Bước đầu đánh giá hiệu quả của phương pháp tạo hình đốt sống qua da trong điều trị xẹp đốt sống mới do loãng xương
31/03/2020 18:40:12 | 0 binh luận
The result of percutaneous vertebroplasty in treatment of recent osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures SUMMARY Purpose: To assess short-term outcomes in patients with recent osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty. Methods : About 15 patients suffered from recent osteoporotic vertebral fractures underwent the percutaneous vertebroplasty between April 2012 and October 2013 at Radiology Department, Bach Mai hospital. The average age of patients was 75.9 years (14 womens). Measurements of pain and mobility were compared at 1 day, 1 week, 1 month and 3 months after the procedure. Results: Pain scores were significantly reduced compared with before treatment at every follow-up period. The preprocedural mean VAS score was 9.1. At follow-up, mean VAS scores ranged from 2.2 to 4.8. The pre-treatment mean RDQ score was 18.8 and it ranged from 8.9 to 11 at follow-up. Conclusion : Percutaneous vertebroplasty offers significant benefits in relief pain and improve mobility for recent osteoporotic vertebral fractures.
Nhận xét kết quả bước đầu vai trò của f-18 fdg pet/ct trong phát hiện vị trí tổn thương ở bệnh nhân ung thư chưa rõ nguyên phát tại Bệnh viện K
18/12/2019 14:29:08 | 0 binh luận
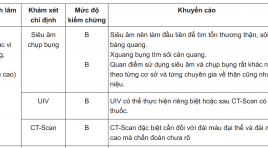
Remarking the first step results of the role of f-18 fdg pet/ct in determining the positive position in the unknow cancer in the cancer national Hospital SUMMARY Carcinoma of unknown primary tumors (CUP) is present in 2% of all patients with malignant neoplasms. However, only 20% - 73% of primary sites are identified before the patients die. Currently, F-18 FDG PET/CT is widely used for the diagnosis of CUP. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of F-18 FDG PET / CT in these patients. Results: 30 patients with unclear cancers were treated with F-18 FDG PET / CT, the mean age of patients was 53.6 ± 9.7. There were 18/30 patients (60%) who were diagnosed with cancer. PET / CT (compared with pathology), the rest is false 12/30 BN (40%). Localized nodal metastases is an area of the neck. The most common pathological anomalies were squamous cell carcinoma (56.7%), adenocarcinoma (16.7%) and noncancerous cancers (26.7%). Conclusion: F-18 FDG PET / CT is a useful method for detecting primary malignant sites in patients with primary tumors.
Đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ của u sợi và u vỏ - sợi buồng trứng
18/12/2019 09:32:38 | 0 binh luận
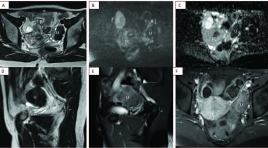
Value of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of ovarian thecomas/fibrothecomas SUMMARY Purpose: Our study aims to study the value of conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) combined with DWI and Dynamic technique in the diagnosis of thecomas/fibrothecomas and differential diagnosis benign with malignant ovarian tumors. Material and method: In total, 68 thecomas/fibrothecomas, 63 malignant ovarian tumors were included in our study. All patients underwent conventional MRI, DWI in 79 cases and Dynamic enhancement (DCE) in 14 cases. The clinical features and characteristics of conventional MRI, DWI and DCE of these two groups were analyzed. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values, Tmax, MRE were measured and compared between groups. Univariate analysis, multivariate logistic regression analysis were analyzed. Sensitivity (Se), Specificity (Sp), Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV) were included. Results: All the fibromas/fibrothecomas showed hypo-isointensity on T1 weighted imaging (T1WI) and 77.9 % lesions showed hypo- to isointensity on T2 weighted imaging (T2WI). After administration of contrast medium, 82,3% tumors appeared as minor to mild enhancement, 71,4% benign tumor had type 1 curve, Tmax cutoff were 230s with Se and Sp 71,4%. MRE were not already measured because of few cases. On DWI, 68,4% fibromas/fibrothecomas manifested no signal intensity or low signal intensity. The ADC cutoff were 1.07 x 10-3 mm2/s to differentiate benign from malignant ovarian tumors. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that only T2WI and ADC were the important indicators in discriminating fibromas/fibrothecomas or benign tumors from malignant ovarian tumors. Conclusion : The combination of DWI, DCE with conventional MRI is of great value in the diagnosis of fibromas/fibrothecomas and differentiation benign ovarian tumors from malignant ovarian tumors Keywords: Fibromas/fibrothecomas, Conventional magnetic resonance imaging, Diffusion-weighted imaging, Apparent diffusion coefficient value, Dynamic contrast enhancement.
Các tiến bộ kỉ thuật cộng hưởng từ trong hình ảnh u não và ứng dụng tại bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy
31/03/2020 16:19:05 | 0 binh luận
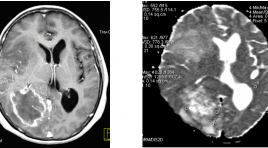
Advanced MR techniques in brain tumor imaging and the application at Choray hospital SUMMARY MRI is the imaging modality of choice for brain tumours. Advanced MRI techniques have significantly developed and used clinically in imaging of brain tumor such as: diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Conventional MR imaging (MRI) provides mainly anatomic or structural information about the brain and tumor. Unlike conventional imaging, advanced MR techniques also provide physiological information concerning tumor cellularity, white matter invasion, metabolism and hemodynamics.These techniques can be used to diagnosis, differential diagnosis, grading, surgical planning, and monitoring of therapeutic response of brain tumors. A principles of the physiology, techniques, and clinical applications of these techniques is provived. Some experience of using these technique in the domain of brain tumor at Choray Hospital were also presented in this article. Key words: Advanced MR techniques, brain tumor, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), conventional MRI.
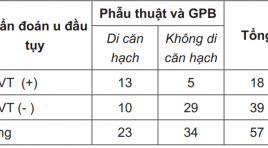
Gía trị của cắt lớp vi tính 64 dãy trong chẩn đoán u đầu tụy
31/03/2020 15:49:48 | 0 binh luận
The value of CT- Scanner 64 multi-detector in diagnosis of pancreatic head tumor summar y Objectives : Evaluating the role of CT scanner 64 multidetector in diagnosing of pancreatic head tumor. Subjects and methods: 57 patients were diagnosed of pancreatic head tumor on MSCT 64 multi-detector and were operated with pathology result confirmed from January 2012 to December 2012 in Viet Duc hospital. Results: The sensitivity, specificity, fault negative rate, accurate diagnosis and positive predictive value of MSCT 64 detectors in definite diagnosis were 96%, 100%, 3.4%, 98%, and 100% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, fault negative rate, accurate diagnosis and positive predictive value of MSCT 64 detectors in local invasive diagnosis were 74%, 87%, 26%, 86%, and 94% respectively. The evaluation vascular invasion were with the Se of 75%, Sp of 95%, FNR of 25%, ACC of 85%, PPV of 88%. The value of metastasis diagnosis were with Se of 57%, Sp of 85%, FNR of 43%, ACC of 71%, PPV of 72%. Accuracy of surgery technique proposing was 87.7%. Conclusion: CT scanner 64 multi-detector has high sensitivity and specificity in definitive diagnosis, evaluating the invasion and proposing the diagnosis possibilities. Key words : CT scanner 64 multi-detector, pancreatic head tumor.
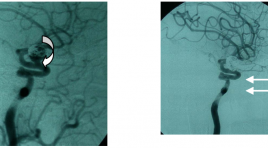
Bước đầu đánh giá tái thông túi phình và vai trò chụp mạch cộng hưởng từ 1,5 Tesla trong theo dõi phình mạch não sau điều trị can thiệp nội mach
31/03/2020 15:44:12 | 0 binh luận
summar y The assessment of aneurysms recanalization and the role of MR angiography 1,5 Tesla in follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolization in comparison with digital subtraction angiography. Purpose : The evaluation of aneurysmal recurrence and the role of three-dimensional time of flight MR angiography in follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolization Material and methods: 66 patients harbored 68 selectivetreated intracranial aneurysms, in which 30 patients were both underwent three-dimensional time of flight MR angiography (MRA) and DSA, 33 patients were done only one method MRA, 0 patient were done only one method DSA. Results: The recanalization was observed in 68 selectivetreated intracranial aneurysms (39.7%), including major recanalization in 11 patients (16.1%). Compared with DSA, the overall sensitivity and specificity of MRA were 100% and 93.75%. MRI found out the ischemie lession concerning aneurysmal embolization about 8.8% and the hydrocephalus about 9.1%. Conclusion: The problem of aneurysmal recurrence shoud be considered. MRA was non-invasive method and was of very high sensitivity and specificity in follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolization.
Đánh giá tình trạng co mạch não ở bệnh nhân xuất huyết dưới nhện bằng siêu âm doppler xuyên sọ
31/03/2020 15:36:51 | 0 binh luận
summary Subarachnoid hemorrage (SAH) is common emergency in patients who got the congenital or acquaired cranio-vascular diseases. This results from some reasons such as: aneurysm ruption, AVM or trauma. Vasospasm increases disability and mortality in patients who have SAH. Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound (TCD) is the good method to diagnose early this stage with many advantages as non-invasive, cheaply, the sensitivity and specification is rather high. Purpose : 1. Evaluating the vasospasm after SAH by TCD; 2. Researching the correlation between the level SAH as well as the clinical state of patients and the velocity blood flow of the middle cerebral artery recorded by TCD. Subjects and methods : We have prospected 20 patients who were diagnosed SAH on Computed tomography. TCD was performed 2 times: the 3rd – 4th day and the 8th – 9th day after getting SAH. Those whose peak systolic velocity in middle cerebral artery was ≥ 120cm/s considered vasospasm. Their clinical states were also recorded at the same times. Results : 2 patients (10%) got vasospasm of MCA at the 8th – 9th day after SAH. The correlation between the level SAH as well as the clinical state of patients and the velocity blood flow of MCA is unclosed. Conclusion : TCD can detect early the vasospasm but the accuracy of this method is higher in the patients whose SAH is primary and non - operated.
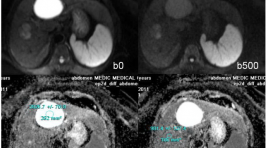
Vai trò của ADC trong chẩn đoán phân biệt giữa tổn thương lành tính và ác tính ở gan
31/03/2020 15:26:23 | 0 binh luận
summary Purpose : Assessing the role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) measurement in differentiation of benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions. Methods and Materials: Retrospectively evaluated the 248 patients cases, executed hepatic MRI at Medic Medical center, from on February 2011 to on February 2013, age range 41 - 78years, with 142 benign hepatocellular lesions (30 FNHs, 9 HCAs, 63 hemangiomas and 40 cysts) and 104 malignant lesions (76 HCC and 28 metastasis) diagnosed, 50 patients had normal liver. All the patients executed Diffusion weighted imaging - MRI with three b values (0, 500, 800 sec/mm2) on the Siemens Avanto 1,5T MRI. Results : We found difference between ADC of benign lesions compared with malignant lesions (mean ± standard deviation): ADC of normal liver (1.242 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.33), FNH-HCA (1.742 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.40), Hemangiomas (2.084 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.46), Cyst (2.861 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.34), HCC (1.093× 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.37), Metastasis (1.126 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.48). ADC of benign lesions: (2.327 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.41), compared with malignant lesions: (1.113 × 10−3 mm2/sec ± 0.39). Conclusion: Mean value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) contribute to differential diagnosis between benign and malignant focal hepatic lesions.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












