ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH SIÊU ÂM, CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ VÀ CHỤP MẠCH SỐ HOÁ XOÁ NỀN CỦA MỘT SỐ BỆNH NHÂN TĂNG SẢN LÀNH TÍNH TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT
17/10/2023 15:05:17 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: Describe Imaging features Ultrasound, MRI and DSA of 14 patients who have benign prostatic hyperplasia with acute urinary retention, were treated by PAE. Method and results: A descriptive study without control in patients hospitalized for acute urinary retention was diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia at the Bach Mai hospital from 07/2017 to 07/2018. The patients were examined clinical, ultrasound, MRI before and after intervention. The average PV (cm3) on ultrasound and MRI are 80,57±50,58 cm3 and 82,35±51.24 cm3, 9 patients have thickening of bladder wall (64,3%), 3 patients have bladder diverticulum (21,4%), 78,6% hyperplasia at the transition zone, 7,1% hyperplasia at the central zone and 14,3% hyperplasia at both the transition zone and central zone. On DSA, with 26 pelvices side were perfomed successful, there were 22 pelvices side with one prostate artery and 4 pelvices side with 2 prostate arteries, the average diameter of prostate with pelvic side which one prostate artery is 1,92 ± 0,52 mm; with pelvic side which two prostate arteries is 1,45 ± 0,16mm. Keywords : prostatic arterial embolization, acute urinary retention, benign prostatic hyperplasia, ultrasound, MRI of BPH.
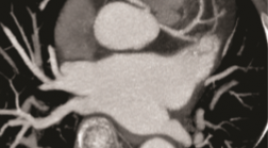
NGHIÊN CỨU TƯƠNG QUAN GIỮA CHỤP CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH 640 LÁT CẮT VÀ CHỤP MẠCH SỐ HÓA XÓA NỀN TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN BỆNH LÝ ĐỘNG MẠCH VÀNH TẠI BỆNH VIỆN ĐA KHOA QUỐC TẾ VINMEC ĐÀ NẴNG
17/10/2023 12:18:28 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purposes: To descriptive coronary artery imaging by the 640 slice coronary computed tomography scanning. To determine the value between coronary computed tomography scanning angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Materials and methods: Describe imaging characteristics and stratify. There are 310 patients with the 640 slice coronary computed tomography scanning Toshiba Aquillion One in the period from 1.1.2019 to 30.8.2021 and among whom 42 cases followed by digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Results: The average age is 59,5±12,5 years old and male/female about 3/1. HR 68,28±18,67 bpm. Radiation dose < 5 mSV (90%), average dose 3,79±0,96mSv. Calcium score is mostly mild level, distributed all arterial branches. LAD is accounted for the highest percentage of calcification(> 50%) and many narrow position. The most narrow position is proximal location and the most narrow level is mild. The value table Value Se (%) Sp (%) Accuracy (%) LM 100 100 100 LAD 97,5 100 97,6 LCx 90,9 90,0 95,2 RCA 93,3 91,7 92,9 Conclusion: .Coronary computed tomography scanning evaluated anatomy, abnormal orginal position, variant and the narrow of position and level. Digital subtraction angiography has difficultly identifying abnormal variant except myocardial brigde. The values with sensitivity, specificity and accurary of coronary artery stenosis assessement by computed tomography scanning angiography showed high. Keywords: coronary aretry, coronary computed tomography scanning, digital subtraction angiography, coronary artery anatomy, coronary artery variant.
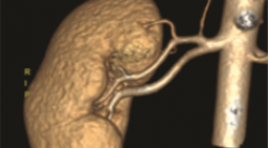
NGHIÊN CỨU GIÁ TRỊ CỦA CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH 256 DÃY TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ GIẢI PHẪU MẠCH MÁU THẬN ĐOẠN NGOÀI THẬN Ở NGƯỜI SỐNG HIẾN THẬN
17/10/2023 11:45:34 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To determine the accuracy of 256-slice computed tomographic angiographyin the evaluation of renal arterial and venous structures of living donor kidney system and its anatomical variations in living kidney donors, and the correlation of CTRA findings with those observed during kidney harvesting Materials and Methods: 202 potential living donor candidates were included to this study, who had CTA for the assessment of their renal vessels in our hospital between January 2021 and June 2022. The number, course, and drainage patterns of the renal vessel were retrospectively observed from the scans. Anomalies of renal arteries, veins and inferior vena cava (IVC) were recorded. Multiplanar reformations (MPRs), maximum intensity projections, and volume rendering were used for analysis. The results obtained were correlated surgically. Results: Two-hundred and two patients who had undergone laparoscopic nephrectomy as living donors were included: 109 female and 93 male donors Mean age of donors was 33.19± 7.09 years. Bilateral renal arteries mostly originate at the level of the L1 vertebral body and the L1/2 disc. Mean diameter of right renal artery was 5.94 ± 0.94mm and left renal artery was 5.90±0.94mm. The mean length of the right renal artery was 33.9 ± 13.5 mm and left renal artery was 27.8 ± 10.1 mm. The distribution of accessory renal artery was 15.3% on right side and 19.8% on left side. 8.9% has multiple renal veins, more common in the right side. Sn, Sp, NPV, PPV compare open oparative nephrectomy 93.75-100%. Conclusion: 256-slice computed tomographic is an accurate, safe and noninvasive diagnostic tool for determination of renal artery and vein abnormalities in living kidney donors preooparative. It helps with surgery planning, choosing operation side and exclusion of donors. Keywords: Kidney transplantation; Living renal donor; Computed tomography angiography; Renal artery

ĐÁNH GIÁ KẾT QUẢ CHỌC HÚT MÁU TỤ NỘI SỌ TRÊN LỀU TỰ PHÁT DƯỚI ĐỊNH VỊ KHÔNG KHUNG VÀ CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH
17/10/2023 11:21:32 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives: To evaluate the results of spontaneous intracranial hematoma aspiration under frameless positioning and computed tomography. Methods: Retrospective study of 55 patients (patients) diagnosed with spontaneous intracranial hematoma (MTNS) by computed tomography (CT) scan from 05/2017 to 04/2022 at 108 Central Military Hospital. Results: The mean volume fraction of residual hematoma was 26.24% after draining for an average of 2-3 days, respectively. There was no significant difference in the percentage of residual hematoma volume after draining. The favorable 1-month outcome with GOS 4 or 5 was significantly better in the group with a hematoma reduction of more than 60% compared with baseline hematoma volume (p=0.047), although no significant difference was observed. told at 6 months after aspiration. The factor that was significantly correlated with favorable outcome after aspiration 6 months was the ratio of final hematoma volume after drainage (p=0.016). Final hematoma volume ≤ 15 ml was correlated with favorable neurological outcomes at 1 and 6 months (p = 0.001 and 0.038). Conclusion: There was no difference in the final residual hematoma volume and neurological outcome after 6 months depending on the time of aspiration aspiration of the hematoma. The factor influencing neurological outcome after 6 months of aspiration is the final hematoma volume remaining after drainage. Final hematoma volume ≤15ml was correlated with favorable neurological outcome at 1 and 6 months. This study provides the goal for hematoma aspiration technique to leave a residual hematoma volume ≤ 15ml. Keywords: Spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hematoma, computed tomography, frameless navigation
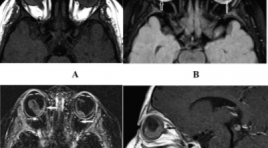
ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ 3.0 TESLA CỦA U NGUYÊN BÀO VÕNG MẠC
14/10/2023 12:30:07 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: To describe the imaging characterization of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of retinoblastoma Material and method: About 50 patients were diagnosed and monitored for retinoblastoma treatment at the National Eye Hospital and performed 3T magnetic resonance at Saint Paul General Hospital from October 2020 to May 2022. Description of tumor intraocular lesion: Number, location of tumor, largest diameter. Description of tumor characteristics: Signals on sequences T1W, T2W, FLAIR, DWI and enhancement properties after injection. Other accompanying features: Intra-tumor calcification, retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, optic nerve invasion, invasion outside the eyeball, intracranial lesions Results: 50 patients in the study had an average age of 21.2 months, and the age of the one-eye disease group was higher than that of the two-eyed disease group. 3T MRI is a good method for diagnosing retinoblastoma tumors, with the largest dimension measuring 13.8 ± 4.2 mm, the tumor distribution is mainly on the retina in the post-equatorial region. Tumor image on MRI compared with vitreous signal, mostly increased signal on T1W (92.6%), decreased on T2W (98.8%), increased on FLAIR (100%), restriction on DWI (100%) and enhancement after injection. Signs of calcification are specific for retinoblastoma, however, on MRI the ability to detect calcification is limited. Although the detection of calcification is limited, it has good ability in invasive assessment such as choroidal invasion (15.6%), scleral invasion (3.1%), optic nerve invasion (31.3). %). Severe prognostic signs such as retinal detachment (34.4%), vitreous bleeding (26.6%). Conclusion: 3T magnetic resonance is a good method of diagnosing retinoblastomas as well as assessing the invasiveness of tumors. Keywords: Retinoblastoma, High resolution magnetic resonance imaging of retinoblastoma

GIÁ TRỊ CỦA CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ ĐỘNG SÀN CHẬU TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN HỘI CHỨNG ĐẠI TIỆN TẮC NGHẼN
13/10/2023 17:58:31 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives : to describe the clinical features and images of MR defecography in patients with obstructive defecation syndrome, afterward evaluating the value of MR defecography in the diagnosis of obstructive defecation syndrome. Subjects and methods: cross-sectional study, 33 patients were diagnosed with obstructive defecation syndrome according to ROME IV criteria, were assigned to have MR defecography at Saint Paul General Hospital, during the period of study from January 2019 to July 2022. Results: About the general characteristics of the study group: mainly in women with 84,8%, the average age is 63.5 ± 12.5 years old. Rectocele is the most commonly detected lesion on clinical examination, with 12/33 cases, accounting for 36.4%. About image characteristics on pelvic floor dynamic MRI: the mean value of H line in normal phase is 4.7 ± 0.9cm, in strain phase is 5.9 ± 1.5cm. The mean value of the M-line in normal phase is 2.0 ± 0.2 cm, and 4.1 ± 0.3 cm in strain phase. Rectocele is the most common lesion, accounting for 63.6%. The detection rate of rectocele and associated lesions (cystocele, uterus descent, cervical descent, vaginal descent) on MR defecography is higher than that on clinical examination, the difference was statistically significant with p<0.05. Conclusion : Our study contributes to clarifying the high applicability of MR defecography in diagnosing the causes and grading of pelvic floor prolapse, pelvic organ prolapse in patients with obstructive defecation syndrome, combined with clinical symptoms to help clinicians make appropriate treatment indications for each patient. Key words: MR defecography, Obstructed defecation syndrome, Rectocele. *

ĐÁNH GIÁ KẾT QUẢ ĐIỀU TRỊ ĐAU DÂY V BẰNG PHƯƠNG PHÁP PHẪU THUẬT GIẢI ÉP VI MẠCH VÀ TIÊM CỒN KHOANG MECKEL
13/10/2023 17:31:51 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To evaluate the results of treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by microvascular decompression surgery and Meckel’s cavity alcohol injection Subject and method: 62 patients with trigeminal neuralgia which medical treatment did not control the pain or had side effects, the patient then received microvascular decompression surgery or Meckel’s cavity alcohol injection performed at Saint Paul general Hospital from January 2017 to June 2021 Results: From January 2017 to June 2021, 62 patients with trigeminal neuralgia underwent microvascular decompression surgery or Meckel’s cavity alcohol injection at Saint Paul general Hospital. Of these, 24 patients were treated by surgical decompression and 38 patients were treated with Meckel’s cavity alcohol injection. The results of pain relief time of both methods in both short and long term are not statistically significant with p<0.05 according to Log rank test. The complication rate of the two methods is similar right after the intervention but will be lower in the surgical group after 3 months of intervention (p < 0.05 in Chi-squared test). Conclusion: The short and long-term analgesic effect of the two methods of microvascular decompression surgery and Meckel’s cavity alcohol injection are similar, the difference is not statistically significant. Key words: Microvascular decompression surgery, Meckel’s cave alcohol injection, Trigeminal neuralgia.
NGHIÊN CỨU KẾT QUẢ SỚM ĐIỀU TRỊ UNG THƯ BIỂU MÔ TẾ BÀO GAN Ở VỊ TRÍ NGUY CƠ BẰNG ĐỐT SÓNG CAO TẦN
13/10/2023 15:24:36 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background: Radiofrequency ablation is a radical treatment with high efficiency in the very early stages (BCLC 0) and early stages (BCLC A). However, with tumors in risk locations, radiofrequency ablation has many difficulties in determining the tumor on ultrasound and the risk of damage to adjacent organs. Objectives: To evaluate early outcomes of RFA in treating HCC patients in risk locations. Subjects and methods: 50 HCC patients in risk locations underwent ablation at the radiology center of Bach Mai hospital. Follow up 3 months to evaluate the effectiveness after the treatment. Results: 50 patients male/ female=41/9, average age = 61.63 years old (35–86). 94% patients with HCC have a history of cirrhosis and 88% patients with HCC have a history of hepatitis. Among the tumors in risk locations, the tumors adjacent to the diaphragmatic accounted for the highest rate of 44%. We infused the artificial ascites in 20 cases(40%) and the pleural effusion in 14 cases(28%). Follow-up 3 months after treatment, there was no the major complication. 7 patients had the atelectasis. The rate of tumor complete response was 92%, the rate of tumor incomplete response was 4%. 2 patients appeared new lesions(4%). Conclusion: Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive, safe and effective method for tumors in risk locations. Keywords: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for HCC in risk locations , the image-guided techniques, the outcome after the treatment.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












