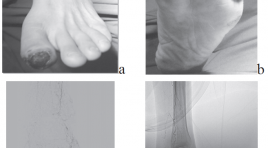
Nghiên cứu tương quan tổn thương động mạch trên chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền với vị trí, mức độ thiếu máu bàn chân trầm trọng
01/04/2020 13:49:07 | 0 binh luận
The correlation between arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography with location and level of critical foot ischemia SUMMARY Purpose: Description characterization critical ischemia and foot arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography. Description correlation between arterial lesion imaging on digittal substraction angiography with location and level of critical foot ischemia. Meterials and methods : 44 patients (28 male and 16 female) with the mean age of 69.3 years, with critical foot ischemia taken DSA from 8/2015 to 8/2012. Description research with prospective and retrospective. The correlation coefficient r and p significance is calculated by Spearman’s method. Results : In 111 critical ischemia regions: 45.95% belong to the posterior tibial artery, 33.33% anterior tibial artery, 20.72% peroneal artery. In 111 critical ischemia regions: 63.97% in the toes, 5.4% feet, 30.63% heel and lateral- anterior ankle. In 44 limbs: 22.7% having 1 critical ischemia regions alone; 34.1% with 2 region and 43.2% with ≥ 3 regions. In this number: 25% limbs with heaviest stage in rest pain, 61.36% in minor tissue loss and 13,64 % in major tissue loss. In 264 arteries: 46.05% with stenosis < 50% and 26.14% total stenosis with ≥ ½ in length. In 129 arteries with stenosis ≥ degree of 3: 28.68% belong to dorsal pedis artery, 48.06% branches from posterior tibial artery, 23.26% branches from peroneal arteries. The correlation coefficient r and significance p between foot arterial lesion and the level of critical foot ischemia, respectively: r from 0.755 to 0.891, all significance p <0.001. Keywords: Critical lower limb ischemia, angiosome of foot, variant anatomy foot artery.
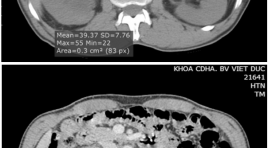
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cắt lớp vi tính 64 dãy trong chẩn đoán u đường bài xuất tiết niệu cao
01/04/2020 13:44:43 | 0 binh luận
Imanging characteristics and the value of 64-slice computed tomography in diagnosis of upper urinary tract tumor SUMMARY Objective: To describe the imanging characterise and analyze the value of 64-slice computed tomography (CT) in the evaluation of upper urinary tract tumors. Patients and Methods: Retrospective review of the patients who underwent 64-slice CT examination, was operated in VietDuc Hospital with upper urinary tract tumor in pathologic result from 8/2013 to 8/2015. This was observation study comparing the imaging finding with the result from surgery and pathology. Result: 56 patients with upper urinary tract tumor (32men, 24women), age 63.9±11.1. The sensitivity of 64-slice CT for upper urinary tract tumor was 92.86%. The accuracy of 64- slice CT in diagnosing T stage was 82.14%. Conclusion: 64-slice CT had high value in diagnosing upper urinary tract tumors. Keywords: 64-slice computed tomography, upper urinary tract tumor.
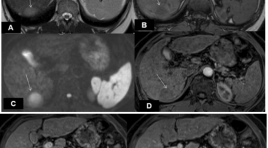
Đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ trong chẩn đoán ung thư gan nguyên phát ≤ 3 cm ở bệnh nhân xơ gan
01/04/2020 13:18:51 | 0 binh luận
Imaging characteristics and values of MRI for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3cm in cirrhotic patients SUMMARY Purpose: To describe the MR imaging features and to evaluate values of MRI for diangosis of hepatocellular carcinomas ≤ 3cm in cirrhotic patients. Materials and methods : 35 patients with final diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)≤ 3cm undergone MRI 1.5 Tesla at Radiology Departement (Bach MaiHospital) from August 2014 to July 2015. Results : The average diameter was 21.14mm, all were solitary, most of tumor locate in right liver. Among 35 tumors detected: 100% was hyperintense on Diffusion; 97.1% hyperintense on T2W; on inphase T1W 11.4% hyperintense, 57.2% hypointense, 31.4% isointense; on outphase T1W 2.9% hyperintense, 82.8% hypointense, 14.3% isointense; 40% tumors have fatty content inside. After contrast gadolium injection, at the arterial phase 71.4% of tumors showed enhancement; at the portal phase 48.57% of tumors showed contrast wash out; at the late phase 68.6% of tumors had contrast wash out and 68.6% of tumors had a rim enhancement. MRI dectected 100% of tumors and diagnosed 54.3% of tumors based on the characteristic arterial contrast enhancement and portal or late phase contrast washout. The combination of ≥3 or ≥4 morphological and hemodynamic signs could increase the diagnostic sensitivity to 91.4% and 60% respectively. Conclusion : Among 35 HCCs ≤ 3cm in cirrhotic livers: 97.1% and 100% appeared hyperintense on T2W and Diffusion respectively, most tumors were hyposignal on outphase T1W, 40% had fatty content. After gadolium contrast injection, 71.4% tumors had arterial contrast enhancement, 68.6% tumors showed portal or late contrast washout, 68.6% had rim enhancement. MRI detected 100% tumors and diagnosed 54.3% of all tumors. Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, cirrhosis, MRI.
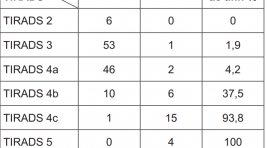
Cập nhật chẩn đoán hình ảnh phân loại bướu nhân tuyến giáp lành tính và ác tính
01/04/2020 12:49:56 | 0 binh luận
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh trên MRI 3.0 Tesla trong bệnh lý u vùng khoang miệng và hầu họng trên xương móng tại bệnh viện ung thư Đà Nẵng
01/04/2020 12:40:19 | 0 binh luận
MRI imaging in oral and pharyngeal cancer in Danang cancer hospital SUMMARY Background: Oral and pharyngeal tumor are more common today and it has complex structure limiting for the paraclinic examination. CT scan was a first choiced to examine the stage of tumor, especially invasion of tumor to the skull base but nowaday CT scan has been displaced by MRI, which has high value to detect soft tissue tumor with high sensitive and acurracy. MRI also gives the best informstion about anatomy in 2D and 3D. Object and Method: Cross study, clinical examination find out tumor in the oral or pharyngeal then takes the MRI picture, we except the patient without hystopathology and treated for cancer before. Coletting the MRI images data in T1W, T2W, STIR, T1W Gd. Object: MRI machine Siemens 3.0Tesla Model Verio A Tim System T-class, Coil 3T neck A Timy System, Dotarem 10ml. Method: We decribe every characteristics of MRI images in TIRM Cor, Ax và Sag T1W; Ax và Sag T2W; Ax, Cor và Sag T1 FS+Gd pulse then comparing this characteristics with grade histopathology. Result: Age: 59.6; male/female=2.5/1; tumor in oral cavity: 35.6%; in hypopharyngeal 23.8%; nasopharyngeal 22% and oropharyngeal 18%. Diameter max: 3.17cm ±1.6. Characteristics in MRI: 80% hypointensity in T1W, 76% hypersignal in T2W, 81% hyperintensity in STIR, 79% medium - strong enhance in T1W Gd with this feature the sensitives and acuracy to diagnostic degree malignant of tumor: sensitives and acuracy in T1W: 86% and 71%; in T2W is 84% and 85%, STIR: 90% and 85%; T1W Gd: 86% and 71%. Conclusion: MRI has high value to diagnostic in oral and pharyngeal cancer. Especially, MRI play an important role to determine the grade of cancer with high sensitive and acuracy. Keywords: Oral and pharyngeal tumor, MRI
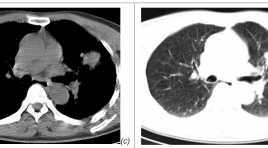
Sinh thiết ngực dưới hướng dẫn của cắt lớp vi tính liều thấp
01/04/2020 12:03:47 | 0 binh luận
The application of low dose CT guided thoracic biopsy SUMMARY Purpose: Study the application of low dose CT guided thoracic biopsy. Materials and Methods : 192 patients with CT guided thoracic biopsy including 100 patients with rutine protocol (group A) and 92 patients with low dose protocol (group B) from 4/2014 to 4/2015. Results: the average total dose length product is 274.3+/- 172.26 mGy in group A and 93.8+/-32.87 mGy in group B (p<0.001). Effective dose is 3.8+/-2.41 mSv in group A and 1.3 +/-0.46 mSv in group B (p <0.01). Pneumothorax are 17 (17%) in group A and 11 (11.96%) in group B. Three cases in group A and two cases in group B have instantly pneumothorax drainage. Hemothorax is 1 (1%) in group A and 1 (1.1%) in group B. All the complication are stable without intervention. Conclusion: low dose CT guided thoracic biosy reduces remarkable radiation dose, neither increases the complication nor degrades image quality or diagnostic accuracy. Key words: CT guided thoracic, low dose CT guided thoracic biosy.
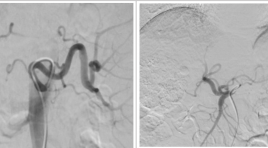
Khảo sát các biến thể động mạch thân tạng ở 378 người Việt Nam trưởng thành bằng hình ảnh học mạch máu số hóa xóa nền
01/04/2020 11:55:32 | 0 binh luận
Variants of celiac artery in vietnamese adult: descriptive statistic in 378 cases by digital subtraction angiography SUMMARY Introduction: Celiac artery, the first branch is given off from abdominal artery when it passes through diaphragm. It is the major source of blood supply to the supracolic abdominal compartment. Anatomical variations of celiac artery and its branching pattern are frequently found during diagnostic radiological imaging and during surgical exploring in current practice. There are many descriptive statistic of celiac variants published on international journal, it is included in many ethnic and national research, but there is no such the same publish in large number in Vietnameses. Purpose: Descriptive statistic of celiac artery variations by Digital subtraction angiography. Material and Method: Descriptive statistic of celiac artery by using digital subtraction angiography which we have done during treating patients at Interventional Radiology Unit, Gia Định Hospital from March 2011 to July 2015. The result is compared to international published data and contributing to Vietnamese population morphology. Results: of 378 celiac arteries we found that 286 arteries (75.7%) are normal which present all three branches such left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery. The remain are variations with 24.3% in total. Among normal variant, we found that there are many small branches are given of directly from celiac trunk. They are such right or left inferior phrenic arteries or dorsal pancreatic artery, which normally are not come from celiac trunk. But due to using classifications from Michel – Hiatt, Song et al.; Benit et al. and Adachi et al., we have to include those data into normal variations when we see all three branches of it. We also found a rare variant which Song et al. has no case; that is type 14 which common hepatic artery, left gastric artery and superior mesenteric artery are same trunk, while splenic artery is directly off from aorta. Conclusion: With current statistic, we hope to contribute to fulfill morphologic database of Vietnamese as well as international population. Key words: Celiac artery (trunk), Digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
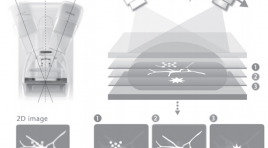
Chụp X quang cắt lớp tuyến vú - phương pháp thăm khám hình ảnh mới trong chẩn đoán ung thư
01/04/2020 10:28:24 | 0 binh luận
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"














