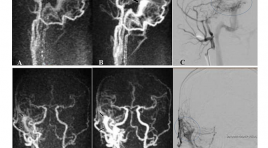
Vai trò của mra có tương phản động học với độ phân giải thời gian cao trong đánh giá rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng nội sọ
01/06/2020 17:09:26 | 0 binh luận
The role of Time-resolved CE-MRA in evaluation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas SUMMARY Objective: We evaluate the role of Time-resolved CE-MRA in diagnosis, localization, and detecting cortical venous drainage of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) in comparison with Digital Subtraction Angiography Subjects and methods : Prospective study between 1/2015 and 4/2019, 93 patients (35 male, 58 female), aged from 11 to 88 (mean 55), diagnosed of DAVF on conventional MRI, 55 of them had Time-resolved CE-MRA and then underwent DSA for confirming the diagnosis. Results: In our study (n=55), Time-resolved CE-MRA showed high sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value in diagnosis of DAVF (98%, 100%, 100%, 83,3%, 98,2% respectively) and in detecting cortical venous drainage (80%, 96,67%, 95,23%, 85,29%, 89,09% respectively). Kappa coefficient showed very good agreement between Time-resolved CE-MRA and DSA in detecting the location of DAVF. Conclusion: The use of Time-resolved CE-MRA is valuable in diagnosis, localization, and detecting cortical venous drainage of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF). This noninvasive examination would be helpful in choosing patients with DAVF, especially patients with high risk of complications for further cerebral angiography. Keywords: DAVF, dural arteriovenous fistula, cortical venous reflux, cortical venous drainage, Time-resolved CE MRA.
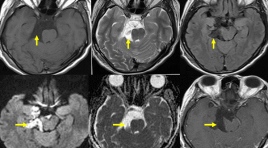
Đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ thường qui và khuếch tán của u nang thượng bì nội sọ
22/12/2019 13:07:55 | 0 binh luận
U nang thượng bì là một tổn thương bẩm sinh có nguồn gốc từ ngoại bì phôi. Bệnh chỉ chiếm 1% trong các khối u vùng nội sọ, là khối u lành tính tiến triển chậm và không có triệu chứng trên lâm sàng.
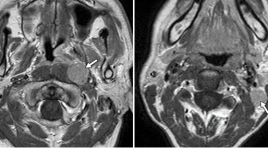
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ thường qui và cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán trong chẩn đoán ung thư vòm họng
25/12/2019 17:54:41 | 0 binh luận
Bệnh ung thư vòm họng (NPC - Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma) ở nước ta có tỷ lệ cao, đứng hàng đầu trong các bệnh ung thư đầu cổ, đứng hàng thứ 5 trong các bệnh ung thư nói chung. Nhưng các triệu chứng lại không điển hình hầu hết là các triệu chứng của các cơ quan lân cận.
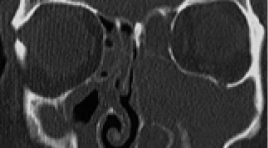
Đặc điểm hình ảnh u nhú đảo ngược mũi xoang trên cắt lớp vi tính
17/03/2020 16:04:59 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics of sinonasal inverted papilloma on CT Scanner SUMMARY Purpose: Describe characteristics imaging of sinonasal inverted papilloma( SIP) on CT Scanner. Methods: Prospective cohort from July 2018 to July 2019, including 50 patients with histopathology inverted papilloma and CT Scanner standards. Results : 50 patients (34 males and 16 females) with SIP in our study. Patients were a mean of 53,86 years old ( range: from 7 to 90) . SIP location: maxillary sinus (74%), frontal ethmoid sinus (66%), posterior ethmoid sinus (40%), ostiomeatal complex (80%), characteristics imaging of SIP: thin sinonasal wall( 72%), bilobed mass(70%), focal hyperostosis(82%), osteochondroma,(32%). Conclusion: Characteristics imaging on CT Scanner: thin sinonasal wall, bilobed mass, focal hyperostosis, osteochondroma is very valuable in diagnosis SIP. Keywords : Sinonasal inverted papilloma. CT Scanner.

Đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của Mri 3.0T trong chẩn đoán hạch cổ ác tính tại Bệnh viện Ung bướu Đà Nẵng
04/12/2019 14:29:09 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics and the value of 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging in malignant cervical lymphadenopathy SUMMARY Purposes: Describe imaging characteristics and assess value of 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating benign and malignant cervical nodes. Materials and methods: There are 96 consecutive patients with cervical nodes were undergone a 3 Tesla magnetic resonance exam from 10/2016 to 9/2017 and compared with histopathological results. Results: The average age is 55 years old, and male/female=2/1. Loss of the hilar fat, irregular margins, heterogeneous parenchyma on fat-suppressed T2-weighted images were found in malignant and benign lymph nodes were 74.5% and 4.44%, 72.5% and 4.44%, 88.2% and 4.44%. Diagnosis malignant lymph nodes based on the diameter has got the high valuation with p<0.001. Different size criteria for benign and malignant lymph nodes found that a 11.5 mm size cutoff in the short axis diameter achieved Se 76.5%, Sp 95.6%, Acc 85.4%. In the 67 histologically proven malignant lymphadenopathies, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value was 0.926 ± 0.133 mm2/sec. In the 29 pathologically confirmed benign lymph nodes, an average ADC value of 1.367 ± 0.165 mm2/sec was found. For differentiating between benign versus metastatic lymph nodes, morphological criteria displayed Se 80.0%, Sp 80.0%, Acc 85.4% whereas combined use of morphological criteria on nodal architecture and ADCs yielded Se 98%, Sp 82.2%, Acc 90.6%. Conclusion : 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive effective technique that can provide useful information in diagnosing benign and malignant nodes in the neck.
Nghiên cứu giá trị chẩn đoán ung thư tuyến giáp của phân độ EU - tirads 2017
04/12/2019 21:35:27 | 0 binh luận
Research into the value in the diagnosis of thyroid cancerof the EU-TIRADS 2017 classification SUMMARY A diagnostic test study was conducted at Bạch Mai hospital to evaluate the efficacy of Ultrasound andthe EU-TIRADS 2017classsification of thyroid nodules. Result: 170 patients with thyroid noduleswere prospectively evaluated by B-mode ultrasound and the EU-TIRAD 2017 classsification, followed by the fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy. The averae age is 46,7 ± 11,5 years old and female/male = 5,5. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, accuracy for the EUTIRADS 2017 were 98,2%; 34,5%; 74,3%; 90,9%; 76,7%.TIRADS 5 is the highest (64,7%). 4 features of high suspicion are irregular margins, microcalfifcations, marked hypoechogenicity, “taller – then -wide” shape; the sensitivity, specificity 70% and 93%; 35% and 91%; 50% and 79%; 58% and 82%. Conclusion: TIRADS 5 is the highest and the EU-TIRADS 2017 classification and pathology indicates strong evidence. Key Words: The EU-TIRADS 2017, thyroid nodules on ultrasound, thyroidcancer.
Giá trị của CHT khuếch tán trong chẩn đoán phân biệt áp xe não và u não hoại tử hoặc u não dạng nang
23/05/2020 12:23:51 | 0 binh luận
Role of diffusion weighted mr imaging in the differentiation between brain abscess and cystic/ necrotic brain tumors SUMMARY Objective: To evaluate the role of diffusion-weighted MR Imaging in the differentiation between brain abscess and cystic/necrotic brain tumors. Material and method: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 53 individuals presenting with rim enhancement intra-axial mass on brain MR image at Da Nang Hospital from August 2012 to August 2013. Diffusion-weighted image were also acquired with b value were 0, 50, 1000 using 1.5T Phillp Achieva MR system. Results: 28 patients had brain abscesses and 23 were diagnosed with brain tumors pathologically. The sensitivity and specificity of MRI in the diagnosis of brain abscess were 96.4% and 96%, respectively. PPV was 96.4% and NPV was 96%. There was a statistically significant difference in mean central ADC value between abscess and tumor, as 0.71 ± 0.24 x 10-3 mm2/s and 2.23 ± 0.44 x 10-3 mm2/s (p = 0,004) respectively. Mean peripheral ADC value showed no difference between 2 groups, as 0.78±0.26 x 10-3 mm2/s for abscess and 0.82±0.28 x 10-3 mm2/s for tumor (p = 0,132). At cut-off point of ADC ≤ 0.86 x 10-3 mm2/s, ROC curve for ADC showed 94.6% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Conclusion: Diffusion-weighted MR image had high sensitivity and specificity in differentiation between brain abscess and cystic/necrotic tumor. Keywords: Diffusion-weighted MR image, brain abscess, brain tumor, ADC value.
Xác định kích thước hố yên người Việt Nam bằng chụp cắt lớp điện toán
02/04/2020 20:52:36 | 0 binh luận
Normal sizes of the sella turcica of VietNamese on computed tomography SUMMARY: Objectives: To determine the normal sizes of the sella turcica of Vietnamese from 1 to 30 y.o. on computed tomography. Methods: cross-sectional description of retrospective study. The length, depth, width and volume of sella turcica were measured on computed tomography of 705 patients at the No.1 Children’s Hospital and the Trưng Vương Emergency Hospital, HCM city, Vietnam , from January to June, 2011. Results: The mean size values of the sella turcica were divided into six age groups:1 - 5, 6 - 10, 11 - 15, 16 - 20, 21 - 25, 26 - 30 with length (7.16 ± 1.43 mm, 8.11 ± 1.09 mm, 8.48 ± 1.14 mm, 9.99 ± 1.47 mm, 10.20 ± 1.16 mm, 10.39 ± 1.17 mm); depth (5.74 ± 1.16 mm, 6.74 ± 1.10 mm, 11.35 ± 1.42 mm, 12.67 ± 1.86 mm, 12.73 ± 1.5 2mm, 12.72 ± 1.41 mm); width (9.14 ± 1.67 mm, 10.44 ± 1.41 mm, 11.35 ± 1.42 mm, 12.67 ± 1.86 mm, 12.73 ± 1.52 mm, 12.72±1.41mm) and volume (196.69 ± 85.28 mm3, 286.33 ± 77.18 mm3, 336.19 ± 90.90 mm3, 491.18 ± 146.68 mm3, 500.05 ± 130.09 mm3, 523.80 ± 119.58 mm3). Conclusions: The sizes of sella turcica increase from 1 to 20 years old; no significant increasing from 21 to 30 y.o. Differences in the sizes of sella turcica between males and females are not statistically significant. Keywords: Sella turcica
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












