Kết quả bước đầu nút thông động tĩnh mạch cửa trong điều trị bệnh nhân ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan
06/05/2021 14:32:25 | 0 binh luận
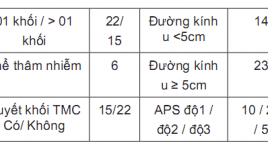
SUMMARY Advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma with arterioportal shunts has worse prognosis and limited treatment. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) use embolic materials is a safe method and have efficacy in treatment. Aims: The aim of this study is to evaluate safety and efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with use embolic materials for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with arterioportal shunts (APS) Materials and Methods: From June 2019 to June 2020, 37 patients who had diagnosis of HCC with major portal vein thrombosis were perfomed TACE with diffrent embolic materials which depend on the level of APSs. The patients were followed after treatment 1 week for the clinical symptom and at 1-3 month after the initial intervention, contrast-enhannced multi slide computed tomography (MSCT) or magnetic resonance image (MRI) or DSA was performed to assess the APS’s treatment efficacy and tumor response by mRECIST and tumor markers (AFP or PIVKA-II). The primary safety endpoint was liver toxicity at 2-5 days and 1 month after intervention. Results: All interventional procedures were successful without any procedure relevant complications. The immediate APS improvement rate was 89.2% (33/37), and the APS improvement rate at first‑time follow‑up was 70.3% (26/37). Radiologically confirmed complete response (CR), partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease at 1 month after first chemoembolization were observed in 3 (8.1%), 17 (45.9%), 13 (35.1%) và 4 (10.9%) patients, respectively. Conclusions: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) use embolic materials is safety and have efficacy in treatmen of arterioportal shunt in patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Key words: Arterioportal shunts (APS), Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Khảo sát mối liên quan độ giãn động mạch chủ ngực với mức độ tổn thương động mạch vành trên cắt lớp vi tính 256 dãy
05/05/2021 12:24:42 | 0 binh luận
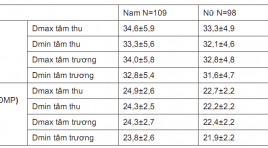
SUMMARY: Objective: The relationship between the thoracic aortic dilatation and the degree of coronary artery injury by 256-slice CT scanning. Subjects and methods: Descriptive cross-sectionalnstudy was performed on 207 patients who was performed coronary angiography by 256-slice CT scanning at Bach Mai hospital from January 2019 to August 2019. Results : 207 patients in study, 107 males (52,7%), 98 females (47,3%). Average age is 62,2±10,3. There was 34 patients with thoracic aortic dilatation (16,4%). There was the significant difference of the Dmax, Dmin diameter at levels (sinuses of Valsalva, sinotubular junction, ascending aorta, descending aorta) and Dmin diameter at level of annulus between the systolic phase and diastolic phase (p<0,001. There was relationship between dilatation of thoracic aorta with valve calcium score (p<0,001). There was not relationship between dilatation of thoracic aorta with coronary artery calcium score and degree of coronary artery stenosis due to atheroma. Conclusion: This study showed significant differences of the thoracic aortic dimensions, between systolic phase and diastolic phase. Dilatation of thoracic aorta was associated with aortic valve calcium score but not with degree of coronary artery injury. Key words: thoracic aortic dilatation, coronary artery, 256-slice CT.
Vai trò của cộng hưởng từ ngấm thuốc muộn trong tiên lượng khả năng phục hồi chức năng thất trái sau tái tưới máu cơ tim ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp
17/03/2020 15:56:04 | 0 binh luận
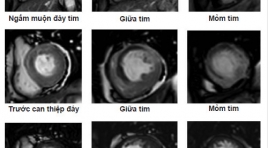
Role of delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the prediction of functional improvement after reperfused acute myocardial infarction SUMMARY Objective : To access the transmural extent of hyperenhancement at delayed contrast enhancement MRI on relating to left ventricular functional improvement in reperfused myocardial infarction and to compare the left ventricular morphology and function on MRI before and post percutaneous coronary revascularization. Methods: Cine sequence and delayed Contrast-Enhanced MRI were underwent in period of 10 days just before or postpercutaneous coronary revascularization on 28 patients suffering from Acute Myocardial Infarction at Bach Mai hospital. Long term follow-up cardiac MRI was done to compare the change in left ventricular morphology and function. Myocardial wall thickening and left ventricular volumes were quantified on cine-images, and the transmural extent of infarction (TEI) was scored on delayed-enhancement images. Results : A decrease in myocardial mass (104,8 ± 23,89 to 95,83 ± 25,81, p<0,05), mean SWT score (16,75 ± 4,7 to 14,86 ± 5,98, p<0,001) and increase the mean ejection fraction (45,74 ± 7,25% to 49,12 ± 9,2%, mean 3,39%, p<0,05), whereas mean end-diastolic volume (109,49 ± 28,53 to 131,73 ± 39,37 ml, p<0,0001) and mean end-systolic volume (59,91 ± 19,13 to 69,19 ± 30,18, p<0,05) did not decrease. Segmental wall thickening did not change (42,12 ± 23,19 to 42,57 ± 23,99, p>0,5). The transmural extent of hyperenhancement at DCE-MRI was related to left ventricular remodeling (r=0,628, p-0,0001) and ejection fraction(r=0,583, p=0,001). Segmental wall thickening improved significantly in segments with<25% TEI(35 ± 7,39 to 48,86 ± 6,65, p<0,0001), tended to improve in segments with 25% to 75% TEI (32,88± 9,78 to 39,67 ± 10,7, p<0,001), whereas segments with>75% TEI did not improve (22,61 ± 14,62 to 19,71 ± 14,56, p<0,05). Conclusion : In patients with recent reperfused MI, functional improvement predicted by delayed contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Key words: Cardiac Magnetic Resonace Imaging, delayed enhancement MRI, late gadolinium, Acute myocardial infarction, transmural extent of infarction (TEI)
Nghiên cứu các đặc điểm hình ảnh và đánh giá kết quả điều trị dị dạng động - tĩnh mạch tủy bằng can thiệp nội mạch
22/03/2020 17:29:46 | 0 binh luận
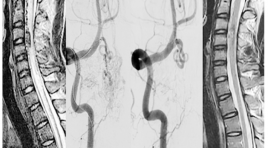
The imaging characteristics and embolization treatment of spinal arteriovenous SUMMARY Purpose: to describe the imaging characteristics and the results of spinal arteriovenous shunt treated by endovascular intervention. Material and Methods: Descriptive and intervention study, patients were diagnosed and treated by endovascular intervention at the Bach Mai hospital from 2012 to 2016. Imaging features were evaluated on MRI and DSA, evaluated of effectiveness of treatment based on the comparison of clinical symtoms, MRI imaging before and after endovascular treatment. Result: Diagnosis and endovascular intervention of 20 patients. On MRI, the sign of spinal cord edema and dilated venous drainage were spotted in almost patients. The rate of complete angiographic obliteration was 60% patients and partial in 45.5% patients. After follow up of 3-6 months, spinal cord damage reduce accounted 88.23% and 11.77% patients remain unchanged, clinically significance improvement was achieved in 82.35% patients,17.65% patients do not improve (3 cases are continous following). Conclusion : MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow up patients with spinal arteriovenous shunt, DSA is the gold standard for diagnosis and to allow intervention treatment with high effective.
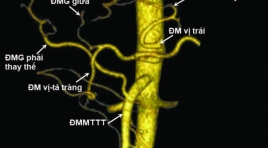
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm giải phẫu động mạch thân tạng và hệ động mạch gan ở người trưởng thành bằng X quang cắt lớp vi tính
05/12/2019 09:11:06 | 0 binh luận
Anatomical study of celiac artery and hepatic arterial system in adults: an analysis using multidectector computed tomography SUMMARY Objectives : The aim of the present study was to evaluate the anatomical chacracteristics of celiac artery (CA) and hepatic arterial system (HAS) in Vietnamese adults by using multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Materials and Methods : Retrospective, cross-sectional and predominantly descriptive study based on the analysis of arterial phase contrast-enhanced CT images of 600 patients between July 2016 and November 2016, at the Radiology Department, University Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City (UMC HCMC). Results : The CA arises variably from the aorta at the level between lower 1/3 11th thoracic and upper 1/3 2nd lumbar vertebrae with more than 70% at the level of lower 1/3 12th thoracic, T12 – L1 junction and upper 1/3 1st lumbar vertebra. The celiac trunk anatomy was normal (Uflacker type 1) in 87.7% of cases and variation of CA was observed in 12.3% with the form of hepatosplenic trunk (Uflacker type 2) was the most common type (4.0%). Ambiguous celiac axis anatomy was seen in 3.1% of patients. CHA originated from celiac axis in 92.7% of cases, followed by SMA (4.0%) and aorta (1.2%). The HAS was described as normal (Michels type 1) in 73% of patients and several variations were noted in 23%. The most common variation was Michels type 2 (7.0%), followed by type 3 (5.7%), type 9 (3.8%) and others. Type\ 10 was not observed in our series. We have noted additional, unclassified variations in 19 cases (3.2%). Mean length and diameter of CA were 28.29 ± 6.68mm and 7.33 ± 1.15mm. Mean distance between CA and SMA was 20.51 ± 4.17mm. Normal measures of CA in women were smaller than in men (p<0.05). Mean length and diameter of CHA were 32.43 ± 8.49mm and 5.40 ± 1.04mm. Mean diameter of PHA was 4.45 ± 0.87mm. Normal measures of hepatic artery in women were smaller than in men (p<0.05). In the presence of anatomical variations, there was a decrease in the arterial diameters of the CA and HAS, decrease in the CA length, but increase in CHA length (p<0.05). In addition, a significant correlation was observed between CA diameter and length; CA diameter and distance to SMA; CHA diameter and length; and CHA diameter and PHA diameter (p<0.05). Conclusion: The knowledge of anatomic characteristics of the celiac artery and hepatic arterial system, including the most common variations of these arteries in population may assist in the selection of treatmen options và surgical planning. As a reliable non invasive method, MDCT can accurately provide detailed information of celiac artery and hepatic arterial system. Keywords: Anatomical variations; Celiac artery (CA); Hepatic arterial system (HAS); Common hepatic artery (CHA), Proper hepatic artery (PHA); Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT).
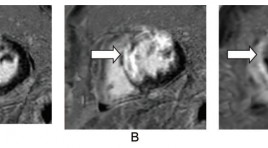
Đánh giá tổn thương cơ tim trên cộng hưởng từ ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp
06/06/2020 10:27:18 | 0 binh luận
Evaluation of myocardium injury on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with acute myocardial infarction SUMMARY Objective: To access the imaging characteristic of the myocardium injury on cardiacmagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in reperfused acutemyocardial infarction (MI) after percutanous coronary revascularization. Materialand Methods: Cine sequence and Delayed Contrast- Enhanced MRIwere underwent in period of 9 days after percutanous coronary revascularization on 50 patients suffering from Acute Myocardial Infarction at Bach Mai Hospital. Left ventricular function was done on cine sequence and extent of infarction, infarct size was evaluated on delayed-enhancement images. Results : A total of 50 patients with acute MI were classified 90% as STEMI and 10% as NSTEMI. The sensitivity of delay-enhancement MRI for detecting MI reaching 98%. The accuracy of MRI for identifying MI location (compared with infarct-related artery perfusion territory) were 92%, kappa=0,842 with all the patients and were 97,8%, kappa=0,952 with STEMI. The infarcted areas in 49 patients were detected by use of cardiac delayedenhancement MRI. There was an excellent correlation between quantitative planimetry and scoring method for the hyperenhancement infarct size (r=0,976, p<0,0001). Infarct size on delayed-enhancement MRI showed a good correlation with left ventricular ejection fraction (r=-0,63,p<0,0001 with planimetry method; r=-0,602, p<0,0001 with scoring method). Conclusion : Cardiac MRI could evaluation of myocardium injury in patients with reperfused acute myocardial infarction. Key words: Cardiac Magnetic Resonace Imaging, delayed enhancement MRI, late gadolinium, Acute myocardial infarction, infarct size.
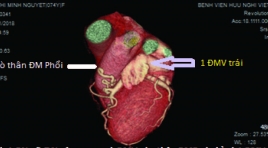
Giá trị CLVT 256 dãy trong chẩn đoán rò động mạch vành và thống kê y văn
04/12/2019 14:41:18 | 0 binh luận
Valuation of 256 - multidetector computer tomographyin detective of Coronary Artery Fistulas and literature review SUMMARY Background: Coronary artery anomalies can be included into anomalies of origin, course, structure and termination. Coronary artery fistula (CAFs) are rare congenital cardiacvascular anomalus with an abnormal connection between coronary artery termination and a great vessel or cardiac chamber. Purpose: The valuation of MDCT 256 – slices findings coronary artery fistula. Material and method: This retrospective cross – sectional study involved 1849 patients underwent 256 - slices coronary computer tomography angiography (CCTA) at the Huu Nghi Viet – Xo hospital between July 2017 and July 2018. We evaluated the quantity and classify of CAFs, the vessel of origin, conduit site, measure of varicose vein, size of aneurysm. We also evaluated the coronary artery attach anomalies. Result : Included in 1849 patients underwent 256 slices CCTA, we determined 17 (0,92%) patients had CAFs (11 men, 6 women; main age 70, age range 54-88 years; 17/17 patients undergoing first time with chest pain). The source of origin of CAFs, 11 (64,7%) patients had two sources. The type of CAFs detected, 15 (88,2%) patients had coronary to pulmonary trunk artery fistula. The CAFs with two sources of origin had most frequency of manifestration for varicose vein and aneurysm. We also findings 6 (35,3%) patients had coronary artery attach anomalies, 4/6 patients had myocardial bringing. Conclusion: The coronary artery fistula are un common congenital cardiac anomalies. Our study dertemined 0,92%, which is higher than the known ratio base on literature review. The most common type of CAFs was coronary to pulmonary trunk artery. Coronary CTA with different rendering menthods had been s useful, noninvasive imaging for the diagnosis of CAFs and other coronary anomalies. Keywords :Coronary artery anomalous, coronary artery fistular, multidetector computer tomography, coronary CT angiography.
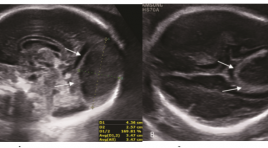
Huyết khối nội lưu các xoang tĩnh mạch màng cứng tổng quan và báo cáo ca
30/03/2020 23:06:20 | 0 binh luận
Dural venous sinus thrombosis: an overview and case report ABSTRACT: Torcular herophili is the site of the confluence of superior sagittal sinus, tranverse sinus, straight sinus and occipital sinus [1]. Anatomy of torcular herophili is highly variable. Dilatation of torcular herophili is presented as an anechoic triangular structure, with venous flow communicated with other sinuses and cerebral veins. Torcular herphili thrombosis is a rare cerebrovascular disorder[9, 11, 13, 15], and the prenatal diagnosis of this condition is difficult. This condition can be caused by the abnormalities that produce prothrombotic states, such as acute fetal distress, and congenital deficiency of anticoagulants such as antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S[8]. Prenatal ultrasound is the firs-line modality for diagnosing and monitoring thrombosis of the torcular herophili. In addition, color-Doppler ultrasound helps to differentiate this disorder from other cerebrovascular malformations such as vein of Galen aneurysmal dilatation[5] and identify the presence of collateral vessels and its relationship with other dural sinuses[6, 7]. As a complementary technique, MRI can provide additional information to rule out secondary cerebral damages and associated brain malformations. Prognosis of this disorder is highly variable, ranging from spontaneous resolution with a normal neurologic outcome to severe neurologic deficits and death. We present 1 case of thrombosis of ectatic torcular herophili with serial sonographic and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations, along with review of literature of this condition. Besides, we have a routine follow-up of the new-born mental development until now. Keywords : thrombosis, torcular herophili, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Method: case-report, prospective study from July 2017 until now.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












