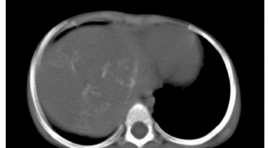
Đặc điểm hình ảnh của u nguyên bào gan trẻ em trên phim chụp cắt lớp vi tính hai dãy đầu thu
31/03/2020 21:48:55 | 0 binh luận
Characteristic of pediatric hepatoblastoma on 2 detector computed tomography SUMMARY: Purpose: to describe the characteristics of hepatoblastoma (HB) on 2 detector computed tomography (CT) images Materials and method: 49 under 15 year-old patiens with pathological results of HB were undergone 2 detector computed tomography from 2010 to 2014. Result: 100% was solid tumor, the average diameter was 8.48mm, most of them were single tumor, located at the right lobe, lobulated and defined margin, heterogeneous structure, 31.5% had calcification, strong contrast enhancement in the arterial phase, less than liver parenchyma in the portal phase. 63% enhanced less than normal liver parenchyma in both aterial and portal phase. Pretext II and III is 81.7%, lung metastasis in 4 cases, portal vein thrombosis in 2 cases, 4 cases infiltrated to extra-hepatic spaces, 1 tumor was ruptured, 2 caseshad hepatic umbilical nodes. Conclusion: HB appears on CT images as a solid tumor, heterogeneous, irregular margin mass, 31.5% had calcification. After injecting the material contrast most of tumors enhance trongly during the arterial phase and less density than the surrounding liver parenchyma in the portal phase. The most common is PRETEXT II and III. It may metastase to lung, lead to portal vein thrombosis, hepatic hilar lymph node. Keywords: hepatoblastoma, liver tumors in children, liver mass in children, hepatoblastoma imaging.
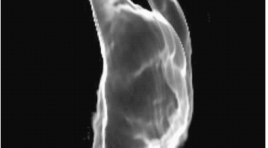
Nhận xét đặc điểm hình ảnh và kết quả chẩn đoán cắt lớp vi tính so với phẫu thuật trong di dạng teo thực quản, rò khí thực quản bẩm sinh
03/04/2020 09:10:39 | 0 binh luận
CT imaging in congenital esophageal atresia, tracheo-esophageal fistula (TEF ) comparing with surgical results SUMMARY: Purpose: To review some CT signs in congenital esophageal atresia, tracheo-esophageal fistula (TEF) and compare the CT findings with surgical results. Materials and Methods: Images, CT diagnostic results were collected and compared with the surgical descriptions in 7 cases TEF from 12/2007-11/2010 at Binh Dinh hospital. Results: Direct signs: atresis image of esophageal was visualized in 100% cases. The image of fistula between proximal esophagus-trachea: true positive is 2/3 cases, true negative is 3/4. The image of fistula distal esophagus-trachea: true positive is 3/6 cases, true negative are 1/1. Indirect signs: pneumonia and esophageal dilatation were visualized in 100% cases. Gaseous distention of the stomach and bowel was visualized in 3/4 cases which exist only lower fistula and 2/2 cases which exist both upper and lower fistula. Conclusion: Between CT with surgery is concordantly in 5/7 cases, nonconcordantly in 2/7. Key words: esophageal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula, congenital tracheoesophagus
Nghiên cứu giá trị chụp cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán viêm ruột thừa cấp
03/04/2020 09:04:58 | 0 binh luận
Value of CT- Scanner in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis SUMMARY: Acute appendicitis is most common in emergency surgical abdominal pathology. CT- Scanner is usually applied in atypical form of acute appendicitis which making difficult for diagnosis. Prompt CT-Scanner diagnosis can reduce the follow–up time, exclude the wrong so as justify the perforated one. Objective: Imaging description and assess the value of CTScanner in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Subjects and Methods: Cross-section descriptions of 92 subjects were clinically diagnosed pre-operation. CT scanner was carried out also before surgery. The CT-Scanner results was confronted to results of surgery and anatomopathology. Study performed in the Department of Surgery of Bach Mai Hospital from December 2008 to July 2010. Results: The average diameter of the appendix inflammation was 10.32 ± 0.49 mm (min 5 mm, max 30 mm). Inflamed appendix diameter was more than 6 mm (83.5%) and wall thickness more than 2 mm (85.7%). Fat infiltration and fluid around the appendix was 84.6% and 50.5%, respectively. Appendix high density was compared with caecum (29.7%) and appendix enhancement was 89.0%. Thickness of caecum localized around the base of the appendix (26.4%). Stone of appendix, ganglion mesentericum and perforation complication were seen in 38.5%, 12.9% and 29.7%, respectively. Conclusion: The CT-Scanner was very effective in diagnsosis of appendicitis, especially in difficult cases. It confirmed the location, size and complications of appencitis. The value of this modality is higher than US. Key words: Acute Appendicitis, Acute abdominal pain, CT scanner.
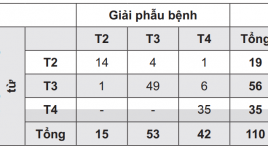
Đánh giá giai đoạn ung thư trực tràng bằng cộng hưởng từ: kết quả 3 năm
02/04/2020 15:12:16 | 0 binh luận
Preoperative staging of rectal cancer by pelvic mr imaging: results after 3 years SUMMARY: Introduction: Colorectal cancer is the most common cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. Rectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Vietnam. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer has an important role to select the most appropriate treatment. Purpose: To access the role of pelvic MR imaging in preoperative staging of rectal carcinoma. Materials and methods: Preoperative pelvic MRI of 110 patients with rectal cancer was performed in University Medical Center at HCMC for 3 years. Staging was made by evaluating images obtained and compared with postoperative histopathologic staging. Results: The accuracy of pelvic MR imaging for defining the T stage of rectal cancer was 89%. The accuracy rate to detecting lymph node metastases was 92.5%. Conclusions: Pelvic MR imaging is a promising technique for accurate preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Keywords: Rectal cancer, MR Imaging, colorectal carcinoma
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị của cộng hưởng từ trong chẩn đoán sỏi ống mật chủ
02/04/2020 16:49:58 | 0 binh luận
imaging characteristic and evaluation of MRI on the diagnosing of extra hepatic biliary stone SUMMARY: Objective: Study of MR imaging characteristic of the extrahepatic CBD & its value about the stone finding. Objet and Method: Retrospectiv of 56 patients having open operation, endo and retrograde endoscopy from 10/2010 - 8/2011 at Bach mai hospital. Means: USG of Philips HD11, MRI units of Siemens Advanto and Essenza 1.5T. Results: Among 56 operated patients for CBD stone, 6 free of stone (4 Oddi stenosis, 1 vater ampulla tumor, 1 unknown cause). MRI detected 49/50, missing 2% . In 49 positiv, 1 having 10 stones (2%), almost 3 (38%), the greatest 20 x 30mm, mainly localized at the III extrahepatic CBD portion (85/153 stones). 1 missing 5mm is at the IV portion, 49% inhomogenous mosaic form,79 strongly hyposignal on T2W. 22 patients (44.9%) associated with lithiasis in right bile duct, left 27 (55.1%), GB 13 (26.5%). Bile duct dilatation up and downward of the stone 23 (46.9%), hepatic abcess 3 (6.1%) Compare USG/MRI. USG: Se 96%, Sp 16.1%, PPV 48%, PPV 48%, Acc 52%. MRI: Se 98%,Sp 83,3%, PPV 98%, NPV 83.3%, Acc 96.4%. Conclusion: MRI is a good means for detecting low CBD stone also for predicting its number, dimension, location and complication also Se, Acc evidently higher than USG.

Đặc điểm hình ảnh x quang cắt lớp vi tính trong chẩn đoán bục xì các khâu nối đường tiêu hóa
17/04/2020 09:38:39 | 0 binh luận
Bục xì các khâu nối đƣờng tiêu hóa (AL) là s ự rò r ỉ ch ấ t trong lòng ru ộ t t ừ v ị trí ph ẫ u thu ậ t n ố i 2 t ạ ng r ỗ ng l ạ i v ớ i nhau. AL là biến chứng nặng. Tỉ lệ AL từ 1-19 %, tỉ lệ tử vong từ 7,5 – 39 % Quá trình lành miệng nối trải qua 3 giai đoạn: Giai đoạn viêm. Giai đoạn tăng sinh. Giai đoạn sửa đổi. Miệng nối yếu nhất vào ngày thứ 3-4. Sau 7 ngày miệng nối có thể tự giữ vững đƣợc. AL thường xảy ra trong tuần đầu tiên sau phẫu thuật. Chẩn đoán sớm để điều trị rất quan trọng ảnh hƣởng đến tiên lượng. Chỉ có khoảng 12 % trƣờng hợp có lâm sàng điển hình. CTScan là phương tiện hỗ trợ chẩn đoán có giá trị cao

Tiên lượng mức độ nặng - so sánh thang điểm LS-CLS-CĐHA bệnh viêm tụy cấp
16/04/2020 16:24:27 | 0 binh luận
Mục tiêu: Tóm tắt một số thang điểm tiên lượng sữ dụng trên LS -CLS trong viêm tụy cấp So sánh khản năng tiên lượng mức độ nặng của VTC giữa các phân loại

Vai trò của hình ảnh học trong nhiễm trùng quanh hậu môn
16/04/2020 16:02:17 | 0 binh luận
Áp-xe & Rò quanh hậu môn ~ Cấp & Mạn tính của cùng một tiến trình bệnh – nhiễm trùng tuyến hậu môn. PTV cần: Phân loại chính xác Rò hậu môn: thông nối bề mặt niêm mạc ống hậu môn – da vùng đáy chậu. - Phổ biến - Dễ tái phát – nguyên nhân ? - X-quang, siêu âm, CHT Áp-xe HM: ổ dịch nhiễm trùng đk > 1cm Đánh giá trước mổ: -> Phân loại. - Lên kế hoạch PT - Loại bỏ đường rò, ngừa tái phát, bảo tồn chức năng cơ thắt Rò HM: thông nối bề mặt thượng bì OHM ↔ da MRI (T2Ws, ± Gd) -> ∆(+)
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"














