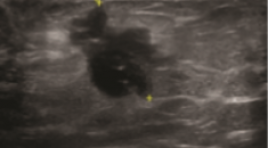
GIÁ TRỊ KẾT HỢP CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI SÓNG BIẾN DẠNG VÀ CHỌC HÚT TẾ BÀO BẰNG KIM NHỎ TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN UNG THƯ VÚ
17/10/2023 12:02:16 | 0 binh luận
Objective: Describe characteristics of 2D ultrasound images and shear wave elastography (SWE) ultrasound breast tumor. Determinate the combined value of SWE ultrasound and fine needle aspiraton cytology (FNAC) in diagnosis breast cancer. Subject and method: 79 female patients with breast tumors were assigned 2D and SWE ultrasound, measure shear wave velocity (SWV) internal tumor and peripheral tumor, classified according to ACR - BIRADS 2013. Patients were assigned FNAC ultrasound guided and histopathological biosy after surgery. Compare the result 2D, SWE ultrasound and FNAC with the result of histopathological biopsy after surgery to determine the combined value of SWE ultrasound and FNAC in diagnosis breast cancer. Result: 79 patients with 37 benign breast tumors, 42 malignant breast tumors. Mean SWV of malignant breast tumors are lower than benign breast tumors (p < 0.01). Cutoff SWV in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumor at peripheral tumor 2.25 m/s; internal tumor 5.1 m/s. SWE ultrasound combined with FNAC has high value in diagnosis breast cancer with Se = 97.6%, Sp = 94.6%, Acc = 96.2%, PPV = 95.3%, NPV = 97.2%, high concordance with histopathological result after surgery Kappa = 0.924. Keywords : Elastography, fine needle aspiraton cytology, cancer, breast.
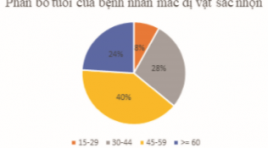
GIÁ TRỊ CỦA CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ DỊ VẬT ỐNG TIÊU HÓA SẮC NHỌN
13/10/2023 17:05:44 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Ingested foreign bodies are one of the reasons why patients need to be hospitalized in the emergency room. Although most gastrointestinal foreign bodies can be eliminated from the body on their own, there are still some cases that cause complications, even death. In terms of foreign body morphology, there are 3 main groups, sharp-pointed foreign bodies, round foreign bodies and long foreign bodies, of which sharp-pointed foreign bodies are the group that often causes complications, especially perforation complications. There are many methods to diagnose this condition such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT) and endoscopy. In recent years, the popularity of CT has made this method widely used in the assessment of sharp-pointed gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Objective: In order to evaluate the effectiveness of CT in diagnosing sharp foreign bodies, we would like to conduct the study "Value of computed tomography in evaluation of sharp-pointed ingested foreign bodies". Subjects and research methods: A descriptive study of 25 patients with sharp-pointed foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract who underwent CT scan at the Radiology Department of Hanoi Medical University Hospital for 2 years, and underwent endoscopic and surgical or percutaneous intervention to remove of foreign bodies. Results: The most common site for foreign bodies was the jejunum, followed by the stomach, colon, and esophagus. Transmural foreign body accounted for the highest rate (14/25 cases). The most common complication of sharp-pointed foreign body on CT is perforation with 16/25 cases, followed by abscess with 04/25 cases. CT scan has high sensitivity and specificity in evaluating complications of sharp-pointed foreign bodies. Conclusion: CT has an important role in detecting and diagnosing sharp-pointed gastrointestinal foreign bodies as well as evaluating associated complications. Key word: Ingested foreign bodies, foreign bodies, complications of foreign bodies, sharp-pointed foreign bodies, sharp-pointed
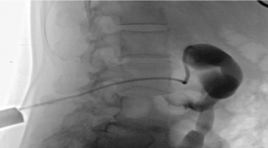
NHẬN XÉT SỰ AN TOÀN CỦA DẪN LƯU BỂ THẬN QUA DA DƯỚI HƯỚNG DẪN CỦA SIÊU ÂM VÀ DSA Ở BỆNH NHÂN TẮC NGHẼN ĐƯỜNG BÀI XUẤT CAO
13/10/2023 16:35:42 | 0 binh luận
SUMMAR Aim : to access the safety and complications of Percutaneous Nesphrostomy in obstructed urinary upper tract. Patients and methods : a cross-sectional descriptive study was performed on 45 patients who were diagnosed with pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis due to obstructed urinary upper tract at the Radiology Department, Ha Noi Medical Hospital from 6/2021 to 8/2022. Results: 100% of patients who have hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis taken broad-spectrum antibiotics before performing percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN). Position to drain into renal pelvis: 93.3% from the inferior pole, 6.7% from the middle pole. 91.1% of patients were performed successfully Percutaneous Nephrostomy the first time and 8.9% of patients needed in the second time. The successful rate of Percutaneous Nephrostomy was 100%. Time to complete procedure on average 19.5±4.5 minutes. Bleeding complications accounted for 2.2% (n=1), Sepsis complications accounted 6.7% (n=3). Catheter obstruction was 18% (n=8). The size of the sonde drainage 8F was used for patients with Hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis in grades I and II. The size of the sonde drainage 10-12F was used for patients with Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis in grades III and IV. Conclusion: Percutaneous nephrostomy is a minimal, safe, effective treatment procedure. Keywords : Renal Nephrosis, Pyelonephritis, Percutaneous Nephrostomy
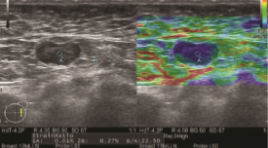
NGHIÊN CỨU GIÁ TRỊ CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI MÔ NÉN TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN HẠCH NÁCH ÁC TÍNH
13/10/2023 12:33:32 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: To evaluate the accuracy of strain elastography in the diagnosis of malignant axillary lymph nodes. Methods: B-mode and strain elastography US were scanned by experienced radiologists on patients with clinical symptoms or suspicion of breast cancer to look for masses or abnormal lymph node. Lymph nodes are evaluated on B-mode ultrasound based on 4 factors: short and long axis diameter, hilum, and cortical thickening. The strain elastography was based on a color scale of 1 to 5 points based on percentage of nodal region on the color chart, and a semi-quantitative B/A index of node stiffness correlation with adipose tissue of the same depth. Results: a total of 41 lympho nodes (benign, n=13, malignant, n=28) from 39 patients were analyzed. B-mode ultrasonography in the evaluation of malignancy had a sensitivity and specificity of 67.9% and 69.2%. Strain elastography for assessment of axillary lymph node involvement had a sensitivity and specificity of 85.7% and 69.2%. The semi-quantitative index B/A had statistically significant difference between the group of benign and malignant lymph nodes (p<0.05) with the cut of is 23.5. Conclusion: Strain elastography is a non-invasive and helpful method, together with B-mode ultrasound, in the evaluation of malignant axillary lymph node involvement. K ey words: axillary lymph node, strain elastography
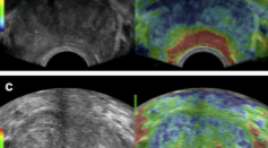
CẬP NHẬN VAI TRÒ CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN UNG THƯ TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT
12/10/2023 15:57:29 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Prostate cancer (PC) is an emerging male health problem in recent years due to new development in diagnostic and treatment modalities that help improve disease prognostic, especially in Eastern countries where PC incidence is high. According to GLOBOCAN 2020, number of new cases of PC reached 1,414,259 while number of deaths was 375,304 cases. In terms of deaths due to cancer in male population, prostate cancer ranks two just after lung cancer. Together with the traditional trio of rectal exam, Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) and transrectal ultrasound, emerging imaging modalities such as elastography ultrasound, multimodality magnetic resonance imaging not only helped physicians better detecting malignant lesions at supra early stage but also guided biopsy for pathological assessment. These new innovations led to preference of target-biopsy with lower rate of re-biopsy and complications comparing to systemic biopsy technique
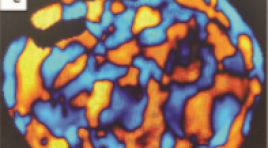
VAI TRÒ CỦA CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ ĐÀN HỒI 3 TESLA TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ ĐỘ XƠ HÓA GAN
12/10/2023 10:53:06 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives: To investigate liver fibrosis using magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and the relationship between MRE and histopathology in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Methods: Retrospective study, description, investigation of the liver by MRE before biopsy in 20 patients with chronic viral hepatitis in Cho Ray Hospital from 11/2019 to 05/2021. Results: The mean age is 51.4 years and 100% of patients are female. The mean liver stiffness (kilopascal = kPa) is 3.1 ± 0.2 (F1, n = 8), 3.6 ± 0.1 (F2, n = 11), 5.3 (F3, n = 1) respectively. The Spearman correlation coefficient is 0.63 (p=0.003), which shows a strong correlation between the liver stiffness measured with MRE and the fibrosis on the liver biopsy sample evaluated by the Metavir scoring system. Based on the ROC curve and the cut-off value of 3.7 kPa, it can be predicted that there is a presence of significant fibrosis (≥ F2), a sensitivity of 58%, and a specificity of 100%. Conclusions: MRE is a safe and non-invasive technique that can replace biopsy in the assessment of the liver fibrosis stage. Keywords: Magnetic resonance elastography, stiffness, liver fibrosis, chronic viral hepatitis, histopathology.
ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH SIÊU ÂM VÀ CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN VIÊM TÚI THỪA MANH TRÀNG
11/10/2023 14:31:15 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives: Describe the characteristics of ultrasound images and computed tomography in the diagnosis of cecal diverticulitis. Subjects and methods : A cross-sectional study on 49 patients who underwent ultrasound and computed tomography at the Center of Radiology in Bach Mai Hospital, diagnosed with cecal diverticulitis on CT, was treated at Bach Mai Hospital from June 2020 to June 2021. Results: ultrasound showed diverticulum 63.3%, inside diverticulum there was fecal stone 18.3%, gas or fecal content 18.3%, fluid 26.5%, diverticulum wall thickness (>2mm) 28.6%, cecal wall thickness 95.9%, fat infiltration around the diverticulum or caecum 81.6%. 47/49 patients had thickened cecal wall, 89.8% thickened around the circumference. CT scan, 71.4% had 1 diverticulum, 20.4% had multiple diverticula, 10.2% had gas in the diverticulum, 55.1% had fecal stones, 26.5% had fluid in the diverticulum, thickened diverticulum (>2mm) 71.4%, 95.9% thickening of the cecum wall. Conclusions : Ultrasonography and CT imaging are very valuable imaging tools for determining the diagnosis, extent of lesions and complications of cecal diverticulitis, and are meaningful in clinical practice for choosing treatment methods. Keywords: cecal diverticulitis, ultrasound, computed tomography

Đánh giá kết quả nút tắc ống ngực điều trị biến chứng rò dưỡng chấp sau mổ ung thư tuyến giáp
25/08/2021 14:21:09 | 0 binh luận
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












