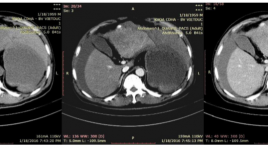
Đặc điểm hình ảnh và kết quả nút mạch cầm máu cấp cứu ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan vỡ
14/04/2020 23:15:45 | 0 binh luận
Evaluate the imaging characteristics of ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma and the effectiveness of embolization for controlling hemorrhage SUMMARY Objecivets: Evaluate the imaging characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ruptured and the effectiveness of transcatheter arterial embolization for controlling hemorrhage. Subjects and methods : analyze retrospectively the outcomes of 22 patients who underwent abdominal CTscanner and urgent transarterial embolization for spontaneous ruptured HCC during the period from 01/2014 to 06/2016 in Viet Duc hospital. Results: Mean tumor size: 83.95mm (longest diameter). 7/22 patients (31.8%) exhibited contrast extravasation on angiography, 2/22 patients (9.1%) exhibited pseudoaneurysm, one patient (4.6%) showed arterioportal shunt, 12/22 (54.5%) showed no vascular injury. The embolization materials we used mostly was Spongel in 18/22 patients (81.8%), histoacryl 4/22 (18.2%). The success rate of embolization in on angiography is 22/22 (100%).1 patient die in one months after the procedure due to liver failure. Conclusion: Large tumors are likely to rupture and active bleeding injuries are uncommon. Transarterial embolization is a safe and effective method for controlling spontaneous rupture of HCC. Key words: angiography, embolization, hepatocellular carcinoma, large tumors spontaneous rupture.
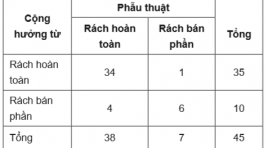
Rách dây chằng chéo sau: Hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ trước phẫu thuật
14/04/2020 23:02:34 | 0 binh luận
Posterior cruciate ligament injury: evaluation with preoperative mr imaging SUMMARY Objective: The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the imaging characteristics and the value of preoperative MRI in posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tears. Material and methods: Between January 2015 and December 2016, 48 patients with a postoperative diagnosis of PCL tear and available MR images of the knee were involved in a descriptive crosssectional study. Imaging characteristics of PCL tears and associated injuries were described and compared with operative report. Results : PCL average diameter was 7,6 ± 2,1 mm, a statistically significant difference was found between PCL thickness < 7mm group and those of ³ 7mm group. Intrasubstance fluid signal intensity of PCL was detected in 79,2% of cases. Anterior cruciate ligament tears commonly associated with PCL tears (64,6%) in multiple ligament injuries. MRI has sensitivity, specificity of 89% and 86% respectively in detection complete PCL tears. Conclusion : MRI provides accurate diagnostic of PCL tear preoperatively, intrasubstance fluid signal intensity, anteroposterior diameter ³ 7mm can be considered evidence of a torn PCL with a high degree of certainly. Keywords : posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tears, posterior cruciate ligament injury, preoperative MR imaging.
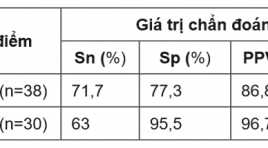
Vai trò của X-quang cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán tụ dịch ổ bụng sau mổ
14/04/2020 22:57:40 | 0 binh luận
Roles of computed tomography in diagnosis of postoperative abdominal fluid collections SUMMARY Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine whether the separate computed tomographic imaging features or their combination with clinical and laboratory parameters could distinguish infected from noninfected abdominal fluid collections after surgery. Materials and Methods: The cross-sectional descriptive study included 68 consecutive patients who underwent portal venous phase CT on 64 and 128 multidetector CT at the University Medical Center HCMC from 01/2014 to 03/2017. Imaging findings included attenuation (Hounsfield unit – HU), entrapped gas, wall enhancement and thickness, fat stranding, and volume of fluid collections. Clinical and laboratory parameters included diabetes and C-reactive protein. The standard of reference for the presence of infection was microbiological Gram stain and culture of fluid samples. A scoring system from 1 to 10 included diabetes: 2 points; CRP ≥ 100mg/L: 1 points; attenuation of fluid collections ≥ 20HU: 4 points; entrapped gas: 3 points. Results : CT imaging features (attenuation of fluid collections, entrapped gas) was significantly associated with the presence of infection. Sensitivities of these features varied between 56.5-87%, specificities between 68.2-81.8%, LR(+) 2.74-3.1, LR(-) 0.19-0.53. Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed attenuation of fluid collections and entrapped gas as significant independent predictors of infection (p<0.01), consecutive OR were 166.1 (95% confedence interval [CI], 7.52-3670) and 14.77 (95% CI, 1.44- 392.78). Based on using the CT-clinical-laboratory scoring system, scores of 3 or lower had a 100% negative predictive value, scores of 6 or higher had an 86,8% positive predictive value and scores of 7 or higher had a 96,7% positive predictive value for diagnosing infected fluid collections. Receiver operating characteristic analysis revealed an area under the curve of 0.86 (95% CI, 0.77- 0.94) for the score. Conclusion : Based on computed tomographic imaging features alone for distinguishing infected from noninfected abdominal fluid collections is still limited. CT had a low capability to confirm and could not be used to rule out the presence of infection. The application of the CT-clinical-laboratory scoring system may improve the ability to predict infected fluid collections after abdominal surgery. Key Words : postoperative, abdominal cavity, fluid collections, abscess, computed tomography (CT).
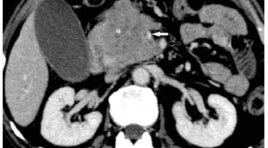
Giá trị của chụp cắt lớp vi tính nhiều đầu dò trong đánh giá xâm lấn mạch máu của ung thư biểu mô tuyến tụy trước phẫu thuật
14/04/2020 22:41:37 | 0 binh luận
Value of multidetector ct in preoperative assessment of the vascular invasion in pancreatic adenocarcinoma SUMMARY Object: The purpose of this study is to assess the accuracy of multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) in preoperative determination of the vascular invasion in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Materials and methods: Multidetector computed tomography, surgery, and pathological results of 39 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma were evaluated retrospectively. MDCT findings were compared with surgical findings to determine the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of MDCT in determining the vascular invasion. Results: 39 patients (21 males, mean age: 58,8 years) underwent surgery. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy of MDCT in determining the vascular invasion of pancreatic adenocarcinomas were 88,9%, 96,9%, 86,5%, 97,5% and 95,9% respectively. Conclusion: The accuracy of MDCT is high in preoperative determination of the vascular invasion in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Keywords: pancreatic adenocarcinoma, multidetector computed tomography, vascular invasion
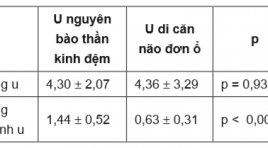
Cộng hưởng từ tưới máu trong chẩn đoán phân biệt u nguyên bào thần kinh đệm và u di căn não đơn ổ
14/04/2020 22:21:45 | 0 binh luận
Perfusion mri in differentiation of glioblastoma multiforme from solitary brain metastasis SUMMARY Objective : Objective of this study is to describe the value of Perfusion MR Imaging in the differentiation of glioblastoma from solitary brain metastasis. Material and Methods : Between 06/2015 and 04/2017, a descriptive cross-sectional study involved 58 patients with solitary brain tumor (26 solitary brain metastases and 32 glioblastomas) underwent preoperative conventional MR Imaging, Perfusion MR Imaging and histopathologically determined glioblastomas or metastases after stereotactic biopsy or partial resection. The conventional MR Imaging and Perfusion MR Imaging in these patients were analysed. Relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) was calculated and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed. To obtain the cut-off value of rCBV presenting a statistical difference between the two tumors groups. Results :Tumoral rCBV ratio presented no significant different between two tumor groups. Peritumoral rCBV ratios of glioblastomas (1,44 ± 0,52) significantly differentiated from those of solitary brain metastases (0,63 ± 0,31) (p = 0,935). The cut-off value was taken as 1,045 in the peritumoral rCBV ratio provided sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of 90,6 %, 92,6%, 96,67% and 89,92%, respectively. Conclusion: Perfusion-weighted MR imaging enable distinction between glioblastoma and solitary brain metastasis. Keywords : Glioblastoma, Solitary brain metastasis, Perfusion MR Imaging.
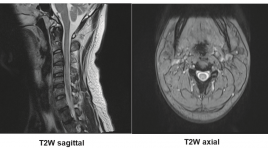
Đặc điểm hình ảnh tổn thương tủy sống gây bởi ngộ độc gây bởi khí Nitrous Oxide - nhân 2 trường hợp
07/04/2020 21:30:59 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Nitrous oxide gas (N2O), known as laughing gas, is widely used in medicine for the purpose of pain relief. However, nowadaysN2O are abused for recreational purposes and causes several harmful effects, especially neurological damages. In two cases of patients with nitrous oxide toxicity, we would like to make some remarks about the characteristic features of myeloneuropathy caused by N2O abuse Key word : metabolic, N2O, nitrous oxide, toxic
Đánh giá đặc điểm hình ảnh của chấn thương cột sống ngực - thắt lưng theo phân loại TLICS
07/04/2020 21:16:42 | 0 binh luận
Evaluating the imaging characteristics of thoracic - lumbar spine injury according to the tlics classification SUMMARY The study was carried out with the purpose of evaluating the visual characteristics of the thoracolumbar spine injury according to the TLICS classification (The Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score). From September 2016 to July 2017, at Viet Duc hospital, 80 patients with thoracolumbar spinal injury had been diagnosed using CT scanner and MRI, as well as receiving treatment at the hospital. The result was that 43 patients received preservative treatment, and 37 patients were operated upon, 14 of whom had TLICS < 4 point. With the use of MRI for evaluating PLC (posterior ligamentous complex), in comparision with post-operative results, the aforementioned methods showedthe sensitivity level of 96% and the specificity level of 100%. Keywords: thoracolumbar Injury, TLICS Classification, ligamentous complex.
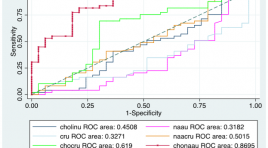
Chẩn đoán không xâm lấn mức độ ác tính của u thần kinh đệm sử dụng cộng hưởng từ tưới máu và cộng hưởng từ phổ đa thể tích
07/04/2020 21:11:36 | 0 binh luận
Noninvasive evaluation of glioma grade using perfusion and multivoxel 3d proton mr spectroscopy SUMMARY The purpose of this study was to clarify the usefulness of perfusion and multivoxel 3D proton MR spectroscopy in glioma grading. Study included 85 patients underwent preoperative conventional MR Imaging, multivoxel proton MR spectroscopy and histopathologically determined gliomas after stereotactic biopsy or partial resection. Receiver operative characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were performed to asscess the cutoff of rCBV and metaboite parameters of which the sensitivity and specificity are highest.A cut-off value of 2,56 for rCBV resulted in sensitivity, specificity of 86,54%, 75,76%, respectively. The cut-off value was taken as 2,76 in the Cho/NAA ratio provided sensitivity, specificity of 89,66%; 88%, respectively. The combination of rCBV and Cho/NAA ratio provided sensitivity, specificity of 71,15%; 78,79%, respectively. rCBV and Cho/NAA can increase the ability of glioma grading preoperatively. Key word : glioma, perfusion MR, spectroscopy MR
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












