Đặc điểm hình ảnh cắt lớp vi tính 256 dãy trong chẩn đoán và theo dõi điều trị ung thư phổi biểu mô tuyến có đột biến EGFR
05/05/2021 12:40:07 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY: Purpose : The characteristics of 256-slice computer tomography in patients with EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma and the tumor response to targeted therapy according to RECIST 1.1 criteria were taken into investigation in this study. Methods: 32 patients with EGFR- mutated lung adenocarcinoma received TKI (tyrosine kinase inhibitor) were underwent 256-slice CT scanner before treatment and 3 months, 6 months of treatment, from July 2017 to July 2019 at Friendship Hospital. Results: Before therapy, on 256-slice CT scanner in patients with EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma, we observed tumors on the right in 56.3% of patients, tumors in the upper lobe in 56.3%, tumors size larger than 3 cm in 81.3%, lobulated or spiculated margin in 100%, pleural effusion in 50%, air bronchogram in 34.4% and cavitation in 3.1%. Metastases was present in lymph nodes in 68.8%, followed by metastatic deposits in lung (56.3%), bone (53.1%), brain (9.4%), adrenal gland (9.4%) and liver (6.3%). After 3 months of treatment , the percentage of partial response was 34.4%, stable disease was 59.4% and progressive disease was 6.3%; after 6 months, these ratio were 40.6%, 43.8% and 15.6% respectively. Conclusion: Common CT scanner features in patients with EGFRmutated lung adenocarcinoma were lobulated or spiculated margin, size larger than 3cm and pleural effusion; cavitation was rarely noticed. Metastases usually presented in lymph node, lung and bone. The disease control rate at 3 months and 6 months of therapy were 93.7% and 84.4% respectively. CT scanner is a potential tool for evaluating tumor response and improving effective treatment in patients with lung cancer received TKI. Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, EGFR mutation, computed tomography.

Thực quản đôi: Một trường hợp hiếm gặp tại bệnh viện Bạch Mai
07/04/2020 21:22:50 | 0 binh luận
Incomplete duplication of the esophagus: a case report SUMMARY Double lumen esophagus is a very rare disease. Approximately 20 cases have been reported in the past. Dysphagia and odynophagia are common symptoms. Symptomatic management is the mainstay of treatment.We report a extremely rare case of 57-year-old woman with a incomplete duplication of the esophagus. Patient‘s symptoms are dysphagia with solid food, regurgitation of great amount of the liquid and chest pain. The exact diagnosis is make by X-ray films of the chest with a water soluble contrast esophagogram, esophagogastroscopyand computed tomography (CT) of the thorax . For its rarity, this case is reported and review about literature of double lumen esophagus. Keywords : esophagus, incomplete esophageal duplication.
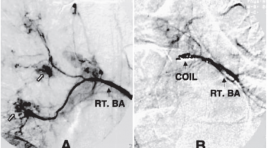
Đánh giá kết quả bước đầu điều trị ho ra máu bằng phương pháp can thiệp nội mạch tại bệnh viện đà nẵng
01/04/2020 11:41:57 | 0 binh luận
Evaluate the initial outcome of endovascular treatment of hemoptysis in Da Nang Hospital SUMMARY Purposes: This study is to evaluate the initial outcome of BAE for moderate, chronic and massive hemoptysis. Materials and methods: Series of 33 patients with the clinical scenario of moderate, chronic and massive haemoptysis was referred to DaNang hospital for digital subtraction angiography and BAE from 2/2009 to 10/2014. Results : The procedure was technically successful in 87.9% (29/33) of patients, within 2 weeks, 78.8% (26/33), within 30 days and 72.7% (24/33), after 30 days. Conclusions : BAE is a useful therapy to control both acute and chronic hemoptysis, BAE may help to avoid surgery in patients who are not good surgical candidates, it is also important to treat the underlying pulmonary desease. Key words : angiography; arterial embolization; bronchial artery; bronchoscopy; hemoptysis.

Khảo sát hình ảnh viêm phổi trên chụp cắt lớp điện toán ở bệnh nhi nhiễm HIV
31/03/2020 14:15:01 | 0 binh luận
Evaluating the images of pneumonia on CT Scan in HIV- infected children summa ry Objective: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the pulmonary lesions on CT of pneumonia in HIV infected children and causing agents. Material and methods : Fifty HIV infected children with pneumonia was selected over a 10-month period at the Chilren Hospital N1. All patients were indicated the chest radiogram, the CT with constrate media and the nasotreacheal aspiration to exame microbiology included bacteria, BK, fungus and Pneumocystis jiroveci. Results : Of 50 patients, 62% is baterial pneumonia, PCP 29% and tuberculosis 18%. Lesions on CT included alveolar condensation account for 88%, ground glass 30%, bronchial syndrome 20% and lymphadenopathy 20%. The ground glass lesion present in all PCP, 100%. Eighty percent of tuberculosis children have lymphadenopathy with central necrosis and peripheral enhancement. These two kinds of lesions present a little in bacterial pneumonia group. Conclusion: Ground glass images on chest CTscans may allow confident diagnosis for PCP in HIV infected children. To diagnose thoracic tuberculosis, CT scans are useful to detect the typic tuberculous lymphadenopathies. Keywords: HIV, pneumonia, children, PCP.
Chẩn đoán hình ảnh lao phổi trẻ em
31/03/2020 14:22:42 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the greates health problems for people living in the developing world. For children the problems are much greater. Imaging methods such as chest X-ray, chest US, chest CT are extremely important tools for the diagnosis of pediatric pulmonary TB. This article presents the common manifestations of tuberculosis in children.
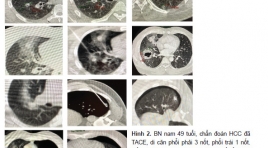
Bước đầu đánh giá kết quả điều trị di căn phổi bằng đốt sóng cao tần tại bệnh viện Việt Đức
17/03/2020 09:49:03 | 0 binh luận
Initial evaluation the result of treatment for lung metastasis by radio frequency ablation in vietduc hospital SUMMARY Purpose : We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and the complicationsof radiofrequency (RF) ablation of metastatic lung tumors Methods: Eight patients with lung metastatic underwent computed tomography-guided percutaneous RF ablation between May 2016 and August 2018. A total of 11 tumors (8 metastatic from hepato cellular carcinoma, 2 metastatic from chorio and 1 metastatic from colon cancer) were treated with RF ablation (9 sessions). Tumor diameter ranged from 0.9 to 1.9 cm (median 1.26cm). Effectiveness of treatment and complications were analyzed. Results :Success rate was 100 % with only one session, local tumor progression hasn’t occurred in 11 tumors. Complications occurred in 5 sessions (55.5%). Chest pain occurred in 2 sessions andpneumothorax occurred in 3 sessions with one requiring image-guided percutaneous chest tube drainage. \ Conclusion: RF ablation is a safe and effective treatment for selected patients with metastatic lung tumors. Key words : radio frequency ablation, pulmonary metastasis, lung cancer.
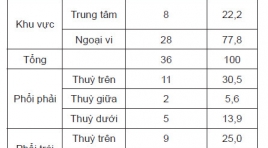
Đặc điểm cắt lớp vi tính ung thư phổi trước điều trị thuốc ức chế tyrosin Kinase và đánh giá đáp ứng theo tiêu chuản Recist 1.1
17/03/2020 10:29:02 | 0 binh luận
Computed tomography features of lung cancer patients before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment and response assessment by recist 1.1 SUMMARY Objective: 1. Describe computed tomography features of non-small cell lung cancer before tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. 2. Treament response assessment by RECIST 1.1. Patients and method : Cross-sectional, retrospective and prospective study of 36 non- small cell lung cancer patients, EGFR mutations positive, treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor from 08/2018 to 06/2018, Results: Tumors located mainly in peripheral of the lung (77,8%). The most common position is the right upper lobe (30,5%), the least common position is the right middle lobe (5,6%). There are 83,3% of tumors with the size over 3cm. 100% of tumor have irregular and spicules magin. Solid mass accounted for 63,9%, partly solid mass (33,3%), one tumor is cavity form. Medium attenuation value is 27 HU in pre-contrast and 57,1 HU in post-contrast CT scan. Lymph node metastasis in 27 (61%) patients. Lymph node metastasis is mainly occured in paratracheal nodes [2,4(R,L), 3] (48%), A-Pwindow, paraaortic nodes (5,6) (12%), subcarinal nodes (7) (16%), supraclavicular nodes (1) (20%). After 3 months treament, partial response: 17 patients (52,8%), stable disease: 19 patients (47,2%). After 6 months treament, partial response: 14 patients (38,9%), stable disease: 20 patients (55,6%), progressive disease: 2 patients (5,5%). Conclusion : 1. Computed TomographyFeatures can be used to diagnose lung cancer. 2. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment is effective inadvancednonsmall cell lung cancer. Keywords : lung cancer, computed tomography, tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment, Recist 1.1

Đánh giá đặc điểm hình ảnh và thể tích khí phế thủng ở bệnh nhân bệnh phổi tắc nghẽn mãn tính bằng cắt lớp vi tính đa dãy
13/04/2020 14:52:16 | 0 binh luận
- Theo GOLD 2016: Bệnh phổi tắc nghẽn mạn tính (COPD) là bệnh lý có thể phòng ngừa và điều trị, được đặc trưng bởi sự hạn chế thông khí không hồi phục. Sự hạn chế này thường tiến triển từ từ và liên quan với sự tăng phản ứng viêm mạn tính của đường dẫn khí và phổi với các phân tử nhỏ và khí độc hại - KPT (hay giãn phế nang) là tổn thương căng giãn thường xuyên và phá hủy không hồi phục ở thành các khoảng chứa khí dưới phế quản tận, thường kèm theo phá hủy thành và không xơ hóa. - Cắt lớp vi tính (CT): chẩn đoán, phân loại, định lượng thể tích KPT -> Đánh giá mức độ nặng, tiến triển và hiệu quả điều trị bệnh.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












