
Cập nhật can thiệp lấy huyết khối cơ học - kết quả và kinh nghiệm của Việt Nam
20/04/2021 13:15:34 | 0 binh luận
Đang cập nhật

Vai trò của CHT bạch mạch: nguyên nhân và hướng dẫn can thiệp
20/04/2021 11:14:43 | 0 binh luận

Thách thức trong cầm máu sản phụ khoa: Một số case lâm sàng tại bệnh viện Bạch Mai
20/04/2021 13:12:30 | 0 binh luận
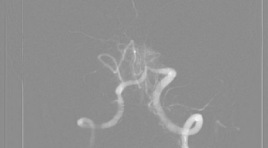
Đánh giá kết quả đặt stent điều trị hẹp mạch nội sọ tại Trung tâm Điện quang Bệnh viện Bạch Mai
06/05/2021 16:47:06 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background & Aims : Evaluation the results of the stenting on treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerosis. Methods: A prospective, non-controlled intervention study in intracranial artery stenosis patients with or without symptoms. The patients were indicated for treatment with stent placement from June 2017 to June 2020 at Radiology Center of Bach Mai Hospital. Results : The study was performed on 18 patients, including 14 patients have acute celebral ischemic stroke with intracranial stenosis and 4 patients have simple intracranial stenosis. : The study was performed including 10 men (55.6%) and 8 women (44.4%). The mean age of patients was 66.28 ± 10.87 years. The rate of successful interventions for intracranial artery stenosis was 94.4%. There are 2 patients (11.11%) had acute or immediately post intervention. Symptoms and complications, especially related to intracranial artery stenosis, were observed in 4 patients (22.22%). After an average of 3 months of follow-up, 1 patient died from perforation causing cerebral hemorrhage (5.56%) and 03 patients from stent-obstructive cerebral infarction after intervention (16.67%). Results of clinical recovery after stenting based on mRs scores with mortality, good recovery and slow recovery were 22.22%, 44.45% and 33.33%, respectively. Conclusion: The results of stent treatment for intracranial artery stenosis in our research have a high success rate. The safety of the intervention and post treatment clinical recovery rate are high. Key words : ICAD, PTAS

Đánh giá hiệu quả giảm đau trong tiêm phong bế rễ thần kinh thắt lưng dưới hướng dẫn của DSA
06/05/2021 15:13:57 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objection. Evaluation of clinical efficacy of lumbar selective nerve root block under DSA guidance Subject and methods: Prospective study on 160 patients at Duc Giang hospital from May 2019 to May 2020 with signs of lumbar radiculopathy. Subjects were undergone lumbar selective nerve root block under DSA guidance and were assessed with visual analog scale (VAS) and Owestry disability questionaire (ODI) prior to procedure and at 3 days, 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month and 2 months follow-up. Results: In 160 patients who undergone lumbar selective nerve root block under DSA guidance, average of age was 63.1±12.8. Female account for 60.6% of participants. VAS and ODI score were significant improve (p<0.05). Conclusion: Lumbar selective nerve root block under DSA guidance was an effective method in the treatment of sciatica. Key words: Lumbar selective nerve root block, DSA, lumbar radiculopathy.
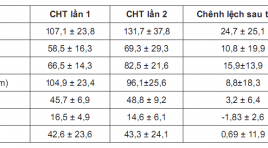
Vai trò cộng hưởng từ ngấm thuốc muộn trong dự báo khả năng phục hồi chức năng tim ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp được can thiệp tái thông động mạch vành thì đầu
01/06/2020 16:20:33 | 0 binh luận
Role of delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance Imaging to predict cardiacfunctional improvement after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for patients with acute myocardial infarction SUMMARY Objective: To access the transmural extent of hyperenhancement and infarct size at Delayed Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) on relating toleft ventricular (LV) functional improvement in reperfused myocardial infarction (MI) and to compare theLV morphology and function on MRI afterprimary percutanous coronary revascularization. Materialand Methods : Cine sequenceand Delayed Contrast- Enhanced MRIwere underwent in period of 9 days after percutanous coronary revascularization on29 patients suffering fromAcute MI at Bach Mai Hospital. Long term follow-up cardiac MRI was done to compare the change in LV morphology and function, infarct size. Myocardial wall thickening and left ventricular volumes were quantified on cine-images, and the transmural extent of infarction (TEI), infarct size was doned on delayed-enhancement images. Remodeling was defined as an increase in LV end-diastolic volume index of 20% or higher at follow up. Results: A decrease in myocardial mass (104,9 ± 23,4 to 96,1 ± 25,6 gram; p<0,05), mean SWT score (16,5 ± 4,9 to 14,6 ± 6,1; p<0,001) and increase the mean ejection fraction (45,7 ± 6,9 to 48,8 ± 9,2%; mean 3,2%; p<0,05), whereas mean end-diastolic volume(107,1 ± 23,8to131,7 ± 37,8 ml; p<0,0001) and mean end-systolic volume(58,5 ± 16,3 to 69,3 ± 29,3 ml, p<0,05) did not decrease. Segmental wall thickening did not change (42,6 ± 23,6to 43,3 ± 24,1%; p>0,5). The infarct size at DCE-MRI was related to LVEDVI (r=0,643, p<0,0001). Infarct size of 29% or more of LV area predicted remodeling with high sensitivity (100%) and specificity (89%). The extent of segments that was dysfunctional but viable was related to improvement in ejection fraction(r=0,56; p=0,002). Segmental wall thickening improved significantly in segments with<25% TEI(35 ± 7 to48 ± 7%, p<0,0001), tended to improve in segments with 25% to 75% TEI (32± 10to38 ± 11%, p<0,001), whereas segments with>75% TEI did not improve (22 ± 15to20 ± 14%, p<0,05). Conclusion :In patients with recent reperfused MI, functional improvement predicted by delayed contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Key word s: Cardiac Magnetic Resonace Imaging, delayed enhancement MRI, late gadolinium, Acute myocardial infarction, transmural extent of infarction (TEI), infarct size.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"












