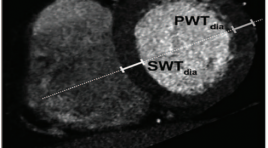
Nghiên cứu vai trò của chụp cắt lớp vi tính 256 dãy trong đánh giá chức năng thất trái trên bệnh nhân có chỉ định chụp MSCT mạch vành
06/05/2021 14:54:54 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To compare DSCT using 256-slice coronary CT angiography (SOMATOMA Definition FLASH, Siemens Medical Solution, Germany) with echocardiography for the determination of left ventrical dimentions, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-systolic volume (ESV), regional wall motion as well as assessing coronary artery image quality and patient radiation dose. Materials and Methods: One-hundred twelve patients were referred for DSCT for evaluation of coronary artery and underwent DSCT and transthoracal echocardiography within 1 week. LV dimentions, EF, EDV and ESV were determined for both DSCT and echocardiography, and the correlation coefficients were assessed. Measurements of dimensions were obtained in standardized planes in end-systole and end-diastole and included the septal and posterior wall thickness, and inner diameter of the left ventricle. Global left ventricular (LV) functional parameters [end-systolic volume (ESV), end-diastolic volume (EDV), ejection fraction] were computed using automated software. ESV, EDV were normalized to the body-surface-area (BSA). Correlation between DSCT and echocardiography was tested through linear regression and Bland- Altman analysis. Regional wall motion is collected by visual (1, normal, 2, hypokinesia, 3, dysphagia or akinesia). Coronary artery segment subjective image quality (1, excellent; 4, poor) and radiation dose were recorded. Results: A direct comparison between 256 slice Dual-Source CT and 2D-echocardiography was performed in 112 patients (43men; 61,26 ± 11,68 mean age years) who were clinically referred for MSCT coronary angiography. LV end-diastolic volumes (LVEDV) and LV endsystolic volumes (LVESV) were determined and the LV ejection fraction (LVEF) was derived. Average LVEF was 66,24± 13,52% (range 23-85%) as determined on DSCT, compared with 65,72±11,31% (range 25-84%) on 2D echocardiography. Evaluation of LVEF by linear regression analysis showed a good correlation between DSCT and 2D-echocardiography (r= 0,715; P < .001). Good correlations between DSCT and 2D-echocardiography were demonstrated for the assessment of LVEDV (r=0,732 ; P < .001) and LVESV (r= 0,841; P < .001). At Bland-Altman analysis, mean differences (±SD) of 1,78 ± 24,10 mL (p <0 .05) and 0,766 ± 13,7 mL (p < 0.05) were observed between DSCT and 2D-echocardiography for LVEDV and LVESV, respectively. LVEF was slightly overestimated with DSCT (0.52 ± 9,59%; p < 0.05). Resultly, the LVEFs calculated by DSCT and echocardiography were not statistically different. However, LVEF, EDV and ESV from MDCT were statistically higher than those from echocardiography (p < 0.05).The average image quality score of the coronary artery segment was 1,79. The mean patient radiation dose was 3,78 ±1,88 mSv. Conclusion: In conclusion, the use of 256-slice DSCT can provide comparable results to those using 2D-TTE for LV funtion include EF, EDV, ESV and regional wall motion assessment in a heterogeneous population. Keywords: DSCT; Coronary Artery Disease; Left ventricular function; Echocardiography; Radiation

Đánh giá chất lượng cuộc sống của bệnh nhân sau điều trị nút mạch u cơ trơn tử cung theo bộ câu hỏi UFS - QOL
06/05/2021 15:46:53 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: The responsiveness of the uterine fibroid symptom after Uterine artery embolization for the treatment of Uterine fibroids with healthrelated quality of life questionnaire (UFS-QOL). Method and objective: Follow- up study from January 2019 to July 2020, we treated 36 patients who manifest symptom cliniclly (mean 38,08± 6.26 year, range 24-59 years). quality of life test before and after treatment for 3 months and 6 months. The find the relationship between treatment outcomes and quality of life. Results: A total of 36 patients with 43 tumors received the intervention, a technical success rate of 100%. Clinically, after 6 months, 80% of patients stopped menorrhagia, 85,7% of patients had stopped abdominal pain, the mean tumor volume decreased after 3 months and% after 6 months (p <0.05). Quality of life score improved 42 points after 6 months. Conclusion: Uterine fibroid embolization seems to lead to notable long-term relief of fibroid- associated symptoms. In comparison with the midterm results, long-term outcome shows a clear continuance of improvement in general quality of life. Key words: fibroid, Uterine artery embolization, quality of life
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh siêu âm doppler trước và sau đốt laser nội mạch điều trị suy tĩnh mạch hiển lớn tại Bệnh viện Bạch Mai
06/05/2021 17:35:33 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: The study is to evaluate the characteristics ultrasound imaging Doppler before and after the laser incineration of the great saphenous veous insufficiency at Bach Mai Hospital. Object research and methods: Uncontrolled intervention study of 41 shaphenous veins with a diagnosis of venous insufficiency on ultrasound, indicated by 1470 nm wavelength intravascular laser burning at Bach Mai Hospital from October 2017 to 12/2019. Results: Among 41 patient intervention. The rate of bilateral venous insufficiency was not statistically significant with p< 0,05. Before the intervention: the mean diameter of great saphenous vein mid-thigh segment was 6,9±2,0 mm, the time of reflux in the mid-thigh was 2161±969,9 ms ( greater than 0,5s). After intervention: completely blocked after 1 month ( n=41), after 6 month (n=39), and 2 years ( n=26), not completely after 1 years, there í one case, accounting for 2,8% ( n=36). Conclusion: Great shapenous venous insufficiency have average diameter > 5 mm with reflux current time > 0,5 s. After 2 years of laser intervention, the veins were completely blocked with the rate of ≥ 97.2%. Keyword: Great shapenous venous insufficiency, imaging characteristic, Doppler ultrasound.
Đặc điểm hình ảnh chụp cắt lớp vi tính 256 dãy đầu thu ở bệnh nhân phình động mạch chủ
06/05/2021 15:25:14 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: to describe the imaging characteristics of aortic aneurysm using 256 rows of detectors computed tomography scanner. Subject and Method: cross-sectional descriptive study on 78 patients with aortic aneurysm, who were diagnostised by computed tomography scanner with 256 rows of detectors from March 2019 to the end of February 2020 at Friendship Hospital. Results: 93.6% in male and almost in elderly (> 60 years old). Risk factors were hypertension, diabetes, cerebral artery accidents due to hypertension and increase of blood lipid concentration. The aortic aneurysm with maximum transversal diameter ≤ 5 cm accounted for 79,8 %; The length of aneurysm from 5-10cm accounted for the highest proportion (50%), other groups were equivalent. Fusiform aortic aneurysm accounted for 88%. Abdominal aortic aneurysm had highest proportion (69%). Common iliac artery lesion was 39,3%, however it accounted for 56,9% of abdominal aortic aneurysms and 94,3% of branch injuries. Aortic aneurysms were often accompanied by atherosclerosis and calcification (83%); wall thrombose (89.6%). There were 7.1% of cases accompanied by endothelial dissection. Conclusions: 256 rows of detector CT scanner allows to diagnosis accurately all lesions of aortic aneurysm and plays an important role in diagnosis and monitoring patients suffering from aortic aneurysm. Key words: aortic aneurysm, 256 rows of detector CT scanner

Đặc điểm hình ảnh và vai trò chụp cắt lớp vi tính 128 dãy tưới máu não trong chẩn đoán nhồi máu não cấp do tắc động mạch cảnh trong
06/05/2021 15:43:05 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Abstract: For acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patient, assessment of cerebral injury plays a very important role in choosing treatment for better outcome and reduces mortality. CT perfusion (CTP) can assess the infarct area and tissue at risk area. Therefore, CTP has a very important role in the choice of treatment and prognosis for AIS patient. Objective: (1) Image features of 128-slice CT perfusion in diagnosis of ASI. (2) Role of CTP in assessing the extent and prognosis of acute cerebral infarction due to internal carotid artery occlusion. Method: A prospective descriptive cross-sectional study of 35 acute ischemic stroke due to internal carotid artery occlusion patients, had 128-slice CT perfusion, and indicated for mechanical thrombectomy in Bach Mai Radiology Center from April 2019 to June 2020. Results: Mean age of 66.57 ± 11.98, the average baseline NIHSS was 17.23 ± 4.47, 32 patients (91.43%) had early infarcted signs on Noncontrast CT (NCCT). ICA occlusion site: ICA 20%, Tandem 42.9%, ICA Terminus 37.1%. Mean volume of infarct core 34.60 ± 33.34 cm3, and penumbra 102.98 ± 40.07 cm3. Mean relative MTT 252.86 ± 81.49%. Mean CBV infarct core 1.19 ± 0.39 ml / 100g. ASPECTS score and infarct core volume, as well as the rate of post-intervention bleeding with infarct core volume were statistically significant (p <0.05). Conclusion: A 128-slicce CTP of AIS due to ICA occlusion is characterized by: mean infarct core volume is greater than mean infarct core volume of AIS due to anterior circulation large artery occlusion (AC-LAO) in general, although the majority of patients were admitted to the hospital early. From the correlation between infarct core volume and the risk of post-intervention bleeding, it is possible to predict patients with AIS due to ICA have higher rate of post-intervention bleeding than patients with AIS due to AC-LAO in general. Keywords: CT perfusion, acute ischemic stroke, AIS, ICA occlusion
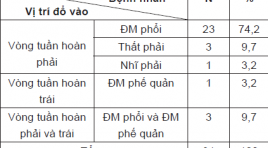
Chần đoán rò động mạch vành trên cắt lớp vi tính đa dãy
06/05/2021 15:51:18 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective : Evaluate the characteristics of coronary artery fistulas (CAFs) by multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Material and methods: During 21 months (between January 2019 and September 2020), study on 31 patients were diagnosed with CAFs on MDCT at Radiology Centre of Bach Mai hospital, prospective descriptive study. Result: We enrolled 31 patients (11 male, 20 female, mean age 56 years) with CAFs on MDCT. 18 patients had multiple fistulas (58,1%), 13 patients had single communication (41,9%). 6,5% originated from the right coronary, 35,5% arose from the left coronary artery system and 58,5% from both right and left coronary artery. 87,1% of fistulas drain to the right side of the circulation(74,2% drain to pulmonary artery). 1 patient (3,2%) had fistula drain to the left side of the circulation (bronchial artery). 3 patients (9,7%) had fistulas drain to both right and left side of the circulation (pulmonary artery and bronchial artery). 10 patients had large fistulas (32,3%), 21 patients had small fistulas (67,7%). 19 patients had aneurysm of fistulas (61,3%), most of them drain to pulmonary artery (73,7%). 38,7% of patients were diagnosed with CAFs by echocardiography (38,7%). 6 patients were examined by DSA: 2 patients were not detected origin of fistulas by DSA, 3 patients were not detected drainage of fistulas by DSA. Conclusion: DSCT is a noninvasive and useful modality for diagnosis of CAFs.
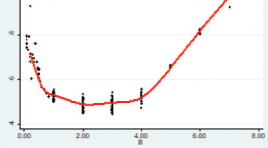
Khảo sát đặc điểm của nhồi máu não cấp trên cộng hưởng từ thường qui và chụp mạch máu bằng kỹ thuật TOF 3D
06/05/2021 16:00:20 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective. To describe the characteristics of acute ischemic stroke on conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and angiography using TOF 3D technique and to evaluate the time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient after cerebral infarction. Materials and Methods. We conducted a retrospective study in 221 patients with acute ischemic stroke who were performed MRI at the University Medical Center Hospital between January 2018 and December 2020. A radiologist who had more than 5 years of experience of MRI evaluates the changes of signal intensity on these sequences: T1- weighted, T2-weighted, FLAIR, DWI/ADC, Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and TOF3D. Results : The study was composed of 221 patients (136 males, 85 females). The mean age of patients was 64.5 ± 13.7 years (range, 28- 96 years). 60 - 79 age group accounts for the majority with 105 people (47.5%). Anterior cerebral artery territory infarcts and cerebral peduncular infarction were the least common (1.1%). The rate of brain parenchymal signal abnormalities on the T1W, T2W, FLAIR, DWI / ADC sequences respectively was 85.5%, 87.3%, 90.0%, and 97.3%. The rate of a significant decrease in vascular signaling on TOF3D was 35.7%. The rate of susceptibility vessel sign and prominent vessel sign on SWI was 21.8% và 9.1% respectively. Immediately following a cerebral infarction, the relative ADC (rADC) value begins to decrease gradually and reaches its lowest level between day 2 and 4. Thereafter the rADC value increases gradually and reaches a pseudonormalization around day 7. Conclusion: Magnetic resonance imaging is of high value in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. Diffusion imaging has the highest sensitivity in lesion detection. TOF3S and SWI were helpful in depiction the vascular signaling, the susceptibility vessel sign and prominent vessel sign. Immediately following a cerebral infarction, the relative ADC (rADC) value begins to decrease gradually and reaches its lowest level between day 2 and 4. Thereafter the rADC value increases gradually and reaches a pseudonormalization around day 7. Keywords : acute ischemic stroke, magnetic resonance imaging.
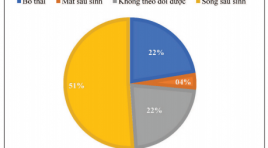
Vai trò của siêu âm trong chẩn đoán bệnh tim bẩm sinh trước sinh
06/05/2021 16:33:50 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: Role of prenatal ultrasonographic in diagnostic of congenital heart defects Subjects and methods: Descriptive study on 98 fetuses diagnosed congenital heart defects (CHDs) from August 2018 to September 2020 at National Obstetric and Gynecology. 50 cases with live birth, 22 cases of pregnancy termination, 4 cases of perinatal mortality, 22 cases of losing follow-up. The patient was performed an prenatal fetal heart ultrasound and follow the outcome. Result: The mean maternal age was 28.5 ± 9.4 yrs old, the mean gestational age at the time of prenatal diagnosis of CHD was 28 ± 6,4 weeks. CHDs accounts for a high proportion on prenatal ultrasound: ventricular septal defect (VSD), atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) and the double outlet right ventricle (DORV) account for 14-15% of CHDs. The mild CHD account for 27.6%, critical CHD was 72.4%. Accuracy of prenatal echocardiography diagnosis was 88%. The severity of CHDs prenatal ultrasound affects pregnancy outcome (p<0.05). Conclusion: Fetal echocardiography has high accuracy in prenatal diagnosis of CHDs. The severity of CHDs in prenatal ultrasound has an impact on pregnancy outcome. Key word: Fetal echocardiography, congenital heart defects.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












