trị trong chọn lọc điều trị ung thư gan bằng vi cầu phóng xạ Y-90 tại bệnh viện Bạch Mai
01/04/2020 16:14:00 | 0 binh luận
Selective internal radiation therapy forliver cancer with Y-90 microsphere at Bachmai hospital SUMMARY Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) for liver cancer is a method to inject Y-90 labeled resin microsphere into the hepatic arteries supplying the tumor. Cancer cells will be annihilate by irradiation with ionizing radiation emitted from Y-90. Theprocedure has been standardized and applied in treatment of liver cancer patients at the Nuclear Medicine & Oncology Center, Bach Mai hospital. Aims of study: To establish and standardize the procedure of SIRT with Y-90 microsphere for liver cancer. - To assess initial results of SIRT for liver cancer at The Nuclear medicine & Oncology Center, Bach Mai hospital. Subject and method : 36 patients with primary or secondary liver cancer confirmation. These patients had been treated with Y-90 microsphere and follow-up assessments after treatment 1 and 3 months. Descriptive and propective study. Establishing a standard SIRT with Y-90 microsphere for liver cancer. Results of study: Procedure of SIRT with Y-90 microsphere for liver cancer has been standardized. Contents of protocol included indications and contraindications; workflow: Arteriographic assessment to map tumor-perfusing vessels and assess portal vein patency; SPECT with Tc 99m MAA to optimize the treatment planning (by dosimetric evaluation) and evaluate hepatopulmonary shunting; inject Y-90 microsphere into the vessels supplying the tumor, SPECT or PET/CT to evaluate the distribution of Y-90 microsphere; Evaluate the outcomes and safety. The initial treatment results of SIRT forprimary liver cancer patients: more than 80% patients responded with treatment, no patient had complication. AFP level reduced in 77.8% and no change in 22.2% patients, AFP reduced from 4660.3ng/ml to 248.4ng/ml; 72.2% patients mean tumor size was decreased from 7.2 cm to 4.3 cm and was stable in 27.8% patients.The patient with secondary liver cancer from colon cancer: CEAreducedfrom1000 ng/ml to 40ng/ml, tumor size 7.0 cm reduced to 3,0 cm. Conclusion: Selective internal radiation therapy with Y-90 microsphere for liver cancer is a new, effective and safe method. Procedure of the technique was standardized and applied for liver cancer treatment at the Nuclear medicine & Oncology Center, Bach Mai hospital. The initial results show the efficacy and safety of the technique and it should be disseminated for primary and secondary liver cancer treatment. Keywords : Y-90 microsphere, liver cancer, Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT.
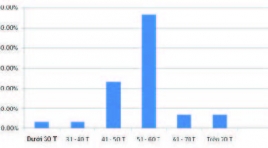
Nhận xét kết quả bước đầu vai trò của f-18 fdg pet/ct trong phát hiện vị trí tổn thương ở bệnh nhân ung thư chưa rõ nguyên phát tại Bệnh viện K
18/12/2019 14:29:08 | 0 binh luận
Remarking the first step results of the role of f-18 fdg pet/ct in determining the positive position in the unknow cancer in the cancer national Hospital SUMMARY Carcinoma of unknown primary tumors (CUP) is present in 2% of all patients with malignant neoplasms. However, only 20% - 73% of primary sites are identified before the patients die. Currently, F-18 FDG PET/CT is widely used for the diagnosis of CUP. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of F-18 FDG PET / CT in these patients. Results: 30 patients with unclear cancers were treated with F-18 FDG PET / CT, the mean age of patients was 53.6 ± 9.7. There were 18/30 patients (60%) who were diagnosed with cancer. PET / CT (compared with pathology), the rest is false 12/30 BN (40%). Localized nodal metastases is an area of the neck. The most common pathological anomalies were squamous cell carcinoma (56.7%), adenocarcinoma (16.7%) and noncancerous cancers (26.7%). Conclusion: F-18 FDG PET / CT is a useful method for detecting primary malignant sites in patients with primary tumors.
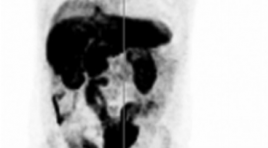
Ứng dụng lâm sàng PET/CT sử dụng dược chất phóng xạ không phải 18F-FDG trong ung thư
31/03/2020 13:59:54 | 0 binh luận
Clinical Non-FDG PET/CT Applications in Oncology SUMMARY In clinical practice 18FDG-PET is applied in almost cancers in staging, re-staging, monitoring therapy response and the follow-up. On the other hand, at no time do all tumors show significant increase of 18FDG uptake on PET imaging. Particularly in prostate cancer, neuroendocrine and hepatocellular carcinoma... In this review we have introduced those already used for clinical applications like 11C- and 18F-Choline, 11C-Methionine and 18F-FET, 18F-DOPA, 68Ga-DOTA-somatostatine analogues, 11C-acetate and 18F-FLT. Choline has indicated a high affinity for prostate cancer, even if low grade being labelled with either 11C or 18F, the former being the preference by dint of lower urinary excretion and patients exposure. The latter is more beneficial for centers without on-site cyclotron. Methionine is required for protein synthesis and tumor cells which have been used for imaging of CNS neoplasms. NET tumors demonstrate an increased activity of L-DOPA decarboxylase, hence high uptake of 18FDOPA. 18F-FLT is a specific marker in application of FLT is lung cancer. Other tracers are used in PET utilized include 18F-MISO, 64Cu- ATSM, 18F-EF5, which highlight the presence of hypoxic areas are useful for radiotherapy. Key words: radiopharmaceuticals, choline, methionine, DOPA, DOTA, FLT.
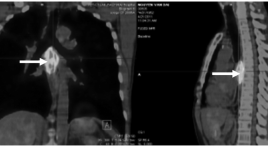
Đo độ tập trung Flouro-Deoxy-Glucose (FDG) ở bệnh nhân ung thư thực quản
31/03/2020 13:40:18 | 0 binh luận
Standardized Uptake Value of Glucose on PET/CT scan of esophageal cancer patients summa ry Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) was determined for 100 esophageal cancer patients on PET/CT. SUV in primary tumors of esophageal cancer was 10.7±5.0; higher than in mediastinal lymph nodes 7.1±0.9; supraclavicular lymph nodes, 6.2±2.5; abdominal lymph nodes 6.9±2.5; metastases of bone 8.0±4.1; lung 3.3±1.7 and liver 7.2±2.6. SUV Index increased proportionally to tumor size, lymph nodes, stage of disease.
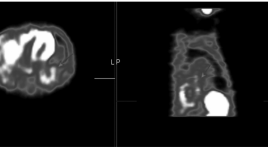
Ghi hình phóng xạ 99mTc-MIBI đánh giá đáp ứng với xạ trị ở bệnh nhân ung thư phổi không tế bào nhỏ
31/03/2020 13:31:33 | 0 binh luận
The role of 99mTc-MIBI SPECT in the assesstment of radiotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer summa ry 48 patients with non-small cell lung cancer underwent a 9mTc-MIBI SPECT studies before starting and after radiotherapy 4-5 weeks. The results indicate that this method is valuable coordinate with CT in evaluation of response to radiotherapy. 99mTc-MIBI SPECT imaging may be useful to differentiate between necrotic tumor tissue and residual, recurrent lung lesions after radiot Key words: 99mTc-MIBI SPECT scan, non-small cell lung cancer.
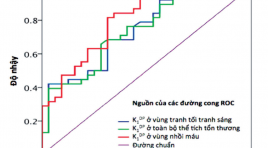
Dự báo biến chứng chảy máu trong ổ nhồi máu bằng chỉ số thấm hàng rào máu não trên chụp cắt lớp vi tính tưới máu ở bệnh nhân thiếu máu cục bộ não cấp tính
03/04/2020 11:22:47 | 0 binh luận
Prediction intra- infarct hemorrhage by blood brain barrier indice on perfusion CT scanner in acute ischemic stroke patient summa ry Background: Haemorrhagic transformation is the leading cause of early neurological deterioration in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. Early prediction of this complication is important for selecting appropriate treatment methods, preventing and planning for the complication. Existing predictors of haemorrhagic transformation remain limitations in prognosis accuracy, clinical practicality and radiation safety. The aim of this study is assess the role of blood-brain barrier permeability in prediction of haemorrhagic transformation. Methods: Blood-brain barrier permeanility was obtained using perfusion CT data with implication of the Gjedde-Patlak plot. The obtained permeability value was used to predict occurrence of haemorrhagic transformation. Results : mean blood-brain barrier permeability in lesions developed haemorrhagic transformation was found significantly higher than the value obtained in the lesion without complications. There were a significant relationship between increased permeability and occurence of haemorrhagic transformation. The threshold of 2.7ml/100g/min was established, above that stroke patients are at high risk of having haemorrhagic transfomation. Conclusion : Increased blood-brain barrier permeability is onf of the factor related to haemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. The perfusion CT obtained permeability is proven as a predictor of haemorrhagic transformation. Together with other clinical and imaging findings, pattern of blood-brain barrier permeability is recommended to be included into initial perfusion CT analysis. This may improve prediction, prevention and planning for medical nanagement in patients with acute ischaemic stroke.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












