
Đánh giá hiệu quả giảm đau bằng têm cồn tuyệt đối diệt hạch đám rối thân tạng dưới hướng dẫn của cắt lớp vi tnh và robot Maxio
25/08/2021 15:39:30 | 0 binh luận

Nhân một số trường hợp thoát vị nội hiếm gặp: Đặc điểm hình ảnh trên cắt lớp vi tính
25/08/2021 15:38:23 | 0 binh luận

Chẩn đoán hình ảnh ống têu hóa và hệ niệu dục trên một trường hợp song sinh dính nhau vùng chậu
25/08/2021 15:36:59 | 0 binh luận

Nút mạch u cơ tử cung qua đường mạch quay: Kinh nghiệm và kỹ thuật bước đầu
25/08/2021 15:35:44 | 0 binh luận

Độ chính xác của cộng hưởng từ trong chẩn đoán lại giai đoạn T của ung thư biểu mô trực tràng sau điều trị tân hỗ trợ
25/08/2021 15:33:07 | 0 binh luận
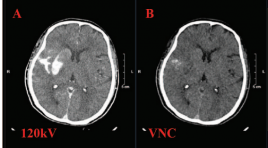
Giá trị của CLVT hai mức năng lượng trong tiên lượng nguy cơ chảy máu não sau lấy huyết khối cơ học
06/05/2021 17:04:08 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: Evaluate the characteristics of Dual-energy CT of the brain performed after mechanical thrombectomy. Acess the capability of iodine extravasation quantification on DECT to predict hemorrhagic complications. Material and methods: Retrospective descriptive study. Thirty consecutive patients who underwent brain dual-energy CT right after mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke between July 2019 and September 2020 in Radiology Center, Bach Mai hospital, were included. Maximum iodine concentration was measured. Follow-up CT or MRI examinations performed at 24hrs after intervention were reviewed for intracerebral hemorrhage development. The correlation between dualenergy CT parameters and intracerebral hemorrhage development was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test and Fisher exact test. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated for continuous variables. Result: Nineteen of 30 patients (63.3%) developed hemorrhage in different grades. On postoperative dual-energy CT, parenchymal hyperdensities and iodine extravasation were present in 19 (100%) of the 19 patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and in 7 (63.6%) of the 11 patients who did not (P = 0.0012). Signs of bleeding were present in 5 (45.4%) of the 19 patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and in none of the patients who did not. Median density of contrast extravasation in hemorrhage and non-hemorrhage is 108.8HU and 33.6HU (P=0.001). Median maximum iodine concentration was 2.9 mg/mL in the patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and 0.59 mg/mL in the patients who did not (P = 0.003). Maximum iodine concentration showed an area under the curve of 0.9 for identifying patients developing intracerebral hemorrhage. Conclusion : DECT helps differentiating haemorrhage from contrast extravasation. The presence of parenchymal hyperdensity with a maximum iodine concentration of >1.1 mg/mL may identify patients developing intracerebral hemorrhage with 94.7% sensitivity and 81.8% specificity. Key words: Dual – energy CT, thrombectomy, iodine extravasation.

Giá trị của CLVT hai mức năng lượng trong tiên lượng nguy cơ chảy máu não sau lấy huyết khối cơ học
06/05/2021 15:29:32 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: Evaluate the characteristics of Dual-energy CT of the brain performed after mechanical thrombectomy. Acess the capability of iodine extravasation quantification on DECT to predict hemorrhagic complications. Material and methods : Retrospective descriptive study. Thirty consecutive patients who underwent brain dual-energy CT right after mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke between July 2019 and September 2020 in Radiology Center, Bach Mai hospital, were included. Maximum iodine concentration was measured. Follow-up CT or MRI examinations performed at 24hrs after intervention were reviewed for intracerebral hemorrhage development. The correlation between dualenergy CT parameters and intracerebral hemorrhage development was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test and Fisher exact test. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated for continuous variables. Result: Nineteen of 30 patients (63.3%) developed hemorrhage in different grades. On postoperative dual-energy CT, parenchymal hyperdensities and iodine extravasation were present in 19 (100%) of the 19 patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and in 7 (63.6%) of the 11 patients who did not (P = 0.0012). Signs of bleeding were present in 5 (45.4%) of the 19 patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and in none of the patients who did not. Median density of contrast extravasation in hemorrhage and non-hemorrhage is 108.8HU and 33.6HU (P=0.001). Median maximum iodine concentration was 2.9 mg/mL in the patients who developed intracerebral hemorrhage and 0.59 mg/mL in the patients who did not (P = 0.003). Maximum iodine concentration showed an area under the curve of 0.9 for identifying patients developing intracerebral hemorrhage. Conclusion: DECT helps differentiating haemorrhage from contrast extravasation. The presence of parenchymal hyperdensity with a maximum iodine concentration of >1.1 mg/mL may identify patients developing intracerebral hemorrhage with 94.7% sensitivity and 81.8% specificity. Key words : Dual – energy CT, thrombectomy, iodine extravasation
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












