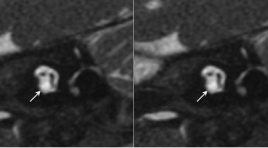
VAI TRÒ CỦA CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH VÀ CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ XƯƠNG THÁI DƯƠNG TRONG CHỈ ĐỊNH CẤY ỐC TAI ĐIỆN TỬ
16/11/2021 09:50:00 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To describe CT scanner and MRI imaging characteristics of temporal bone of sensorineural hearing loss patients to select patients for cochlear implantation. Material and Methods: Description of inner ear and cochlear nerve imaging combined with hearing assessment to give cochlear implant indication in 132 sensorineural hearing loss patients. Cochlear nerve was evaluated on high resolution T2 3D gradient-echo MRI. Inner ear image was evaluated on high resolution MRI and CT scanner. Results: The study included 132 patients with 264 ears in which 161 ears (61%) with no inner ear malformations, 34 ears (12,9%) with normal cochlear and cochlear nerve deficiency, 65 ears (24,6%) with inner ear malformation and 4 ears (1,5%) with labyrinthine ossification. The patients with cochlear nerve aplasia and no V ABR wave on hearing assessment, the patients with severe cochlear malformation and severe cochlear ossification are not indicated for cochlear implantation. Conclusion: Indications for cochlear implantation depend on the condition of the inner ear and the presence of cochlear nerve on imaging or auditory response on hearing assessment. Key words: Inner ear malformation, cochlear nerve deficiency, cochlear implant indication.
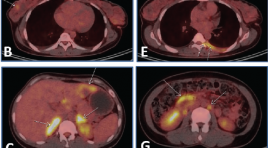
ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH FDG PET/CT CỦA U LYMPHO KHÔNG HODGKIN TẾ BÀO T
16/11/2021 09:46:25 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) is a group of uncommon lymphomas, accounting for about 12% of all cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The purpose of this study is to investigate the sites and metabolic activity of lesions in T-cell NHL on FDG PET/CT images, and to determine the correlation between metabolic activity and Ki67. Patients and methods: A retrospective study of patients with T-cell NHL who underwent FDG PET/CT examination for initial disease staging from 2009 to 2019. Results: A total of 62 patients (37 men and 25 women) with mean age of 44.8 were included in this study. There were 30/62 patients with histopathological subtypes, in which the highest frequency was peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified, and extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type with 8 cases (26.7%) each. PET/CT images showed the frequency of lesions in the lymph node regions in descending order of neck (67.7%), axillary (41.9%), mediastinum (40.3%), abdomen (40.3), inguinal area (37.1%). There were 32 extranodal sites/organs involved in T-cell NHL, most commonly in the spleen (27.4%), nasal cavity (24.2%), bone marrow (22.6%), nasopharynx (21%) with a frequency greater than 20%. The mean SUVmax of lymph nodes in descending order was 9.9 (in the abdominal lymph nodes), 7.7 (in the cervical lymph nodes), 7.7 (in the axillary lymph nodes), 6.2 (in the mediastinal lymph nodes), 5.9 (in the inguinal lymph nodes). The majority (81%) of lesions in extranodal sites/organs had a mean SUVmax ≥5. Sites/organs with high frequency of lesions having the highest mean SUVmax were skeletal muscle (17.3), nasal cavity (12.3), skin/subcutaneous tissue (11.7), nasopharynx (10.2), lung (6.9), pleura (6.8), bone marrow (5.3), liver (5.0) and spleen (5.0). Analysis of the linear correlation between SUVmax of the lesion at the biopsy site and the percentage of Ki67 was performed in 24 patients, and the results showed no correlation (r=0.03). Conclusion: In patients with T-cell NHL, FDG PET/CT is useful for detecting lesions in many sites/organs in the body. The metabolic activity of the lesions was high, but there was no correlation between SUVmax and Ki67. Keywords: T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, FDG PET/CT, Ki67.
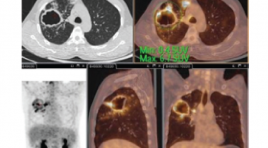
NGHIÊN CỨU ỨNG DỤNG QUY TRÌNH CHỤP 18FDG PET/CT CHO BỆNH NHÂN LAO PHỔI
16/11/2021 09:40:38 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY The study was performed on a PET/CT system provided by Philips Health Care System, radioactive drug 18FDG of the 108 Military Hospital. The procedure was based on recommendations of EANM (European Association of Nuclear Medicine) and protocol. PET/CT scan of the Ministry of Health. The technique was performed on 15 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of pulmonary TB by microbiological results being treated with anti-tuberculosis drugs. Results: There are two patterns of 18FDG uptake in TB patients: the lung parenchyma and the lymphatic system. Before treatment: Metabolic change in the mean SUVmax index found in lung parenchymal lesions was 6.75±3.01. Mediastinal lymph nodes were found in 10/15 patients (66.7%), in which 8/10 lymph nodes increased FDG uptake with mean SUVmax of 3.14±1.5. Keywords: 18FDG PET/CT, pulmonary tuberculosis.
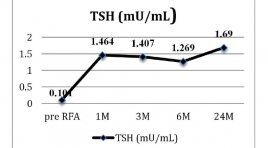
MÔ TẢ KẾT QUẢ ĐIỀU TRỊ NHÂN NÓNG TUYẾN GIÁP BẰNG PHƯƠNG PHÁP ĐỐT SÓNG CAO TẦN
16/11/2021 09:35:56 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background: Some patients with autonomously functioning thyroid nodules (AFTN) are not suitable for surgery or radioiodine therapy. Therefore, minimally invasive alternative treatments, such as ethanol ablation or radiofrequency ablation (RFA), are necessary. Methods: This study included seven patients (7 toxic and 10 pretoxic patients; male to female ratio = 1:7.5; mean age, 46.47 ± 13 (range, 22–66) years) who were not eligible for surgery or radioiodine therapy. All of the patients showed hot nodules with suppression of normal thyroid gland in 99mTc pertechnetate scintigraphy. RFA was performed using a 18 Gauge internally cooled electrode. Nodule volume, thyroid function, scintigraphy, symptom score (visual analogue scale, 0–10cm), cosmetic grading score (4 point scale), and complications were evaluated before treatment and at 1, 3, 6 and 24 months follow-up. Results: Mean volume of the index nodule was 13.07 ± 8.44 (range, 2.2–35.5) mL. After RFA, The volume reduction at 1month, 3 months, 6 months follow up was 42.77 % , 63. % và 78.3 % . Initial mean T3, FT4, and TSH were 2.59 ± 1.19nmol/L, 16.3 ± 5.78pmol/L, and 0.101 ± 0.178 mU/mL, respectively. A significant improvement of mean T3, FT4, and TSH were observed after 1month (T3: 2.18 ± 0.753 nmol/L, p = 0.001; FT4: 14.78 ± 2.86 pmol/L, p = 0.001; TSH: 1.464 ± 0.844 mU/mL, p = 0.001), after 6 months (T3: 2.07 ± 0.614 nmol/L, p = 0.012; FT4: 15.12 ± 2.0 pmol/L, p = 0.001; TSH: 1.269 ± 0.398 mU/mL, p < 0.001), after 24 months ( T3: 2.05 ± 0.523 nmol/L, p = 0.016; FT4: 16.43 ± 1.39 pmol/L, p = 0.001; TSH: 1.69 ± 0.654 mU/mL, (p <0.001). After ablation, 17 patients became a cold nodule after 3 months. After 24 months, the mean symptom was reduced from 3.47 ± 1.9 to 0.06 ± 0.25 (p = 0.001) and cosmetic grading score was reduced from từ 3.59 ± 1.1 tới 1.19 ± 0.403 (p <0.001). No major complications were encountered. Conclusions: RFA was effective and safe for treating autonomously functioning benign thyroid nodules.
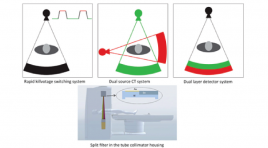
ỨNG DỤNG CỦA CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH HAI MỨC NĂNG LƯỢNG TRONG VIÊM TUỴ CẤP
15/11/2021 17:44:18 | 1 binh luận
SUMMARY Acute pancreatitis is one of the most common GI conditions requiring acute hospitalisation and has a rising incidence. Moderate or severe pancreatitis has a high mortality. Evaluation of acute pancreatitis severity on CT plays an important role. DECT has been a modern technology with many promising applications, including diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. DECT has a good assessment of local complications such as necrosis; area of decreased enhancement; hemorrhage; vascular complications such as splenic vein thrombosis, portal vein thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm. DECT plays a prominent role in evaluating areas of pancreatic necrosis and areas of decreased enhancement. This article introduces some recent DECT systems, DECT technique in acute pancreatitis and the role of DECT in diagnosis acute pancreatitis Keywords: acute pancreatitis, dual energy CT, necrosis, vascular complication
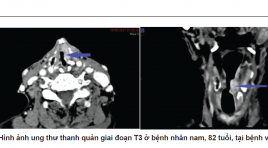
TƯƠNG QUAN GIỮA HÌNH ẢNH CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH, NỘI SOI VỚI MÔ BỆNH HỌC SAU MỔ TRONG PHÂN GIAI ĐOẠN T UNG THƯ THANH QUẢN
15/11/2021 17:30:57 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: Correlation between preoperative computed tomography, endoscopy with postoperative histopathology in the staging of laryngeal cancer. Methods: Cross- sectional study of patients with cancer larynx who were taken a preoperative neck CT scan. Classify T stage by blinded reading of CT combined with laryngoscopy, compared with surgical results, histopathological T-stage. Analyzing the sensitivity and specificity of CT, endoscopy to staging T. Results: There were 105 patients including 96 male patients and 9 female patients. Patients were aged from 38 to 87 (mean, 61 years). 16 (15%) patients had hypopharyngeal tumor, where's 89 (85%) had pharyngeal tumor.Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of CT in staging T were 68%, 93%, 70%, 92% , 88% Conclusion: MSCT could serve as a powerful auxiliary method for staging T laryngeal cancer, special in the evaluation of T3 and T4 tumors. Combinate information from MSCT and laryngoscopy makes improve sensitivity, specificity of preoperative staging T Keywords: Laryngeal cancer, multislice computed tomography, laryngoscopy, T-stage.
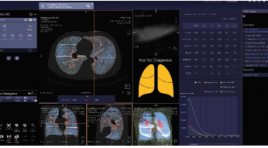
Nghiên cứu giá trị của chụp cắt lớp vi tính 128 định lượng trên bệnh nhân bệnh phổi tắc nghẽn mạn tính trước và sau ghép tế bào gốc tự thân
06/05/2021 15:35:43 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background: Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT) has been used for many years worldwide to evaluate and quantify lung parenchymal lesions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including emphysema quantification (LAA-950), air-trapping assessment area (LAA- 856), bronchial wall area (WA), percentage of wall area (% WA), bronchial lumen area (LA), bronchial wall thickness (WT), studies show that QCT is highly accurate, strongly correlated with the respiratory function test (FEV1, FVC), grade classification according to GOLD. We applied this method to evaluate the indicators of emphysema (LAA-950), air-trapping (LAA-856), RVC¬856-950, bronchial wall area (WA), bronchial lumen (LA) and bronchial wall thickness (WT), percentage pulmonary vascular (%HAV) of COPD patients before and after autologous stem cell transplant from adipose tissue and bone marrow. Method: The study was conducted from 10.2019 - 10.2020 on 32 COPD patients diagnosed with COPD according to GOLD 2018 standards, patients with FEV1 <60% were selected for the autologous stem cell transplant study at The Respiratory Center - Bach Mai Hospital (4 GOLD II patients, 17 GOLD III patients, 11 GOLD IV patients). The patient was given quantitative CT scans 2 times, the first time before transplant and the second after 6 months after transplantation with a 128-detectors scanner of Siemens (Somatom Definition Egde) at Dien Quang Center - Bach Mai Hospital. Results: Percentage of emphysema (LAA-950) before grafting 31.49% ± 8.19, after grafting 32.8% ± 7.13), percentage of air-trapping in then exhalation (LAA-856) before grafting 63.65% ± 8.74, after transplant 61.41% ± 7.4 (statistically significant difference p = 0.026), RVC856- 950 before transplant 0.83 ± 1.82, post transplant 3.58 ± 1.76 (significant difference p = 0.000), these indicators are linearly correlated with FEV1, BODE and GOLD classification. The percentage of wall area (%WA) after transplantation was changed in the bronchial branch of segment 1 (70.74% before transplantation, 67.59% after transplantation, p = 0.02) and in branch of subsegment 1 (79.19% before transplantation, after transplantation 75.90%, p = 0.01), lumen area (LA), inner diameter (ID) of the posttransplant bronchial all increased in the segmental and subsegmental bronchial branches RB1, RB4, RB10, wall thickness (WT) decreased in the sub-branches RB1-1, RB4-1, RB10-1 (however the difference was not statistically significant with p <0.05). Conclusion: Emphysema (LAA-950), air-trapping (LAA-856, RVC856-950), percentage of bronchial wall (% WA), lumen area (LA), inner diameter (ID), thickness bronchial wall (WT) measured on QCT correlated with FEV1, FVC, GOLD, BODE before and after stem cell transplantation, can be used to assess the extent and stage of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, pre- and post-assessment of autologous stem cell transplant therapy. Keywords: Quantitative CT COPD, Quantitative CT after autologous stem cell tranplantation
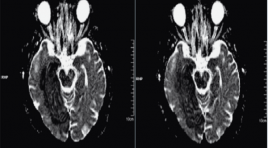
Cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán: Ứng dụng lâm sàng
24/12/2019 18:00:25 | 0 binh luận
Ứng dụng chính của Cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán - DWI MR đã được dùng là hình ảnh não vì chủ yếu là độ nhạy tinh tế với đột quỵ thiếu máu-một bệnh lý thường gặp xuất hiện trong chẩn đoán phân biệt ở tất cả các bệnh nhân có triệu chứng thần kinh.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












